If you run a successful business, deciding to expand it internationally is just a matter of time.
To raise the chances of successful expansion, learn how to localize your website. Why? Simply because localized websites bring more local traffic, leads, and, ultimately, customers.
Numbers don’t lie: As much as 60% of web shoppers prefer localized websites. Clearly, website localization strategy is the ticket to global success. Industry leaders have been using localization to drive international traffic for decades. And with our simple guide, you can do it too.
What is website localization?
Website localization involves adapting a website's content, design, and functionality to suit a new locale. It’s more than just translation—it requires a deep understanding of the target audience’s culture, values, and preferences. The content that often needs localization includes product pages, service pages, and sometimes even blog posts.
How to localize a website in 8 steps
1. Set localization goals and KPIs
Define what you are seeking to achieve with your localization efforts in specific terms and set measurable goals. For example, “improving performance” is not a very well-defined and useful goal. Here is what a more concrete, achievable goal might look like instead:
- tapping into new geos to expand your customer base
- generating more demand for your digital products or services
- get highter conversion rates from the existing traffic
- boost website’s stats with organic international traffic
- increase your brand’s visibility and authority in new markets
With clear, specific goals, it is much easier to plan and carry out all the adjustments that will make your localization worthwhile.
For example, to attract new customers, it’s best to focus your localization efforts on the evergreen blog articles that have the biggest traffic-generating potential. To get more sales from the existing traffic, localizing landing and product pages should be enough.
Depending on your goals, your website localization KPIs might look as follows:
- Visitor volumes for localized pages
- New leads from localized pages
- Product demos requested from localized pages
- SEO keyword ranking in the target markets
- Conversion rates on localized pages
2. Conduct market research
Conduct thorough market research to discover markets ripe for expansion. The research will also help you understand the competitors and how to surpass them. It goes like this:
2.1 Analyze your traffic
Analyze your website’s traffic to discover audiences that come to your website from overseas. This analysis can also help you understand the type of content they prefer.
For starters, analyze organic search traffic:
- Open Google Analytics 4 and go to Reports
- In the Users subsection, click Demographics
- Choose the Demographic details option
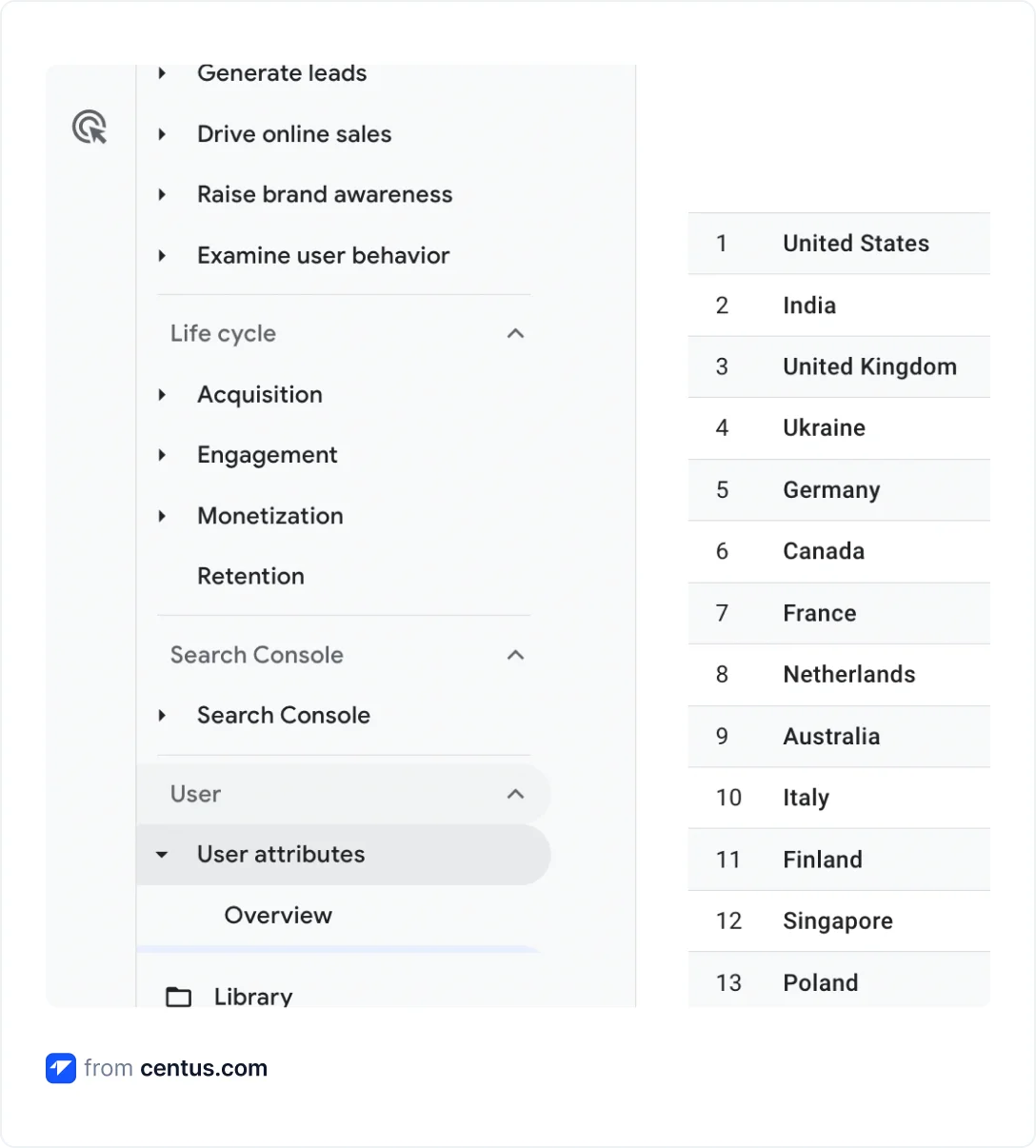 Now you can see the breakdown of your website’s organic traffic by country. For more details, use the Region and City filters.
Now you can see the breakdown of your website’s organic traffic by country. For more details, use the Region and City filters.
The next step is to examine pages that bring the highest volume of international traffic.
- In the Reports section, click Engagement
- In the Landing page tab, review landing pages
- Click + Add filter and select the dimension Country
- Choose the country
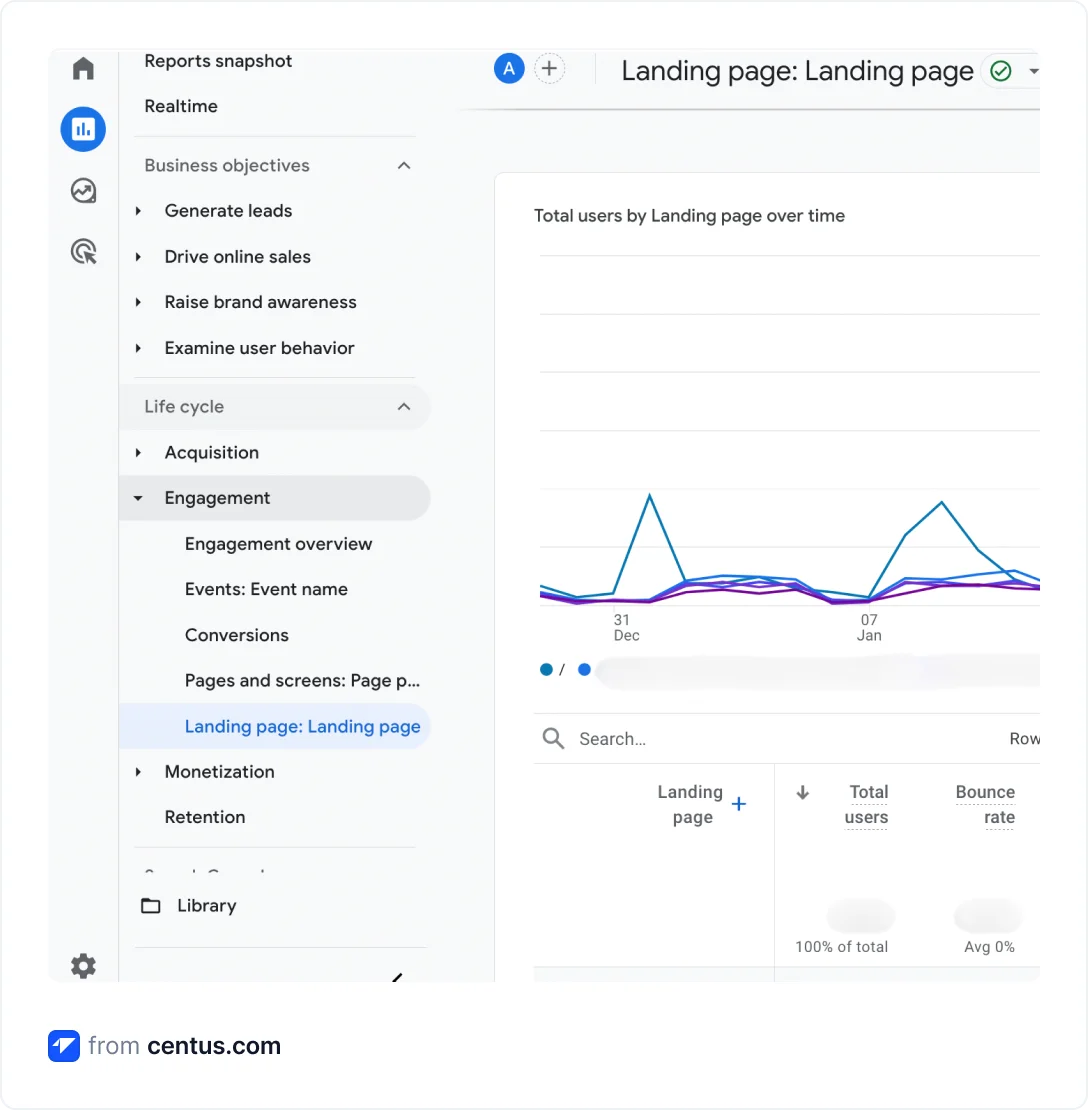 The pages bringing the bulk of international traffic should be your highest priority for localization.
The pages bringing the bulk of international traffic should be your highest priority for localization.
2.2 Analyze competitors’ traffic
Chances are at least some of your main competitors have localized their website. It’s also a safe bet that they already derive traffic from it. If that’s the case, then you can analyze their approach and glean valuable insights.
To analyze competitors’ traffic, use SEO tools like Moz or Ahrefs. Here’s how to do it using Ahrefs:
- Open Ahrefs and go to the Site Explorer section
- In the search bar, enter a competitor’s website
- Apply the location filter to examine traffic in different areas
- Click Show results
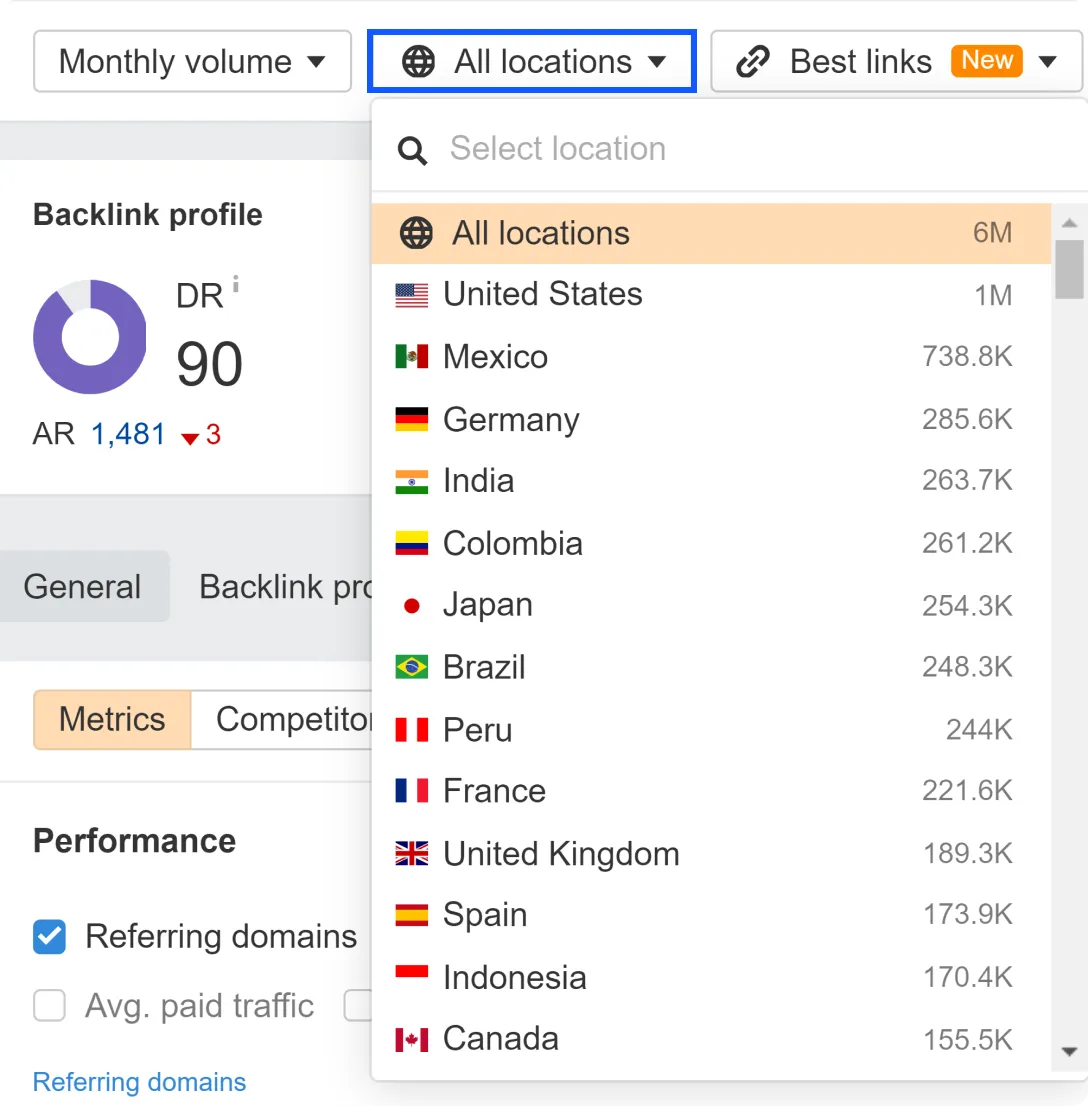 Now you can see the estimated number of visitors for each location, paid keywords, organic keywords, and much more.
Now you can see the estimated number of visitors for each location, paid keywords, organic keywords, and much more.
2.3 Define your target audience
Understand the people you want to localize your website for. Are they business owners? Perhaps they are industry professionals looking for specific advice. Or maybe you are localizing for a diverse mix of individuals. These answers could be different for each target market.
Note how simple it is. But if you want to go beyond answering a few simple questions, create a buyer persona. To this end:
- Interview potential customers in the local market
- Organize and analyze your data
- Segment buyers by use cases, pain points, and company size
3. Conduct keyword research
To ensure your localized content is favored by Google, conduct keyword research. Later, at the translation stage, incorporate the discovered keywords into the content.
To perform keyword research, identify the keywords you want to rank for. Then, use SEO tools like Ahrefs to gather additional information about them.
Let’s say, you’re in the business of selling solar panels and want to enter the Spanish market. You start by directly translating the keyword “solar panels” into Spanish—“paneles solares.” After checking it on Ahrefs, you are happy to discover that it has 12,000 monthly searches.
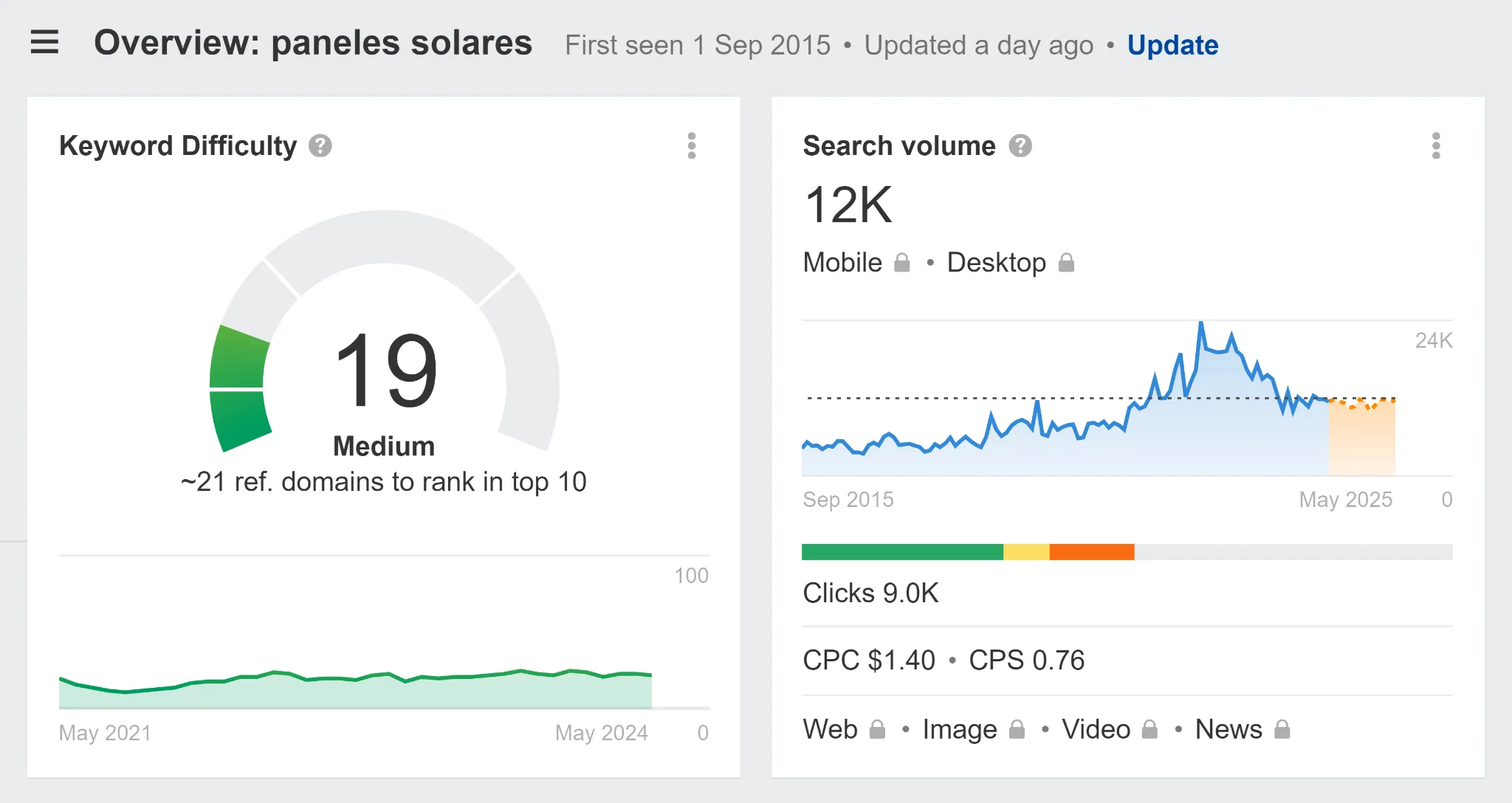
Should you start optimizing your pages for that keyword?
Not so quick! You can triple that search potential with a better keyword.
Just by analyzing the SERP, you might discover that a similar keyword “placas solares” has a monthly search volume of 33,000.
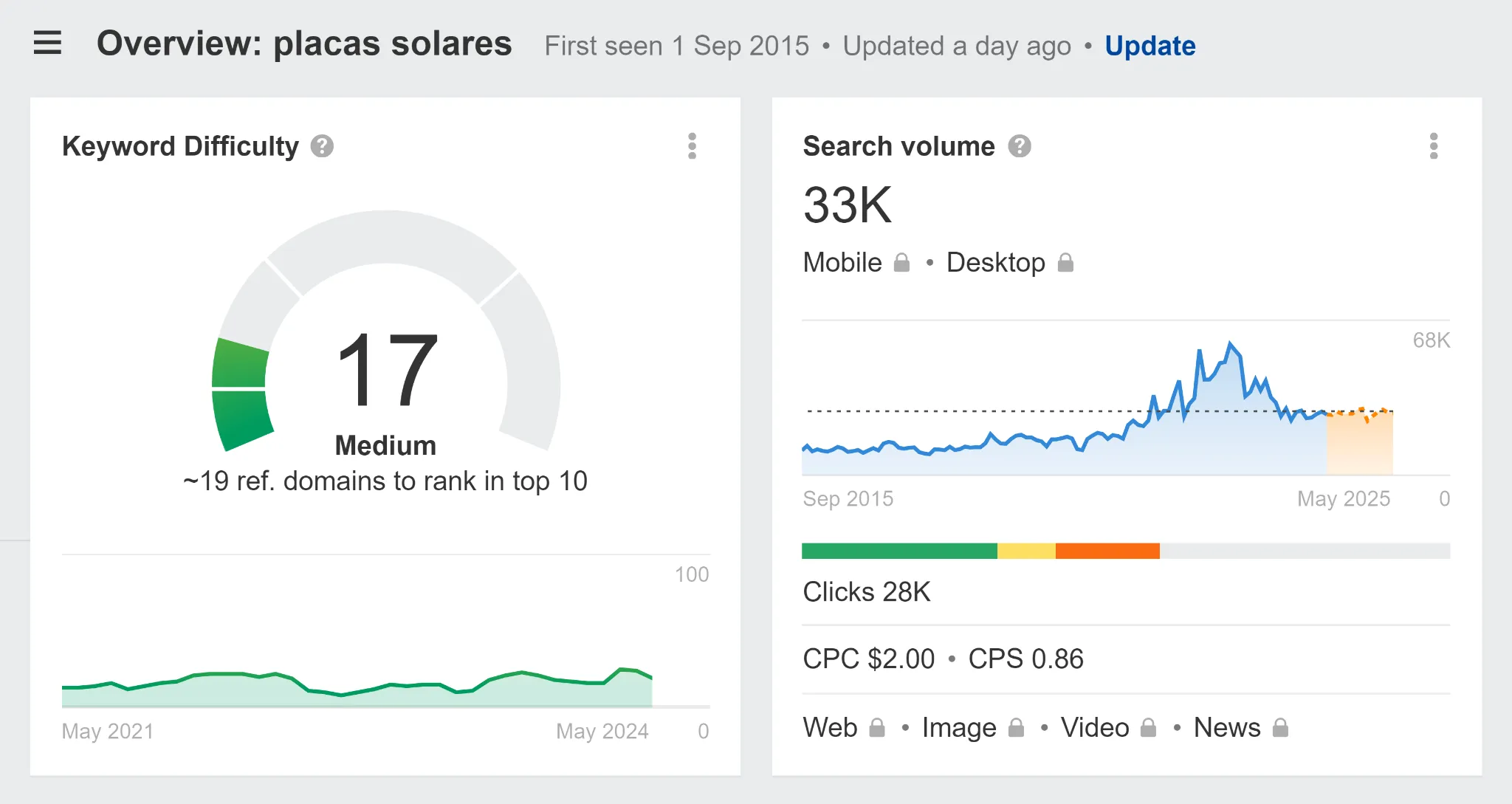
Whether you optimize your local pages for one, the other, or both, the key point is not to neglect keyword research during website localization.
Along with Ahrefs, use Google Keyword Planner to gain additional insights into local keywords. The tool allows you to find related keywords for any term you enter. It can also be used to get keyword suggestions for your website. The best thing? Google Keyword Planner is absolutely free for basic research.
Here’s how to use Google Keyword Planner for international keyword research:
- Choose the target location in the billing section
- In the main menu, click Discover new keywords
- Enter a keyword describing your services
- Enter your website URL
- Click Get results
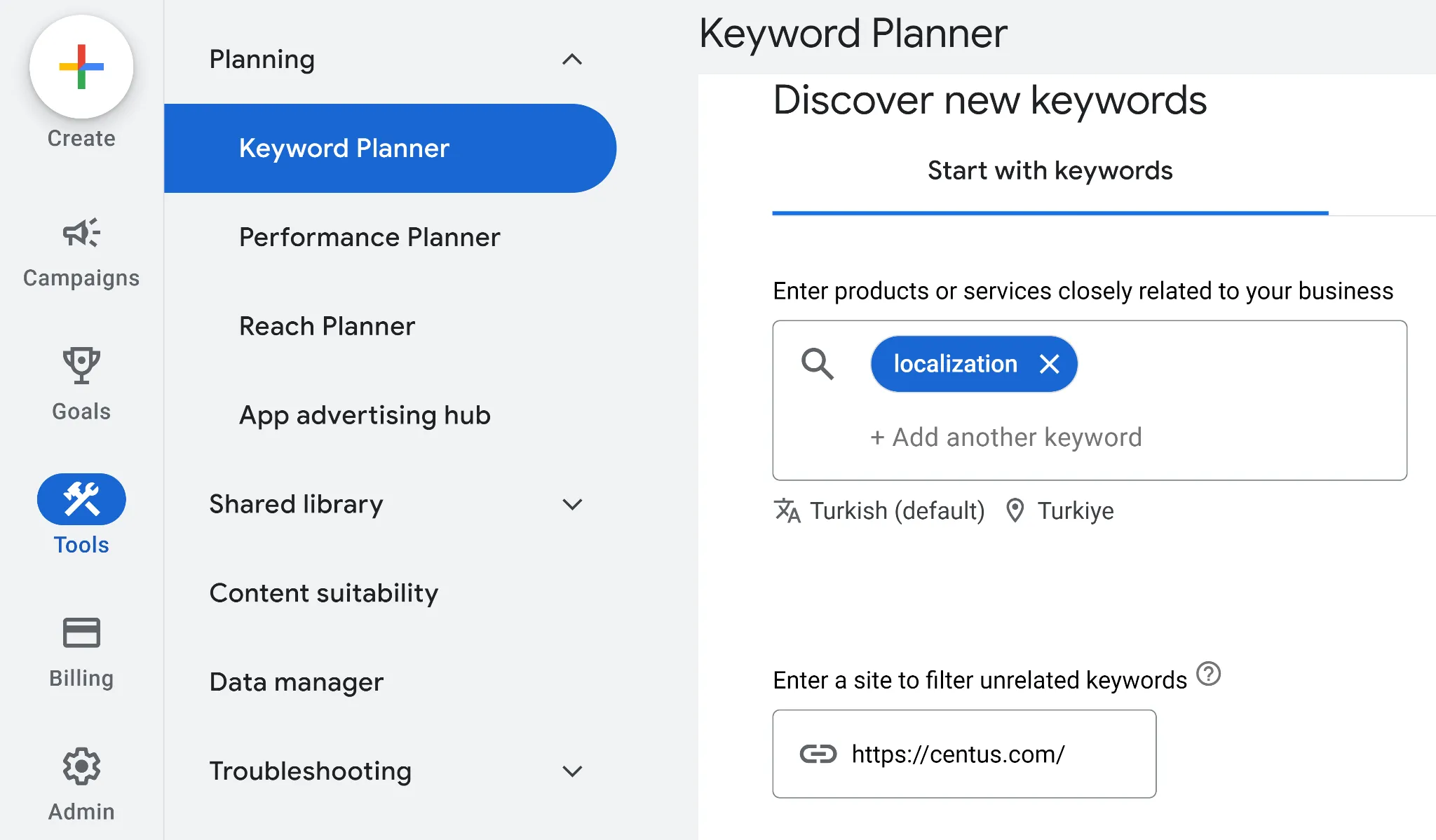 The next step is to translate keywords and check them once again using SEO tools.
The next step is to translate keywords and check them once again using SEO tools.
You might discover that some translated keywords don’t have enough search volume. You might also realize that some keywords are related to a different content topic and require the creation of additional content. Take your time and double-check the relevance of all translated keywords.
4. Internationalize your website
Now that you know your target markets and keywords, it's time to set up your website’s technical foundation. Many companies jump straight into translation, only to realize their code isn’t ready for multiple languages.
Internationalization (i18n) is the process of making your website adaptable to different languages, cultures, and regions. It allows you to change language and formatting without modifying the code. The best part? You only need to set it up once during development.
In simple terms, i18n replaces hardcoded text with a key-based system that dynamically swaps content at runtime.
<!-- Before -->
<h1>Welcome to our store!</h1>
<!-- After -->
<h1>{t('welcome_message')}</h1>
The text content is stored in separate locale files by assigning values to each of these keys. This allows you the flexibility to pass text values to display website
For instance, in the above example, you can pass “Welcome” or “Bienvenue” or “Allo” as a value to the welcome_message key and that will be displayed on the front-end!
Also, separating content from code helps you build and scale translations and updates as your team grows—simply put, your translation team never needs to touch code.
Once you’ve covered all text snippets, you need to look for values that may have been hardcoded for a specific locale.:
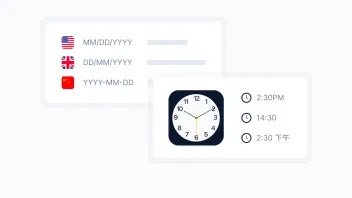
- Number formats (1,000 vs. 1.000)
- Dates (MM/DD/YYYY vs. DD/MM/YYYY)
- Currencies ($100 vs. 100€)
- Time zones (accounting for regional business hours)
- Text direction (left-to-right vs. right-to-left languages)
ICU MessageFormat helps manage these complex language rules behind the scenes instead of having to code everything by hand.
When translating text snippets, there's also the issue of text length. For example, German translations can be 30% longer than English, while Arabic text may be 25% shorter. Make sure to design containers that automatically adjust to these changes without breaking your UI.
If you want to further simplify things for your end-user, implement language detection:
- Browser language settings
- IP-based geolocation
- User language preferences
Set up language fallbacks for missing translations. When content isn't available in the user's preferred language, your site should automatically display it in a fallback language, typically English. Use the hreflang="x-default" tag for this.
And this one is important for your development and translation team and especially helpful when new people join in. Create documentation that talks about:
- Translation key naming conventions
- Date and number formatting rules
- Currency display preferences
- Default fallback language rules
- Character encoding standards
While this may sound like a lot, missing these i18n fundamentals can lead to complicated user experiences and unnecessary, expensive rebuilds. But a proper internationalization setup helps make things simpler for you in the long term.
4.1 Choose a URL structure
Selecting the right URL structure is key when targeting international audiences. It affects both your site's SEO and user experience, and different options offer varying levels of flexibility, localization, and ease of management.
- Country Code Top-Level Domain (ccTLD): best for large companies that require a highly localized presence.
Example: website.de (German ccTLD).
- Subdomain: ideal for an international approach that maintains brand consistency while offering flexibility.
Example: de.website.com.
- Subdirectory: perfect for smaller businesses with limited resources, as it's easier to manage.
Example: website.com/de/.
4.2 Add hreflangs
Use hreflang tags to specify the language of your content and link to the corresponding localized versions. Hreflang is an HTML attribute that helps search engines understand which language or regional version of a page to show to users.
Example:
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en" href="https://centus.com">
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="ar" href="https://centus.com/ar">
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="es" href="https://centus.com/es">
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="de" href="https://centus.com/de">
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="x-default" href="https://centus.com">
The x-default tag is optional, but it’s useful if you want to specify which language version should be shown to users from regions that aren’t supported.
5. Translate website content
Website translation is not a one-person job. If your budget allows it, hire an experienced website localization team. The barebones team should have at least one localization manager who will collaborate with freelancers to translate your website content.
Another way to do it is to hire professional translation services for the project. This can be more cost-effective, but has its pitfalls. For example, you will need to create detailed briefs for your contractors, educating them on your brand’s values, tone of voice, positioning, etc.
📘 Further reading: Website Translation Costs
Whether you go for in-house translators or an agency, use translation management software (TMS) to streamline the website localization workflow. In either case, using TMS, like Centus, will save you time, money, and spare you unnecessary busywork.
Here’s how to translate website content:
- Sign up to Centus and create a new project
- Enter project details and choose a base (source) language
- Click Create project
Now, go to the Imports section and add your files for translation. These could be XML, YAML, JSON, HTML, or many other file types.
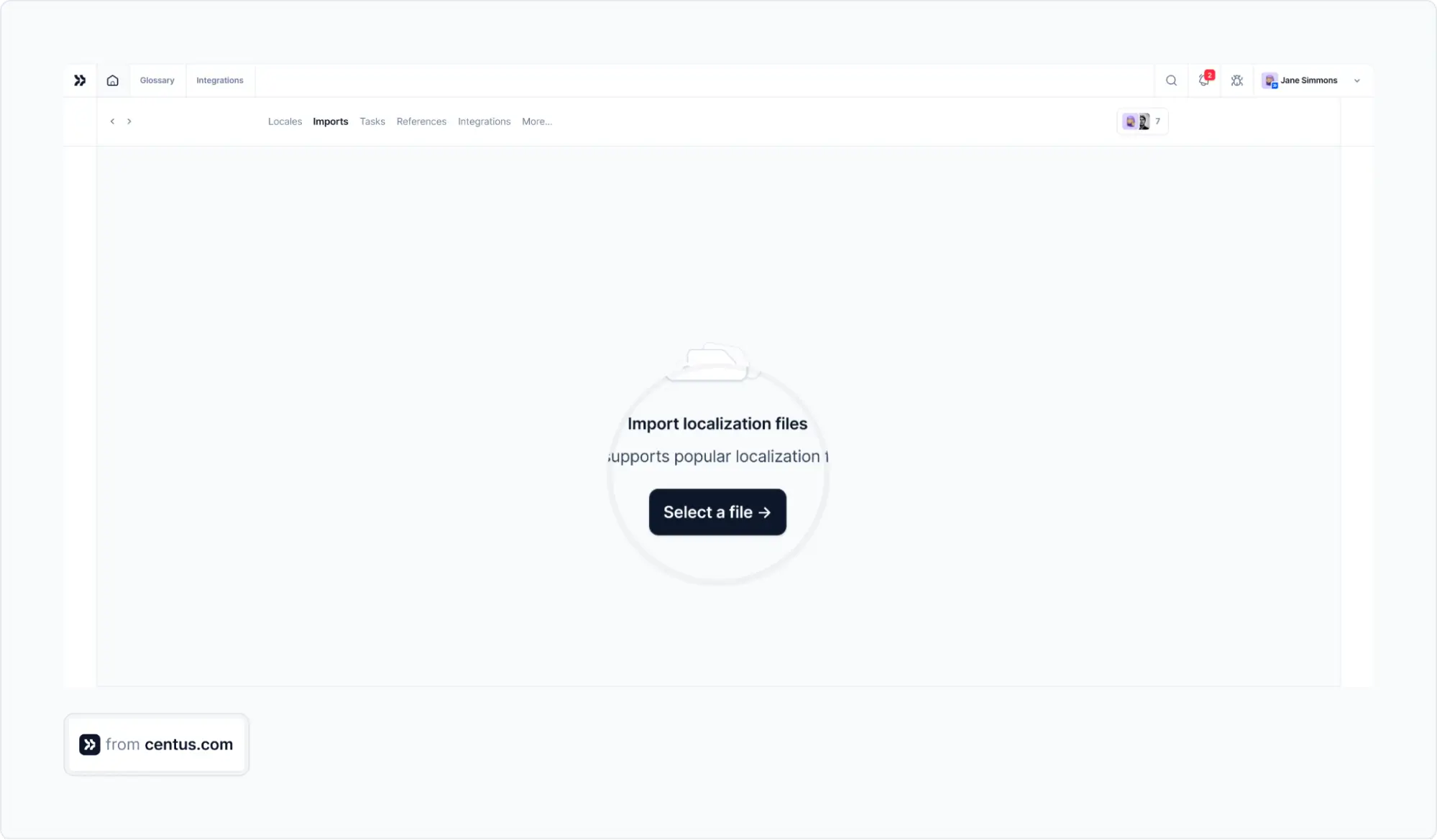
Pro tip: Centus will soon have plugins for popular CMSs, making file importing effortless. Stay tuned!
Now, everything is ready for translation. Go to the Editor section, where you’ll see automatically segmented content
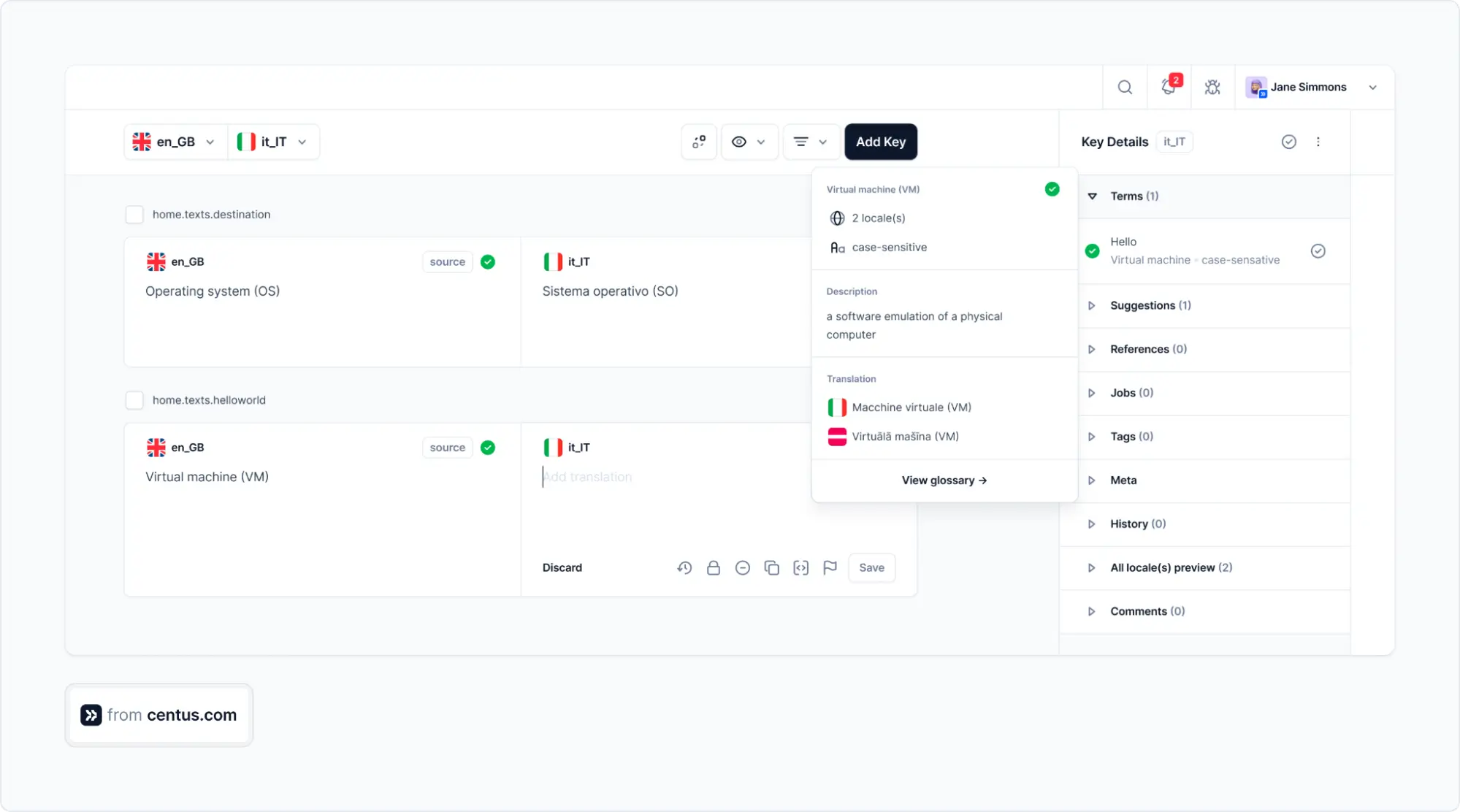
Here you have two options: automatic translation and manual translation.
The best choice? Combine both!
Start by automatically translating your website segments with Google Translate, DeepL Translate, or Microsoft Translate. Thus, you can save time and launch your website faster. But don’t stop there.
Since Google and DeepL aren’t 100% accurate, you want your team’s translators to review automatically-translated content before publishing it.
Centus makes reviews a breeze:
- In the Contributors section, click Add people
- Enter your translator’s name and other details
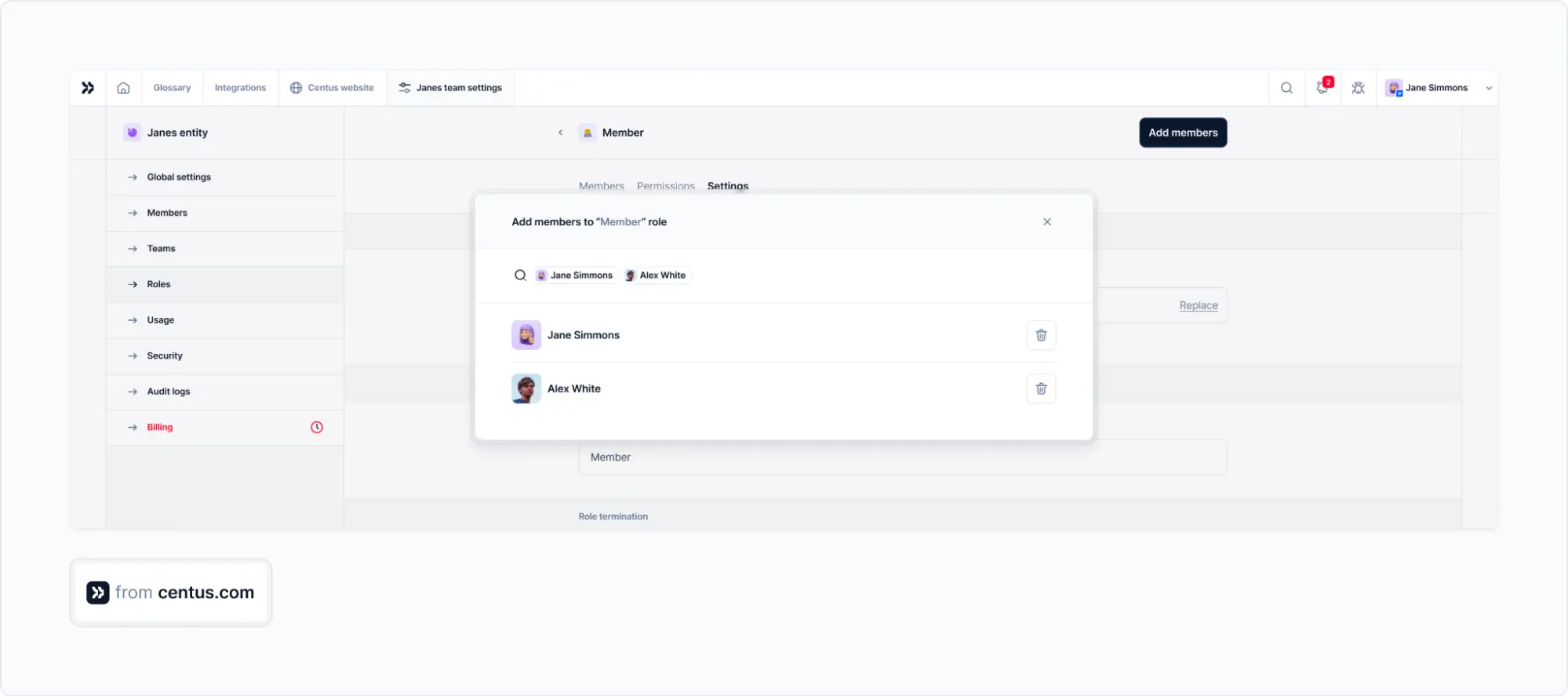
- In the Access section, select the translator’s role and administrative permissions
- Click Save
Follow the same steps to add other project contributors such as editors, managers or designers. They can review translations and leave feedback.
When all the reviewers are happy with translation, go to the Export tab. There, choose the desired file format and click Download export.
Now you have your website content accurately translated. All the steps from above can be applied to translate your ebooks, white papers, or any other downloadable content you might have.
6. Localize UX and UI
The process of localizing a website goes beyond content translation. Everything, including the website’s design and layout should be adjusted to suit the preferences of the new target audience.
For example, if you are marketing to Middle Eastern audiences, use images that reflect local customs and traditions, aka depict modestly dressed people and contain no controversial/offensive products (e.g. alcohol, bacon, etc.)
The image below shows IKEA’s website localized for Jordan.
 Source: IKEA
Source: IKEA
Nike offers another example of properly tailoring website imagery to a local audience. The company uses traditional Chinese colors and symbols on its localized website.
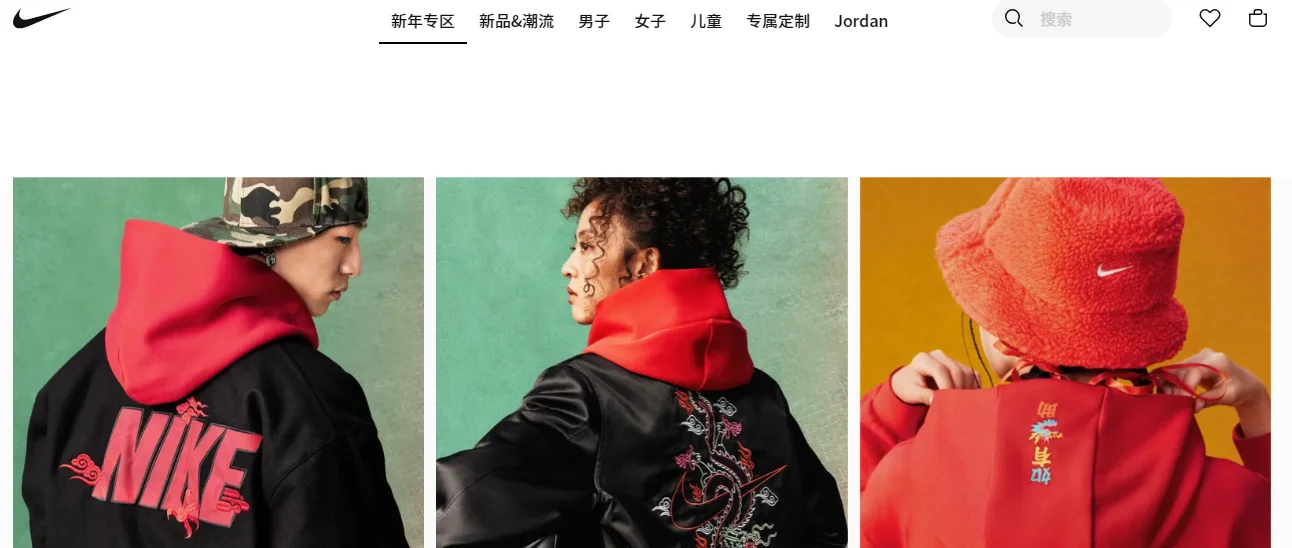 Source: Nike
Source: Nike
When performing UI/UX localization for your website, keep these tips in mind:
- Adjust website colors
- Use culturally relevant images and symbols
- Adapt website fonts
- Adjust website for locally-preferred navigation
- Adapt currencies and numerals
- Adjust forms for locally-preferred user input
- Adjust calendar formats to user expectations
- Set the appropriate time zones
Sounds like a daunting task? Well, it certainly can be.
Fortunately, using a localization management tool, you can help your team manage the localization of visuals. Just install the Centus plugin for Figma to pull translations into designs automatically. Thus, you can spare your designer a ton of manual effort.
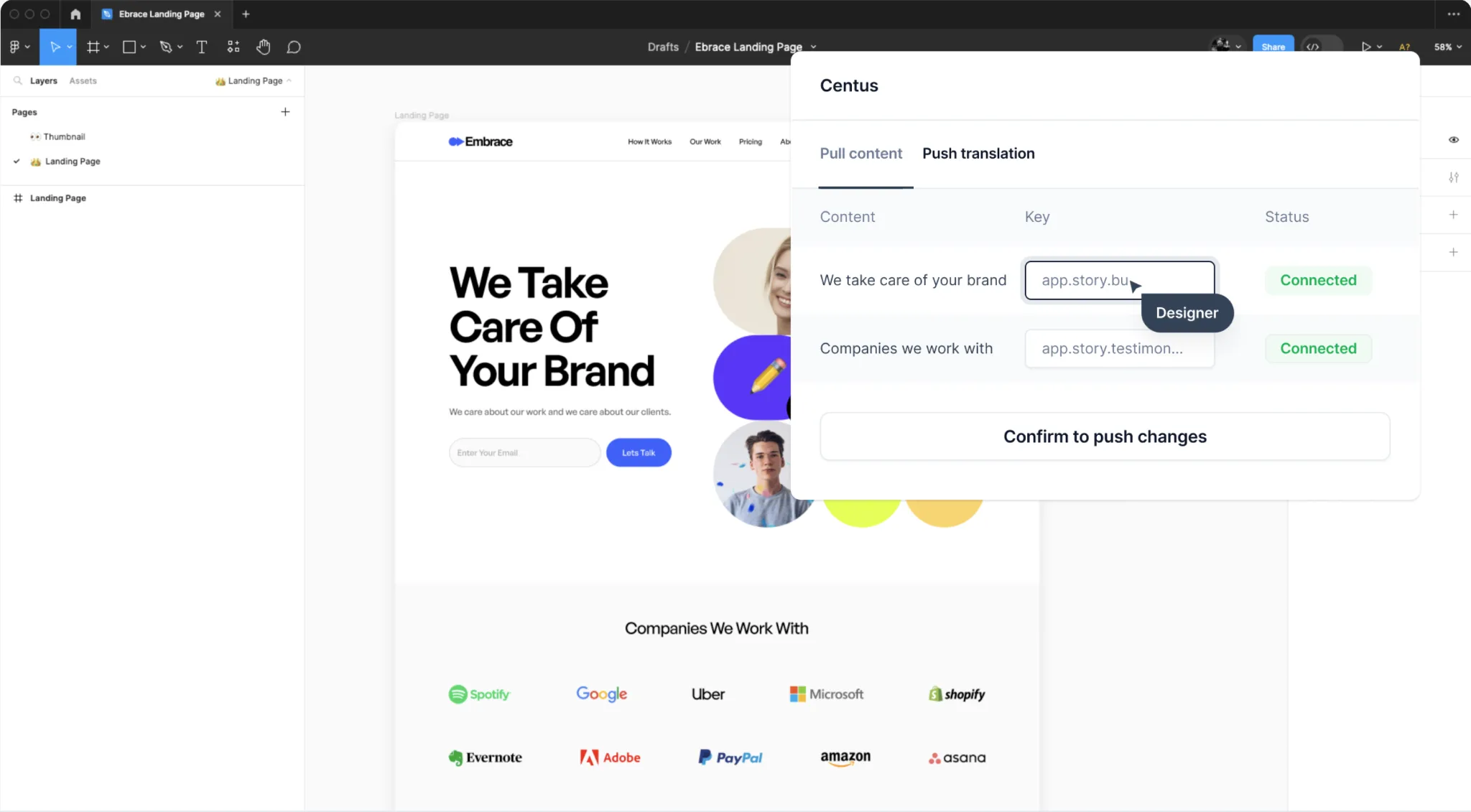
Centus is particularly helpful for tricky tasks like localizing website UI with right-to-left (RTL) languages, and other situations when manual copying has the potential for multiple errors.
For more information, refer to our UI/UX localization and RTL localization guides.
7. Perform website localization testing
Once your website is localized, one final step is to thoroughly test everything: translations for accuracy, user interface for functionality, layout for consistency, etc. The last thing your need is any mishaps when it’s live.
Website localization testing involves checking both functional and linguistic parameters.
Functional testing of a localized website includes:
- Hardware compatibility
- Names, time, date, weights, measurements, etc.
- Upgrades
- Entry fields
- Hyperlinks
- Image appropriateness
- Broken strings/design
- Form functionality
- Shopping cart
- Payment processing
- Loading time
- Downloads
Linguistic parameters you should check before website launch are:
- Spelling and grammar errors
- Punctuation errors
- Cultural appropriateness
- Misuse of keywords
- Readability and appeal of a message
- Untranslated strings
You can conduct website localization testing using a variety of methods, including
- In-person testing to observe user behavior and ask questions.
- Remote user testing to observe user behavior remotely.
- Method of comparison to compare the performance of two versions of your website content.
To make sure your localization resonates with the intended audience, it’s best to hire a native speaker as a consultant/editor. Your expert should be culturally knowledgeable of or representing the demographic you are marketing toward. This way, you will be able to test most efficiently.
8. Promote your website
When the new version of your website goes live, don’t neglect to promote it in this language, market, and geo just as you did for your original version. Without this, getting local traffic and conversions will be difficult. Tailor your promotional strategy for the language and cultural context:
- Craft localized digital marketing campaigns
- Adapt existing email campaigns to include local holidays, seasonality, etc.
- Adjust imagery and messaging to resonate with your new audience
- Partner with local influencers
- Contact influencers whose audience overlaps the most with your target demographic
- Create a brief with talking points that wed your sales goals with their authentic style
- Take part in community life
- Sponsor local teams and community events to create exposure and build a reputation
- Consider becoming a donor for a local charity or cause that aligns with brand values
- Collaborate with local businesses
- Partner with other local businesses for more visibility and wider reach
- Participate in cross-promotions, joint events, and referral programs with local brands
- Leverage localized content marketing
- Create blog posts, videos, and infographics addressing the concerns and pains of your local audience
- Speak their language: hire local creators to leverage your audience’s vernacular authentically for more compelling content.
Get the week's best content!
By subscribing, you are agreeing to have your personal information managed in accordance with the terms of Centus Privacy Policy ->
Keep learning
7 min. read
How to Make a Multilingual Website in 6 Steps
9 min. read
Website Language Selector UX Best Practices
3 min. read
How to Translate a Web Page in Any Browser
10 min. read
Master Localized Numbers in 5 Minutes
11 min. read
What Is Localization? A Comprehensive Overview

11 min. read