Content drives traffic, traffic drives sales. So far so simple.
Unfortunately, it gets more complicated when you try to translate content for a new market. Worse yet, multiple markets.
But worry not, this comprehensive guide to content translation will help you avoid pitfalls and increase your global presence.
What is content translation?
Content translation is the process of adapting written, visual, or multimedia content—such as blogs, videos, ads, and social posts—into another language and cultural context. The goal is to preserve the content’s intent, resonate with the target audience, and drive engagement, trust, and conversions in new markets.
Why bother with content translation?
If your content is in English, it’s already accessible to many customers worldwide. Why bother with translation?
Global content translation moves your business goals by enticing your audience to read, share, and, eventually, convert.
The key benefits of content translation and localization are:
- Broader audience reach
- Higher engagement
- Higher conversion rates
- Improved brand visibility
- Improved brand trust
- Higher customer loyalty
- Enhanced user experience
📘 Relevant reading: 10 Best Online Translators: Free & Professional
How to organize the content translation process
Here’s how to get started with content translation:
1. Define translation goals and priorities
This step means figuring out what your prospects are looking for. And it also means figuring out what you expect them to do once they find your content.
For instance, your prospect stumbles upon a blog post detailing how to solve their problem. Hopefully, you’re a good host who set up treats around the said post: CTAs, ebooks, and free trial buttons.
Intrigued, the prospect clicks the link—only to discover an untranslated page. They are frustrated; they leave.
Therefore, you should know exactly what you’re translating your content for.
Want more traffic? Translating your blog should suffice.
Want more conversions? Translate product, trial, and pricing pages as well. Marketing content translation also won’t hurt.
To define your translation priorities, start with these broad translation goals:

Identify the most impactful goals for your business. Then, narrow them down using the SMART framework:

2. Research your target market
This step builds on the previous one: after you identify your translation goals, learn your customers' needs.
Essentially, know thyself and know thy customer.
To this end, examine your competitors’ content to see how popular it is among customers. SEO tools, such as Moz or Ahrefs, are invaluable for getting a pulse of your target audience.

Use SEO tools to understand the content and language preferences of your prospects.
Thoroughly analyze the number of visitors in each location, organic keywords, paid keywords, and other SEO metrics. For more information, read our website localization guide.
3. Set and allocate a translation budget
This step is simple to describe—I already did it in the subheader above. If only it were so easy to perform. But, worry not, I’m here to help you guesstimate your content translation budget.
Here are the average translation rates for the world’s most popular language pairs:
| Language pair | Price per word |
|---|---|
| English-French | $0.07 |
| English-Italian | $0.07 |
| English-German | $0.08 |
| English-Spanish | $0.07 |
| English-Mandarin Chinese | $0.23 |
| English-Arabic | $0.1 |
| English-Japanese | $0.25 |
Don’t forget to budget for content editing:
| Language pair | Price per word |
|---|---|
| English-French | $0.03–$0.07 |
| English-Italian | $0.04–$0.07 |
| English-German | $0.15–$0.30 |
| English-Spanish | $0.03–$0.07 |
| English-Mandarin Chinese | $0.10–$0.15 |
| English-Arabic | $0.05–$0.10 |
| English-Japanese | $0.12–$0.18 |
📘 Relevant reading: Localization costs and rates
4. Assemble a team and start content translation
Now is the time to assemble the team and organize the translation process.
Your team should have:
- Localization manager—a specialist who manages the localization process
- Freelance or in-house translators to perform translations
- Editors to review and polish translations
If the translated content needs to be published, also add a person responsible for that. It could be either a content manager or a member of your development team.
With your A-team in place, organize the translation process.
To this end, create a Gantt chart to track who translates what and when it will be done. Then, go full Jackson Pollock with the color coding for clarity.
You’ll also need a project management system to assign tasks and communicate with translators. While good ol’ Jira might do the trick, it’s better to use tools specifically designed for translation management—TMSs. More on it below 👇
5. Use a TMS
I’ve mentioned TMSs several times throughout this article. It’s only because managing content translations without a professional translation tool is a chore. A nightmare. A money drain. Seriously, don’t do it.
A reliable TMS can substantially increase the translation speed while also improving translation accuracy. By simplifying machine translation post-editing, a TMS can also reduce your translation expenses by up to 90%.
Use a TMS that meets your budget and integrates well with your content production and management technology. Use a TMS that your entire team could master without a steep learning curve. Use a TMS like Centus.
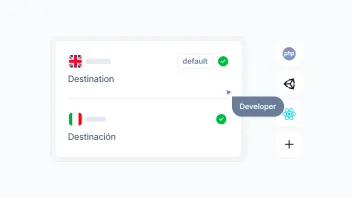
With Centus, you have a bird’s-eye view of your entire content translation project:

You can also track the translation project milestones using the notification panel.

And, of course, you can communicate with your translators, editors, and managers without ever having to open your email client. Convenient? You bet!
As you can see, it’s much easier to manage the translation process, with the right tool at hand. Try Centus now!
Content translation mistakes to avoid
Even with the best strategy on paper, you are still bound to run into translation challenges. Here are some of the most common:
- Incomplete content briefing: Make sure to provide your translators with sufficient contest and background information about your brand’s voice, values, target audience, and project goals. It’s easier to avoid misunderstanding than to clean up the mess of inconsistent translation.
- Poor quality control: Never assume your experts provide flawless translations. Always review for accuracy, consistency, and cultural appropriateness before publishing your content translation for the whole world to see.
- Lack of consistency: Allowing different translators to interpret terminology independently leads to variations and inconsistency within the project or across multiple different projects. To avoid inconsistency, use CAT tools with terminology management and translation memory features.
- Lack of cultural nuance: Sometimes even experts might translate content too literally or overlook cultural sensitivities causing, at best, misunderstanding and, at worst, offense to your audience.
- Lack of SEO optimization: Without an SEO strategy, your customers might not find your perfectly translated multilingual website.
Parting thoughts
Properly translated content is accurate and culturally correct. It speaks to the audience in their own language, while leaving no gaps in the original meaning.
Properly translated content has traffic potential and conversion potential. It’s great not only for your audience but also for your business.
Hopefully, my guide has shown you how to set up a proper translation process, helping your content reach its full potential.
Happy translating!
Get the week's best content!
By subscribing, you are agreeing to have your personal information managed in accordance with the terms of Centus Privacy Policy ->
Keep learning
7 min. read
Ecommerce Website Localization Guide

9 min. read
7 Best Machine Translation Software Tools
8 min. read
How to Choose the Right Translation Technology in 2025

11 min. read
Content Localization: What to Localize and How to Do It
3 min. read
How to Translate Documents: A Simple Guide
18 min. read