Software Internationalization Best Practices for Developers
Expanding your software to a global audience sounds exciting—until you’re faced with unexpected challenges. Strings embedded in code, UI elements breaking under longer translations, or cultural formatting that feels “off” to users can quickly turn your project into a logistical nightmare.
This is where software internationalization (i18n) proves invaluable. By designing your software with global scalability in mind, you can avoid costly reengineering, streamline localization efforts, and ensure your product resonates with users worldwide.
But what does software internationalization really involve, and why is it a critical step for developers and businesses? In this guide, we’ll break down the process, share actionable best practices, and highlight tools like Centus that simplify the journey.
What is software internationalization?
Software internationalization (i18n) is the process of preparing software to work seamlessly in different languages and regions without needing significant code changes. It’s like laying a solid foundation for your software so it can be easily adapted for any market.
Here’s how internationalization of software works:
- Separating Text from Code: Instead of hardcoding text like “Sign Up” into your app, use placeholders (e.g., {{signup_button}}) that can be replaced with translations later.
- Handling Different Formats: i18n ensures your software can handle various formats for dates, times, currencies, and more. For example, it recognizes that 12/31/2024 in the U.S. is written as 31/12/2024 in Europe.
- Adapting to Languages: From left-to-right languages like English to right-to-left languages like Arabic, i18n helps your software adjust layouts and text flow automatically.
By investing in internationalization, you make localization easier, faster, and less expensive. You’re not just solving problems for today—you’re preparing your software to grow with your business.
Pro Tip: Before starting localization, try pseudo-localization to simulate translations and test UI adaptability. This helps catch issues with layout, character limits, and cultural compatibility early in the process.
Internationalization vs Localization vs Globalization
The terms internationalization (i18n), localization (l10n), and globalization are often used together, but they mean different things:
- Internationalization (i18n): The technical process of designing software so it can easily support multiple languages and cultural norms. Think of it as building a flexible framework.
- Localization (l10n): The next step—adapting your software for a specific language and culture, like translating text, adjusting layouts, or formatting dates and currencies.
- Globalization: The overall strategy of making your software usable and appealing worldwide. It includes both internationalization and localization.
Why are these steps important?
- Internationalization lays the groundwork, ensuring your software can handle diverse languages and formats without breaking.
- Localization makes the software feel personal and relevant to users in a specific market.
- Globalization combines these efforts, helping you reach and satisfy users across the globe.
Pro Tip: Start with internationalization during development to save time and money when you’re ready to localize. It’s much easier to add translations to a well-prepared product than to fix one that wasn’t built with global users in mind.
How to internationalize software
Preparing your software for global markets involves a few essential steps. Here’s how to ensure your product is ready for seamless localization:
1. Plan for multinational users
Start by identifying the markets and audiences you want to target. Consider factors like:
- Languages: Which languages will your users need? For example, Japanese, Spanish, or Arabic?
- Cultural Preferences: Are there regional differences in how dates, currencies, or numbers are displayed?
- Legal Requirements: Are there local regulations, like GDPR for Europe, that your software needs to comply with?
2. Separate text from code
Hardcoding text like button labels or error messages makes future translations difficult. Instead:
- Store all user-facing text in external files (e.g., JSON, XML, or YAML) that can be easily updated.
- Use placeholders to dynamically insert text based on the user’s language.
Example: In Ruby on Rails:
<h1><%= t 'welcome.header' %></h1>
This code uses a translation key (welcome.header) instead of hardcoded text, allowing flexibility for translations.
For example, here’s what strings with translation keys look like in a localization management platform, Centus:
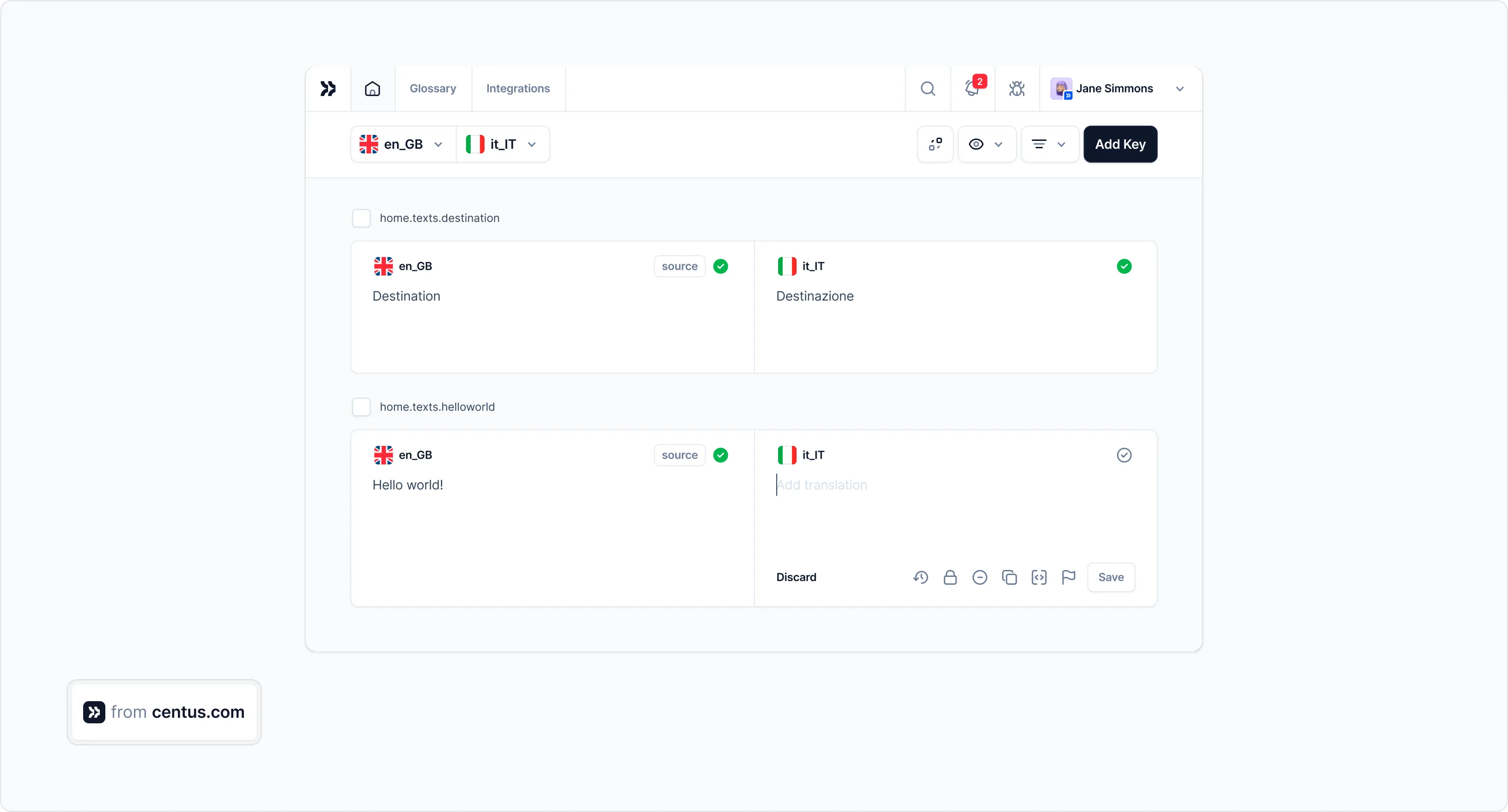
Using Centus API, you can automatically push the strings for translation right from your code repository into Centus Editor. There, the strings can be automatically translated and then refined by human editors.
3. Accommodate international formats
Adapt your software to handle different regional settings, such as:
- Dates: 12/31/2024 (U.S.) vs. 31/12/2024 (Europe)
- Currencies: $1,000.00 (U.S.) vs. €1.000,00 (Germany)
- Text Flow: Left-to-right languages (e.g., English) vs. right-to-left languages (e.g., Arabic)
Using libraries like ICU (International Components for Unicode) or JavaScript’s Intl API can simplify this process.
4. Implement internationalization (i18n)
Once you’ve laid the groundwork for internationalizing your software, implement it within your chosen framework. To make this process smoother, we’ve compiled practical guides tailored to different frameworks:
- Angular / Angular with ngx-translate
- Django
- Java
- JavaScript
- PHP
- Laravel
- NextJS
- NodeJS
- NuxtJS
- Vue
- Rails
- React Native / React-i18next / React-intl
- Spring Boot
- Svelte
- Python
- Gettext
5. Test with pseudo-localization
Before localizing your software into actual languages, try pseudo-localization. This involves:
- Replacing text with longer or accented characters (e.g., [Buy Now] becomes [Búý Ñøw]).
- Testing your UI to ensure it can handle different text lengths, fonts, and scripts without breaking.
Pro Tip: Tools like Centus allow you to automate pseudo-localization, helping you spot issues early.
Software internationalization best practices
Implementing software internationalization effectively requires careful planning and execution. Here are the best practices to ensure your software is ready for global audiences:
Start internationalization early
Begin the internationalization process during development, not after. Building flexibility into your software from the start saves time, money, and effort when localizing later.
Why It Matters: Retrofitting an existing codebase for internationalization is more expensive and error-prone than designing with it in mind.
Use placeholders for text
Avoid hardcoding text into your software. Instead, use placeholders that dynamically pull in translated strings from external resource files.
Example: For a button text like “Sign Up,” use a placeholder:
{
"button.signup": "Sign Up"
}
This placeholder can then be replaced with translations like “Registrarse” (Spanish) or “Anmelden” (German) without touching the core code.
Support Right-to-Left (RTL) languages
If you plan to reach users in regions like the Middle East, ensure your software supports RTL languages like Arabic and Hebrew. This includes:
- Mirroring UI layouts (e.g., navigation bars on the right instead of the left).
- Adjusting text alignment and fonts to display properly.
Pro Tip: Use CSS frameworks like Bootstrap RTL to simplify the implementation of RTL support.
Test the software
Before releasing your software, test it under conditions that mimic global use:
- Pseudo-Localization: Add dummy translations to check text expansion and UI behavior.
- Stress Testing: Ensure your software can handle different character sets, scripts, and formats without breaking.
Pro Tip: Tools like Centus can automate testing workflows, helping you catch issues early and save time.
Use unicode for character encoding
Support global character sets by implementing Unicode (UTF-8 or UTF-16) encoding in your software. This ensures compatibility with languages that use non-Latin scripts, such as Chinese, Arabic, or Cyrillic.
Example: Using UTF-8 ensures that characters like ñ (Spanish) or ж (Russian) display correctly without breaking.
Avoid text in images
Using text directly in images can create significant localization challenges, as every language requires separate image versions. Instead:
- Use text overlays for UI elements that contain text.
- Design images to be universally understood without requiring text.
Example: Instead of embedding “Sign Up” in an image, use a transparent button with a placeholder for the text:
<button>{{cta.signup}}</button>
Build accessible software
Design your software to be inclusive for all users, including those with disabilities. Follow accessibility standards like WCAG 2.1 to ensure your software is usable for a wider audience. Key considerations include:
- Supporting screen readers for visually impaired users.
- Ensuring sufficient color contrast for text.
- Using easily resizable UI elements.
Why It Matters: Accessibility broadens your audience and meets legal requirements in many countries.
Automate translation workflows
Integrating a Translation Management System (TMS), like Centus, into your development workflow can save time and reduce manual errors. Automation helps by:
- Syncing translations directly with your code repository.
- Triggering updates automatically when new content is added or modified.
- Enabling translators to work in context, improving translation accuracy.
Pro Tip: Use APIs, CLI tools, and webhooks to streamline your workflows further.
Comply with regional laws and standards
Different regions have unique legal requirements, from data privacy regulations to censorship laws. To ensure compliance:
- Research legal requirements for each target market (e.g., GDPR for Europe, CCPA for California).
- Adapt your software to meet those regulations, such as offering users options to delete their data or handle restricted content.
Get the week's best content!
By subscribing, you are agreeing to have your personal information managed in accordance with the terms of Centus Privacy Policy ->
Keep learning
21 min. read
Software Localization Guide for Developers

11 min. read
How to Perform Mobile App Localization: The Right Way
3 min. read
How to Translate a Web Page in Any Browser

9 min. read
7 Best Machine Translation Software Tools
10 min. read
Master Localized Numbers in 5 Minutes
8 min. read