How to Choose the Right Translation Technology in 2025
Imagine you could halve your localization project costs. All while maintaining high translation quality and meeting deadlines. Sounds good? Welcome to translation technology.
Whether you are a professional translator or an entrepreneur, the skillful use of translation technology services can be a life changer. And to help you usher in that positive change, I’ve created the ultimate guide to translation tech.
What is translation technology?
Translation technology is a set of tools that streamline and automate content translation. These tools assist with translation, project management, and quality assurance.
The key benefits of using language translation technology include:
-
Increased project efficiency: Automating repetitive tasks, such as terminology checks and formatting, frees up human translators to focus on complex and creative aspects of translation.
-
Improved translation quality: Translation technologies can help assure quality and maintain consistency in terminology and style across different languages.
-
Improved collaboration: The use of TMS enables collaboration between translators, editors, and project managers.
-
Reduced costs: Automating tasks and leveraging reusable content can help you reduce the overall cost of localization projects.
5 Types of translation technology
Let’s explore the five key translation technologies that have reshaped how translations are done today.
- Machine translation
- AI translation
- AI-powered real-time translation
- Computer-assisted translation (CAT)
- Translation management systems (TMS)
Machine translation technology
Machine translation (MT) tools use algorithms to translate text or speech from one language to another without human input.
👉 Examples include Google Translate, DeepL, and Microsoft Translator.
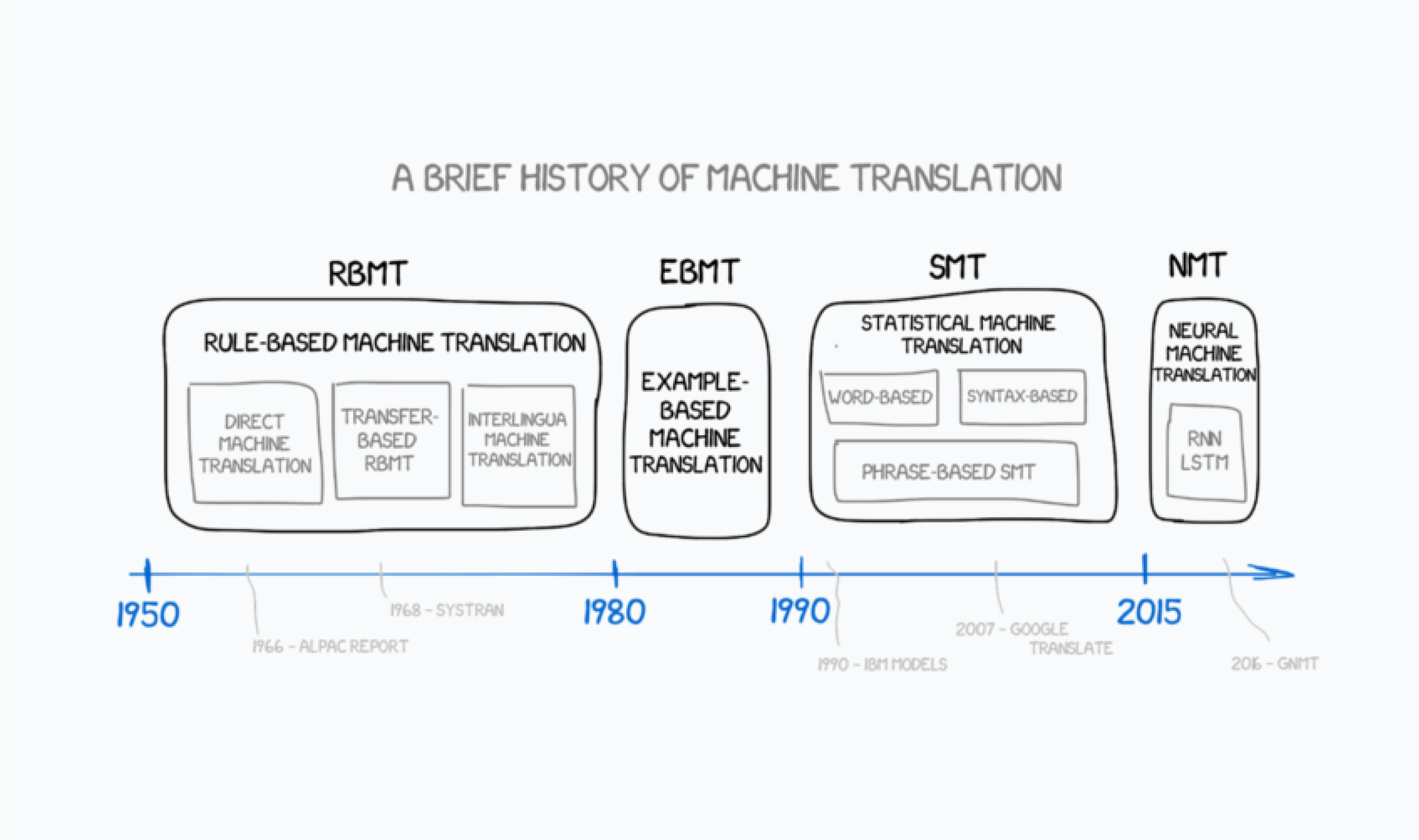
There are four main types of MT engines:
-
Rule-based machine translation (RBMT) relies on a set of predefined rules about grammar, syntax, and vocabulary to translate text.
-
Example-based machine translation (EBMT) uses bilingual sentence pairs to derive rules that can be applied to produce new translations.
-
Statistical machine translation (SMT) analyzes vast amounts of existing translated content to identify statistical relationships between source and target languages.
-
Neural machine translation (NMT) uses deep learning algorithms inspired by the human brain to translate text. NMT revolutionized the industry by introducing context-aware translation that captures stylistic, grammatical, and lexical nuances that traditional MT typically misses. This includes better translation of complex sentences, slang, and idiomatic expressions.
Note: NMT systems are trained on massive datasets and refined through ongoing human feedback, improving accuracy. This places the NMT technology at the intersection of traditional MT and AI translation tools.
Today, NMT is the underlying technology that powers features in CAT tools, TMS platforms, real-time translation applications, and AI-driven translation systems.
 Source: FreeCodecamp
Source: FreeCodecamp
Now, let’s break down the pros and cons of MT:
| Pros 👍 | Cons 👎 |
|---|---|
| Instant translation | Low accuracy |
| Easy implementation | Needs post-editing |
| Cost-effective | No style adjustments |
| Lacks termbase adherence |
Raw and post-edited machine translation
MT lacks accuracy and consistency, but translation speed and cost are decisive factors for many businesses. Machine translation post-editing (MTPE) serves as a middle ground, combining the efficiency of MT with the improved accuracy of human editors.
💡 Pro tip: You can stick with raw MT for less important content like internal documentation, but for key content like contracts, homepages, or sales presentations, MTPE is the way to make sure everything’s polished and accurate.
AI translation
AI translation systems automatically convert text or speech from one language to another without human input. Unlike traditional MT, which relies on rules, examples, and statistics, AI uses advanced technologies like neural networks (NMT), deep learning, and sentiment analysis to process language contextually, improve quality, and adapt over time.
👉 Examples include AI capabilities of Google Translate and Microsoft Translator, ChatGPT.
AI system capabilities often go beyond automated translation and localization. They may also analyze and summarize text, detect emotions, scan text for images, identify terms, generate multilingual content, and learn from user feedback, delivering a multifunctional tool.
| Pros 👍 | Cons 👎 |
|---|---|
| Instant content-aware translation | Low accuracy in technical content |
| Multi-language support | Inconsistent terms |
| AI tool integration | Lack of transparency |
| High setup costs |
Real-time translation solutions
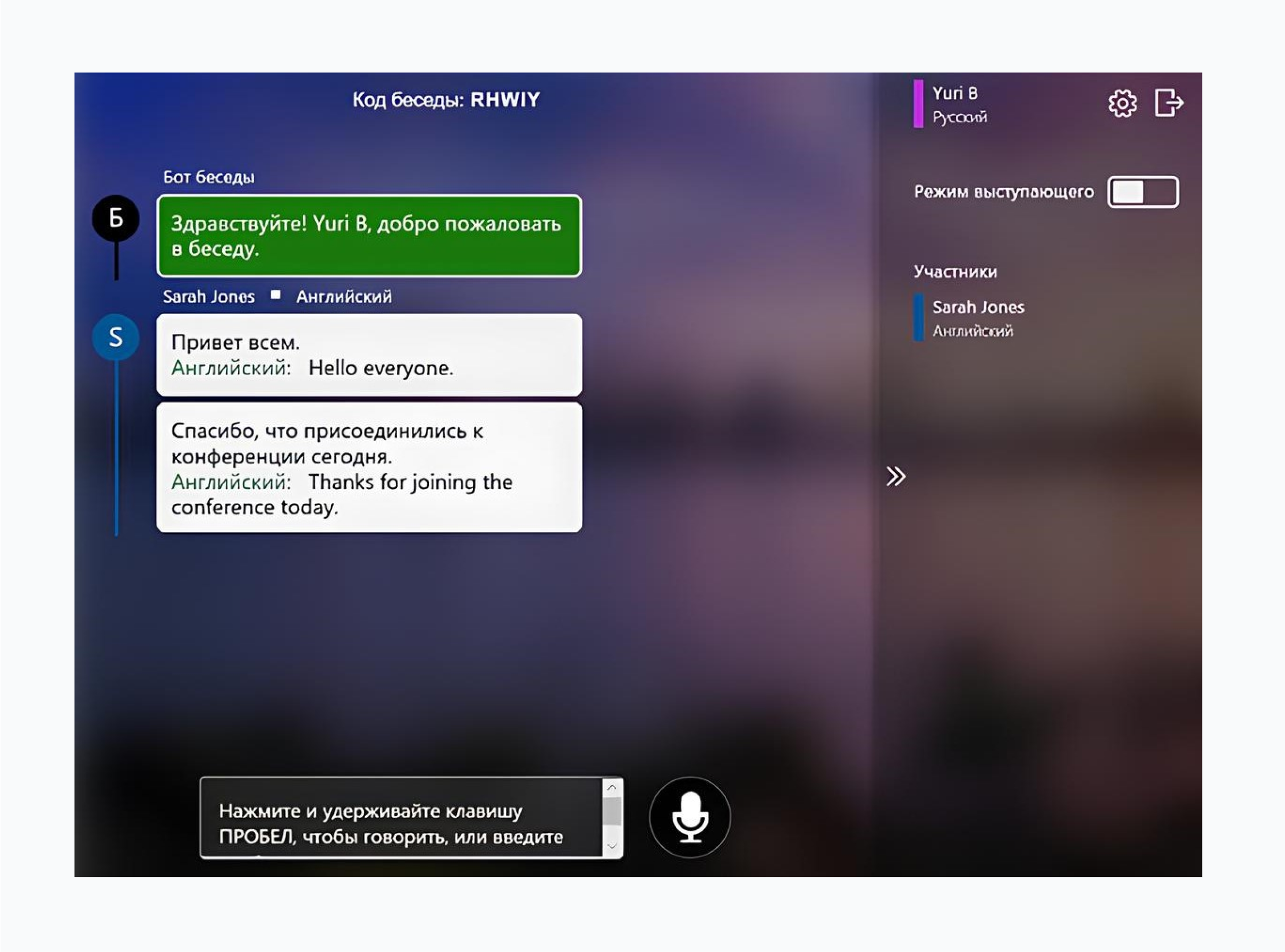
Real-time translation tools instantly convert spoken or written conversations from one language to another. They rely on AI technologies like natural language processing and speech recognition to translate in real time during live chats, video calls, and conferences. This allows you to communicate smoothly without needing an interpreter.
👉Example: Microsoft has brought Teams and Translator together for seamless cross-language communication. Users can chat or speak in their own language, and the app instantly translates their messages or speech into captions, so conversations flow smoothly, no matter the language.
Source: Microsoft
| Pros 👍 | Cons 👎 |
|---|---|
| Real-time communication | Lags and delays |
| Context-aware translation | Low accuracy in complex phrases |
| Multi-language support | Inconsistent terms |
| Integration with video and messaging apps | Lack of transparency |
| Tech dependency |
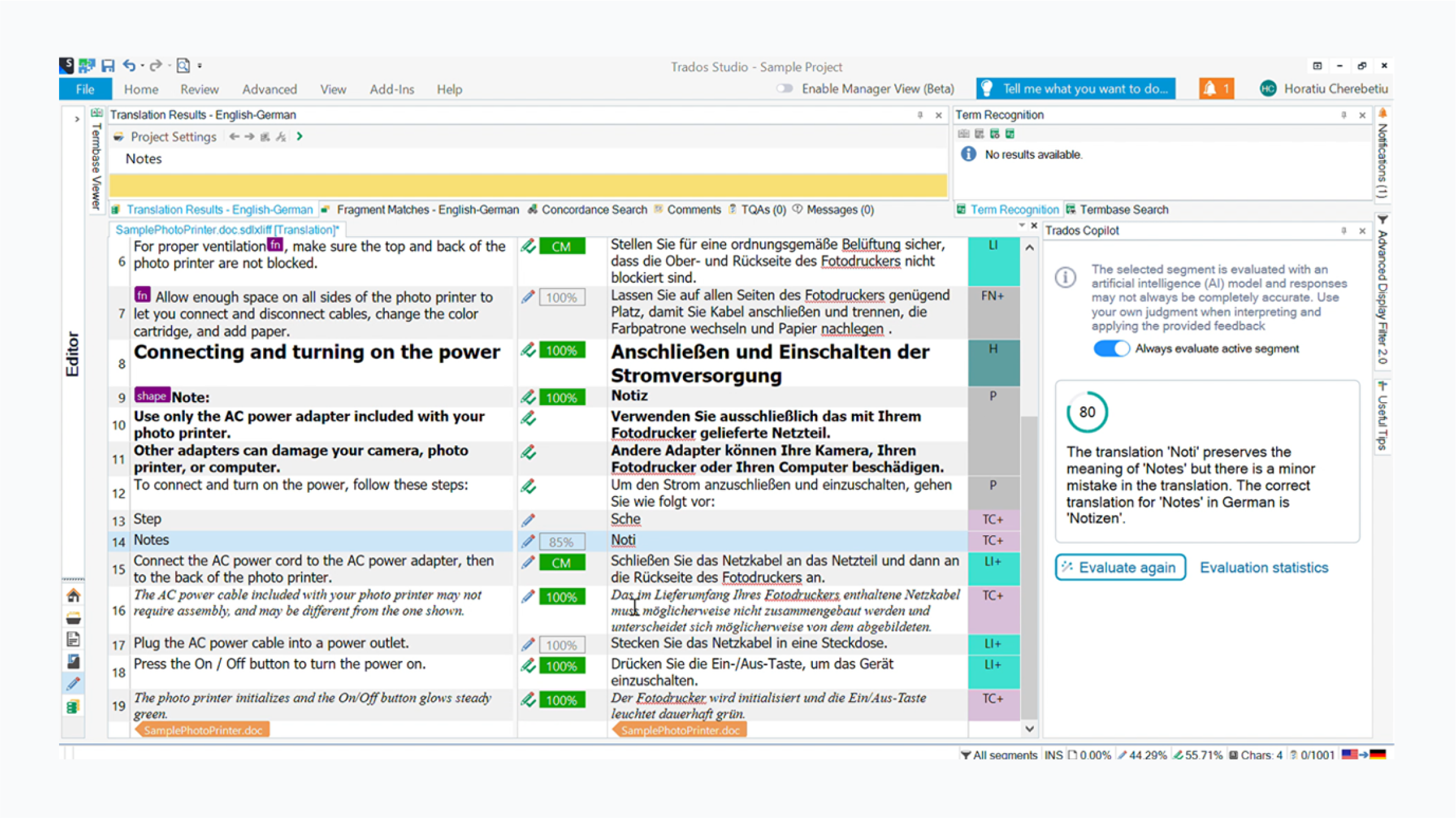
Computer-assisted translation (CAT) tools
CAT tools streamline the translation process without fully automating it. Think of them as editing environments providing translators with powerful, time-saving features to enhance efficiency and consistency.
👉 Examples include SDL Trados Studio, MemoQ, and Smartcat.
 Source: Trados
Source: Trados
CAT tool features
-
Segmentation to break text into easily manageable phrases.
-
Translation memories that offer matches of previously translated phrases.
-
Termbases and glossaries to collect and organize approved term translations.
-
Quality assurance checks to ensure consistent use of terminology and avoid typos.
If you’re hoping for “set-it-and-forget-it” software for automated translation and localization, CAT tools probably aren’t what you’re looking for. These tools are designed for professional translators, not for hands-off use.
As a business owner, you’ll need a dedicated manager to coordinate with translators, maintain the CAT software, and keep translation memories in check. And yes, it’s often even more complicated than it sounds 🥲
Here is what Yulia Zubkova, Localization Manager at NAKIVO, has to say on this:
💬“CAT tools can simplify a translator's work, but for a localization manager, they often make localization feel like a true test of patience: managing dozens of translators across multiple languages, ensuring the quality and consistency of translation memories, and dealing with constant integration challenges.”
| Pros 👍 | Cons 👎 |
|---|---|
| Increased efficiency | Steep learning curve |
| Cost reduction | Complex setup |
| Consistent translations | Translation memory errors |
| Formatting issues (PDF, XLSX, HTML) | |
| Limited integrations |
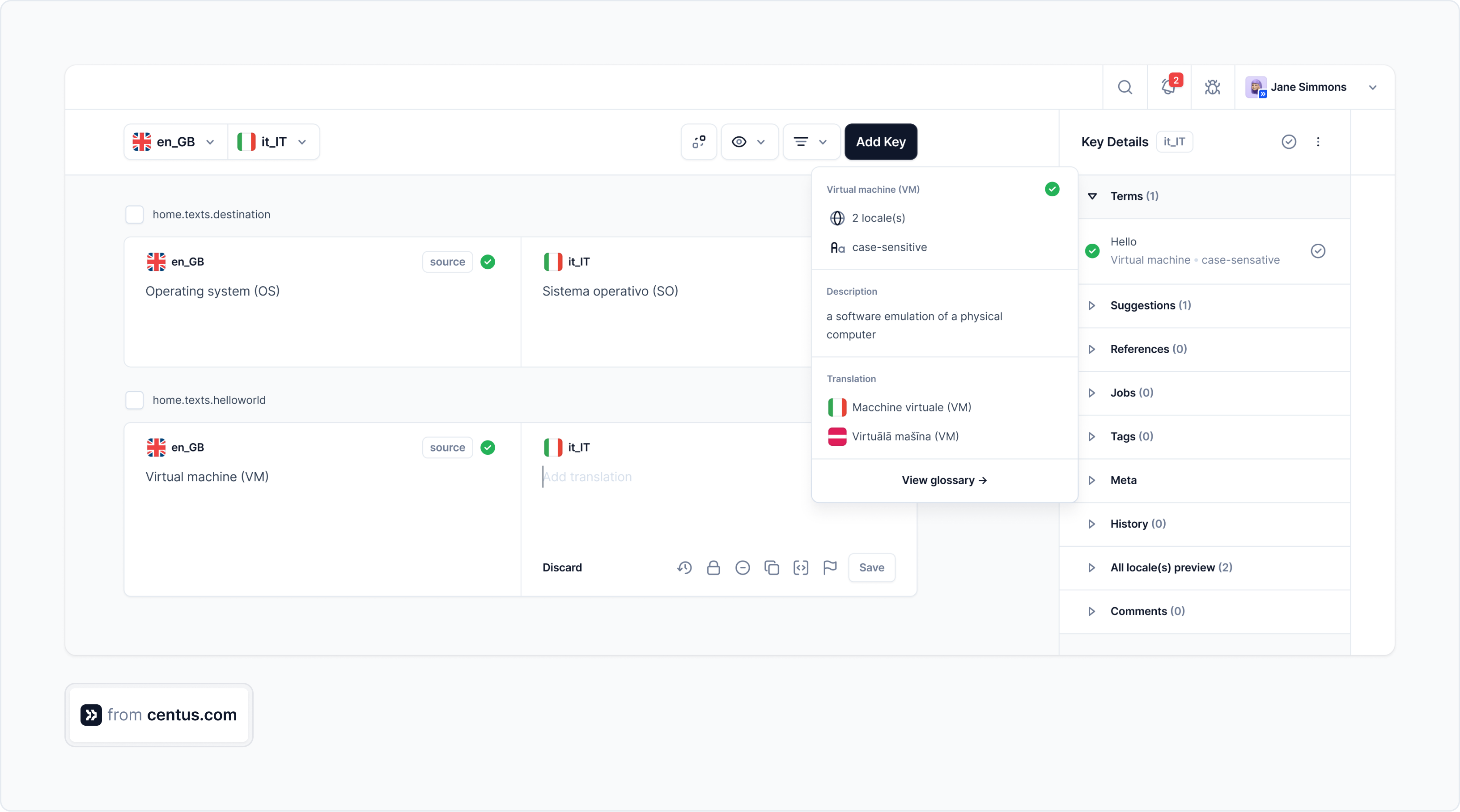
Translation management systems (TMS)
Translation management systems are cloud-based platforms for centralizing and managing the entire localization workflow.
Unlike CAT tools designed for individual translators, TMS are comprehensive solutions that streamline localization projects for entire teams, including translators, developers, designers, and managers. In addition to project management features, TMS incorporate all CAT tool functionalities and integrate with machine translation engines and AI-powered translation platforms.
👉 I could list a dozen TMS options…But honestly, Centus does the job so well, why not start (and end) there? Try Centus now and see for yourself.
TMS features
- Project management features to create, manage, and track translation projects.
- Vendor management functionality to hire third-party translators and editors.
- Collaboration tools to communicate and collaborate with team members and external contributors.
- Workflow automation to eliminate repetitive tasks such as file updating, terminology management, and quality assurance.
- Tool integrations to connect design, development, and other tools for customized localization workflows.
- Reporting and analytics features to monitor project progress and resource allocation.
- CAT features to boost translators’ productivity.
| Pros 👍 | Cons 👎 |
|---|---|
| Easy project management | High initial costs |
| Automated workflows | Unsuitable for individual translators |
| Advanced quality assurance | |
| Ideal for large teams |
What translation technology should I choose?
Choosing the right translation technology tool can make or break your localization projects. But with so many options available, how do you know you're getting the best fit?
To help you decide, let’s look at how MT, AI, CAT, and TMS tools stack against each other.
Note: I don’t include real-time translation technology because it’s designed for instant communication rather than handling complex business needs like content localization or large-scale translation management.
| MT | AI | CAT tools | TMS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ease of use | Generally user-friendly and intuitive | Generally user-friendly and intuitive | Steep learning curve | Might require training to navigate |
| Translation speed | Almost instant | Almost instant | Depends on human input | Fast, optimized by workflow automation |
| Accuracy | Low accuracy, term inconsistency | High for general content, but struggles with nuance and specialized terminology. | High, especially with experienced users | Extremely high, blends automated and human translation |
| Cost efficiency | Often free or low cost | More affordable than human translation | Requires investment in software and translators | Higher initial cost, but cost-efficient for large projects by combining technologies |
| Integration capabilities | API | A wide range of integrations | Very limited | A wide range of integrations |
| Scalability | Ideal for large volumes of general and low-impact content | Highly scalable for large volumes of general content with better context accuracy than MT | Good for individual projects | Ideal for handling multiple, large-scale projects |
| Quality control | Basic spellcheck, requires human post-editing | Limited; requires human post-editing for accuracy and consistency | Glossary and translation memory checks (often manual) | Comprehensive automated and manual checks |
| Best used for | Quick translations, informal or low-impact content | Quick translations, dynamic content, customer support and real-time communication | Professional, detailed work | Managing complex, multi-language projects |
| Users | Casual users, content consumers | Casual users, customer service teams | Professional translators | Localization managers, teams |
Parting thoughts
Picking the right translation technology can make all the difference in your localization projects. Whether you need speed, accuracy, or seamless team collaboration, there’s a tool for that.
However, translation technology is just one piece of the localization puzzle. Without effective management, things can get messy very quickly. If you want to streamline your localization workflow, our localization management guide breaks it all down for you.
Happy translating!
Get the week's best content!
By subscribing, you are agreeing to have your personal information managed in accordance with the terms of Centus Privacy Policy ->
Keep learning

5 min. read
Is DeepL Accurate? 2024 Research
11 min. read
How Accurate Is Google Translate for Your Business? 2024 Research

9 min. read
7 Best Machine Translation Software Tools
15 min. read
ChatGPT for Translation: Your Go-To 2025 Guide
6 min. read
How to Organize Content Translation Process
11 min. read