Technical Translation: Definition, Types, and Best Practices
You’re a technical translator or a localization manager racing against a clock to deliver a project on time.
Your challenge? Well, there’s more than one.
You need to translate specialized terms with clarity, concision, and correctness. You need to deal with misstatements and errors in the original. And, above all, you need to ensure that the quality of translations doesn’t fall victim to tight deadlines.
Worry not. I’ve put together a comprehensive guide to help you achieve just that.
You’ll learn how to create the ultimate technical translation workflow for any technical content, such as user guides, datasheets, or manuals.
Let’s begin.
What is technical translation?
Technical translation is the process of accurately translating specialized technical documents, such as user manuals, datasheets, and patents, from one language to another. It requires proficiency in both the source and target languages, as well as deep knowledge of the subject matter to ensure clarity, precision, and consistency.
Below is an example of technical translation: a coffee maker user manual translated into French.
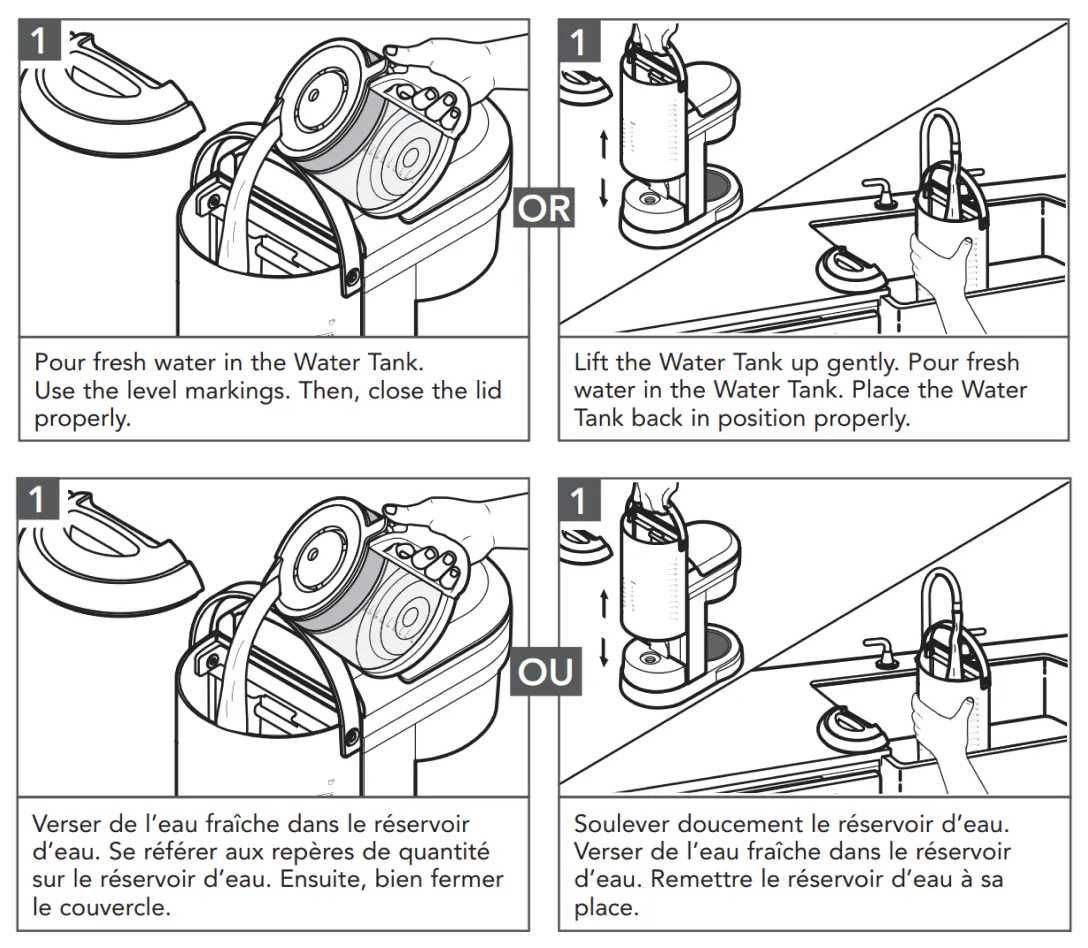
The manual explains everything from unpacking, initial cleaning, and assembly, all the way to tips for maintenance and descaling. An entire team of language professionals worked to help users make that perfect cup of coffee. And for a very good reason.
As businesses continue to expand internationally, they prioritize building a stellar customer experience across all touchpoints. Technical translations are an important piece of the puzzle here.
Before we dive further, let me draw a distinction between a technical translation and a scientific translation. Because most clients, and even some translators, confuse the two.
Technical translation vs scientific translation
Technical translation deals with technical texts, the sole purpose of which is to convey information clearly. Scientific texts, on the other hand, are designed to explain, analyze, and evaluate information. As such, the language used in technical and scientific texts varies substantially.
There’s no room for linguistic creativity in technical language translation. But scientific discourse might welcome it. Scientific translation calls for accurate rendering of individualism and style, requiring you to translate culture-bound metaphors such as the Big Bang, string theory, or greenhouse effect.
Put simply, technical translation is much more objective and impartial than scientific translation.
Types of technical translation
Well-translated technical documents make the end customer feel seen and respected. Moreover, they ensure practical information is accurate, clear, and easy to understand.
The less cognitive strain for the user, the better.
Let’s now take a look at different types of technical translation and why they matter:
- User manuals: Technical documents explaining how to use and maintain a product.
- Patents: Technical documents that describe the concept of the product and protect intellectual property rights, most commonly inventions.
- User guides: Textual or video materials for the audience that already has a basic understanding of a product.
- Product descriptions: Technical translations of the product’s benefits, features, specifications, and more.
- Knowledge bases: User manuals are accessible from a website or from within a software.
- Safety data sheets: Documents that provide guidance on proper storage and handling of hazardous chemicals.
- Software strings: Translatable text in software or apps.
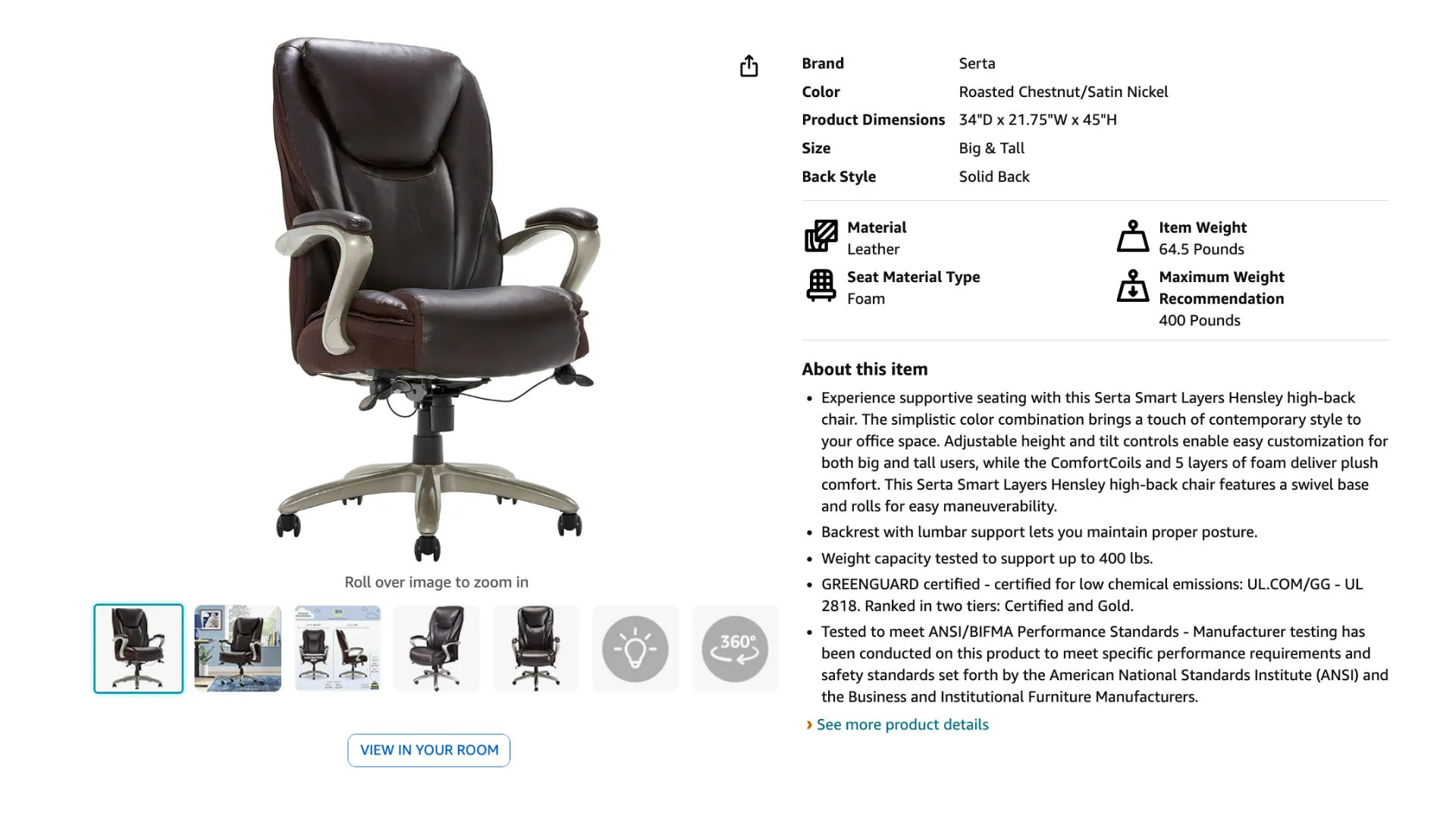
As an example of simple technical content, consider this product description on Amazon.
And here’s the translation for Spanish-speaking customers.
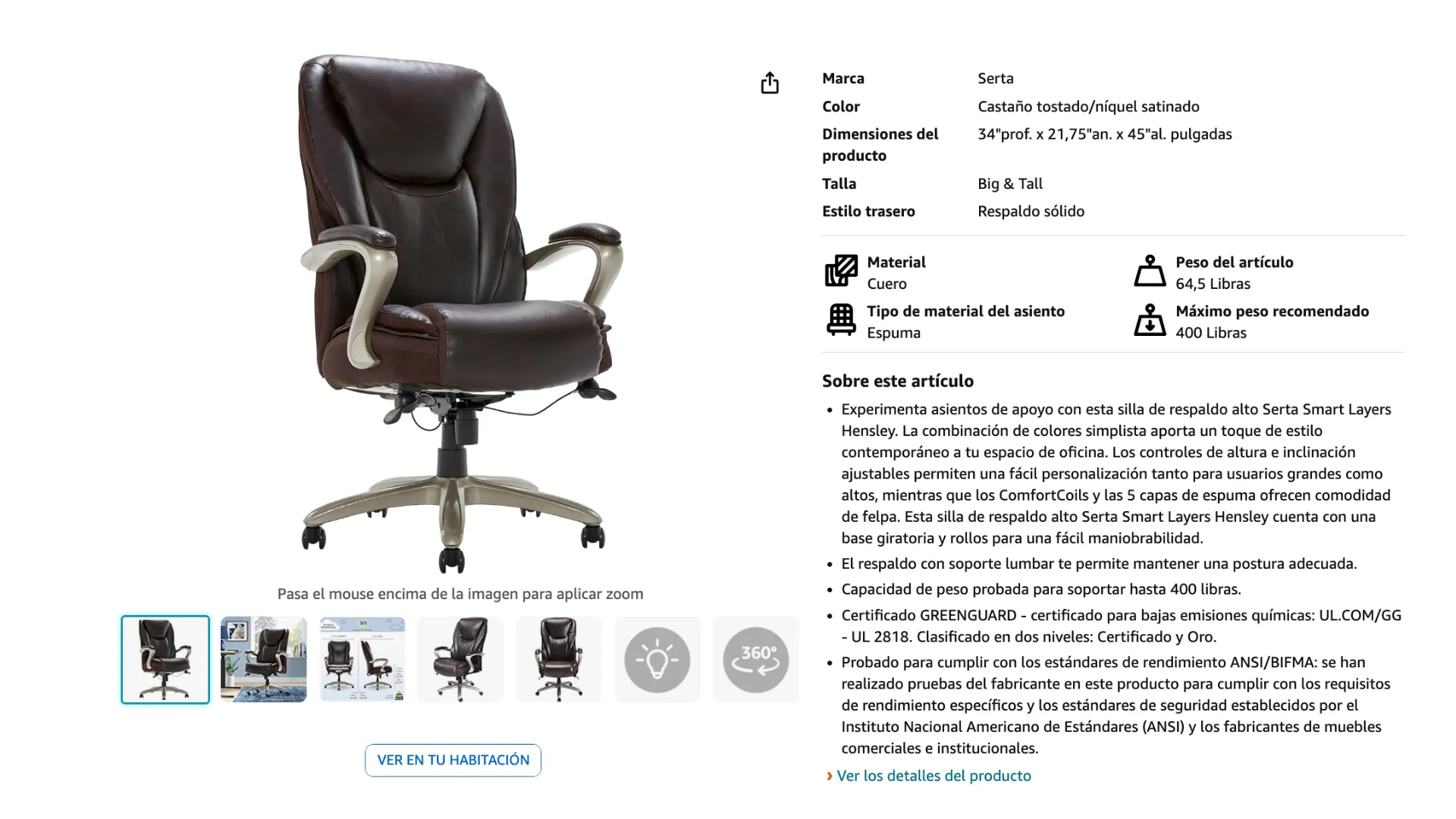
Did you know? Take a closer look at the product dimensions in both visuals. Note a period as a decimal separator in the English version 21.75″ W and a comma in the Spanish version 21,75″ AN. It’s not an accident! Learn more in our guide to localizing numbers
Amazon is well known for the lengths it goes to engage global audiences. In this case, the technical translation of the product description provides a great experience for Spanish-speaking customers.
The truth is, people are more likely to buy the product when they encounter useful content in their own language. It’s all about equipping them with the right information to make an educated buying decision.
Technical translation examples and best practices
With the fundamentals out of the way, let’s add basic translation of technical terms to your toolbox. The techniques will give you roundabout routes for situations where literal translation doesn’t work.
Borrowing
Use borrowing when there’s no similar word or concept in the target language.
| English example | Spanish translation |
|---|---|
| modem | módem |
| laser | láser |
| drone | dron |
| pixel | píxel |
Calque
When there are no alternatives in the target language, use calques created by recognized authors. Avoid creating your own calques.
| English example | Spanish translation |
|---|---|
| hardware | equipo físico |
| keyboard | teclado |
| wireless | inalámbrico |
| chat room | sala de chat |
Equivalence
Use equivalence to preserve the idiomaticity of the original text. You might want to create equivalent translations for warning notifications or messages.
| Original phrase | Modified phrase |
|---|---|
| Update available | New version ready |
| File not found | Unable to locate file |
Modulation
Present information from a different point of view i.e. modulate it. In most cases, modulation is as simple as swapping a negative sentence with a positive one.
| Original phrase | Modified phrase |
|---|---|
| Do not disconnect the unit | Keep the unit connected |
| Easy to use | Not difficult |
Particularization
Sometimes you might need to replace a generic term with a more specific term to avoid ambiguity in the target text.
| Original phrase | Modified phrase |
|---|---|
| Network | LAN or WAN or Wi-Fi |
| Storage device | hard drive or SSD or USB flash drive |
When technical translation goes wrong
Mind you, inaccurate technical translations can cause serious harm depending on the scenario. This is especially true in healthcare and nutrition. Here’s one unfortunate example.
In 2001, Mead Johnson Nutritionals had to recall ~4.6 million cans of ready-to-use baby formula from the Spanish market. Why? Because the preparation instructions in Spanish were incorrect.
Adding an incorrect amount of water could alter the formula’s precise mixture of nutrients. If a child drinks it for several days, they could suffer seizures, have heartbeat problems, or even die.
Clearly, a precise translation workflow and rigorous quality control are a must. Let’s see how to implement them.
How to perform technical translation for documents
Now comes the fun part: the actual technical translation workflow.
The reason most translation projects go south? Lack of preparation and clarity on a team level.
Assuming you’re in the manager role, your job is to oversee the entire translation project. Not only that, but you have to quickly identify any bottlenecks, resolve misunderstandings and conflicts, and manage timelines. Dang it, that’s a lot.
But don’t panic yet. I outlined the key steps in the technical translation workflow:
1. Define the scope and budget
Take your time before kicking things off. You need to fully understand what the source technical content is about. It’s equally important to have an internal consensus on the translation budget.
Did you know? Average technical translation rates are between $0.15 and $0.35 per word, depending on the complexity of the project. If you’re outsourcing translation services, make sure you ask the agency how they handle bulk translations and if that affects the rates.
Here’s what you need to do next:
- Define the amount of content, its complexity, and language pairs
- Make sure your translators will have access to any previous translations
- Define the tools the team will use and prepare any necessary onboarding materials
- Set expectations in terms of project milestones, deadlines, and communication channels
2. Assemble a team
The number of needed hands on the deck depends on the size and complexity of the project. In any case, you need the following people (it’s the bare minimum):
- Technical translation project manager (or localization manager)
- Technical translators
- Editors
- Subject-matter experts
Note: If your budget permits, also add a QA expert to your team.
After assembling a team, organize a project kick-off call.
The kick-off call should be no longer than 45 minutes. It should serve as an introduction to how you’ll be leading the project. Make sure every team member understands their role, the tools they will be using, and deadlines. Encourage them to ask questions.
Pro tip: Ensure your team can collaborate efficiently. The easiest way to achieve this is with the help of professional translation management tools, like Centus. Using Centus you can bring your entire team together under one digital roof, where they can translate, edit, and share feedback.
3. Create a termbase
If you are joining an ongoing project, you are in luck: there’s a termbase you can use to ensure consistent translations. But if it’s a new project, make sure to create a termbase. Without it, you and your team will have to continuously translate the same terms, wasting time and creating inconsistent translations.
Here’s how your termbase might look like:
| Term | Part of speech | Definition | Usage example | Spanish translation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| API | Noun | A set of rules for guiding communication between software. | The new API simplifies integration with third-party services. | API |
| Bandwidth | Noun | The amount of data that can be transmitted over a network in a given amount of time. | High bandwidth is necessary for streaming videos smoothly. | Ancho de banda |
| Cloud computing | Noun | The delivery of computing services over the internet. | Cloud computing enables businesses to scale their operations easily. | Computación en la nube |
When translating technical documents, you can maintain your termbase using a spreadsheet. All team members can have access to it and expand it as necessary.
But, there’s a catch:
Using a spreadsheet as a termbase means your team will have to manually search for each term. This introduces countless opportunities for errors, not to mention wasted time. A better way to handle this is with the Centus translation management platform.
Simply add terms and their translations in the languages of your project.
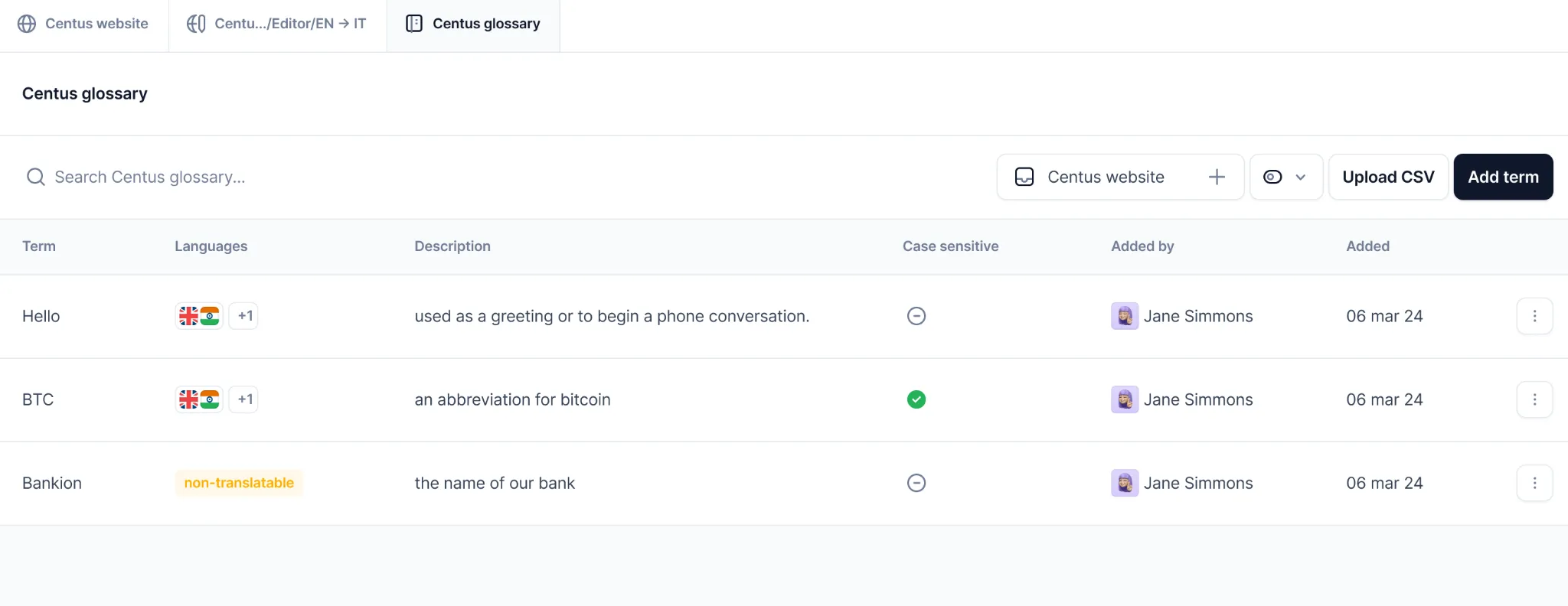
The terms will automatically appear as suggestions in the Centus Editor. Thus, instead of translating the same terms over and over, you can add them to your target text with a single click.
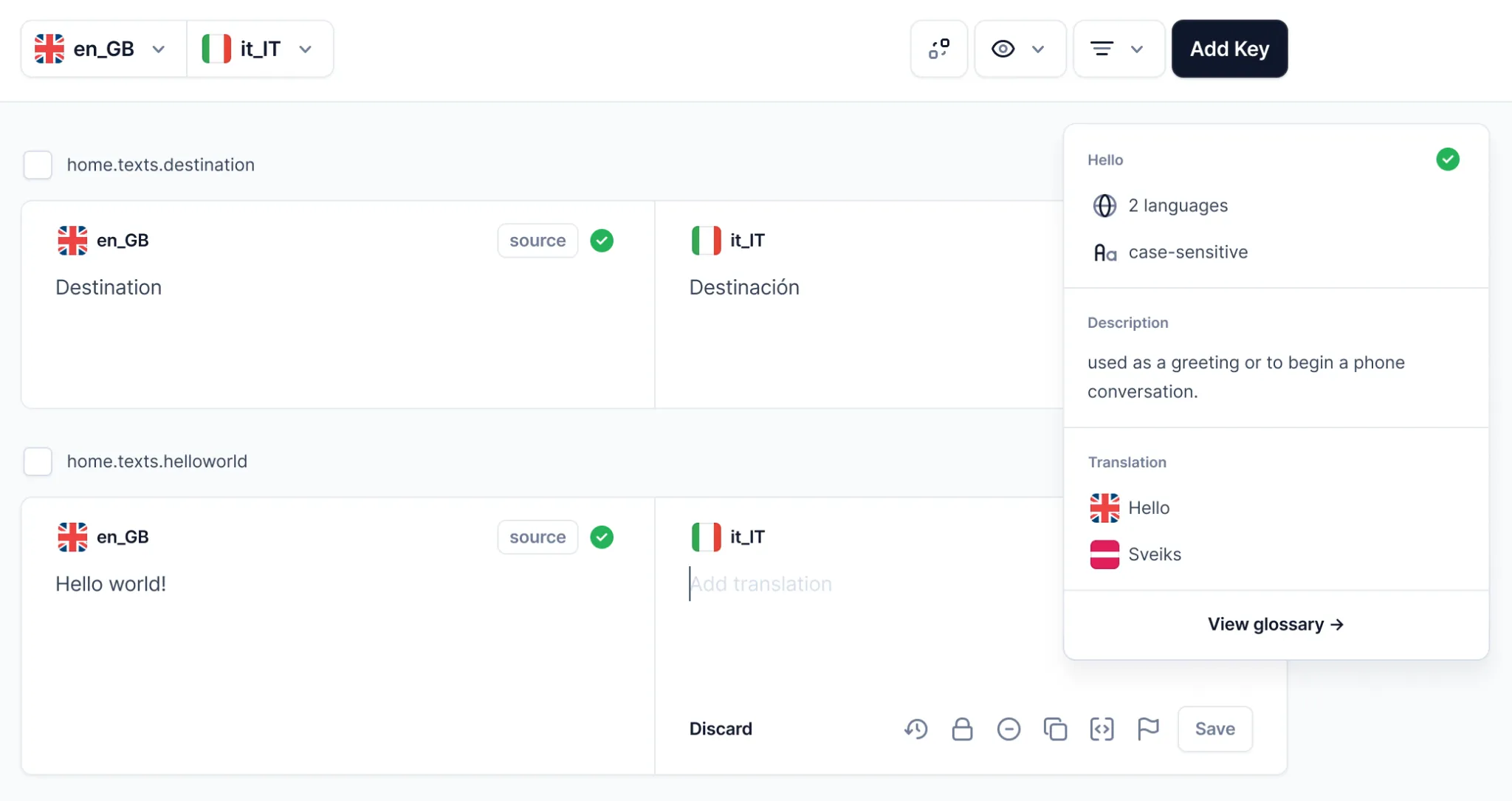
In the same vein, Centus can store previously-translated phrases in its translation memory. Instead of translating the same content twice, re-use old translations suggested in the Centus Editor.
Now everything is ready to perform technical documents translation.
4. Perform translation
For best cost efficiency, opt for machine translation post-editing (MTPE), where humans edit machine-translated text. If you have a great glossary and translation memory in place, this is really a no-brainer. Machine translation allows you to:
- Cut down costs
- Speed up your translation significantly
- Scale by creating a repeatable editing process that’s easy to follow
Ideally, you would have a bilingual subject-matter expert to check and edit MT output for accuracy. They should also make sure that the content reads naturally in the target language.
Here’s how to effectively organize MTPE for your technical documents and manuals:
- Sign up to Centus and create a new project
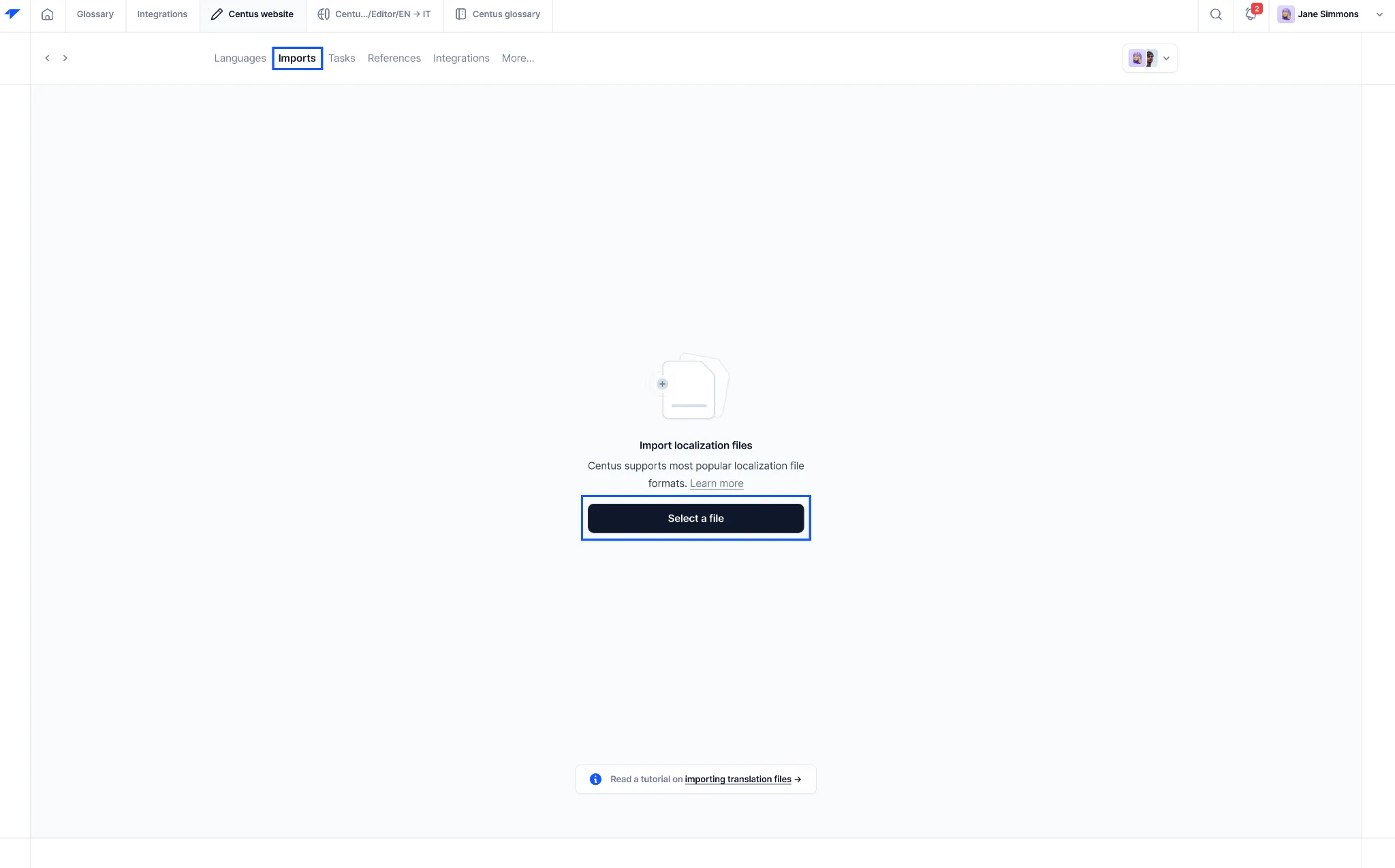
- Navigate to the Imports section and upload one or multiple source files
- In the Editor, review automatically segmented content
- Choose among translations created by Google Translate, DeepL, or Microsoft Translate
- Click Save
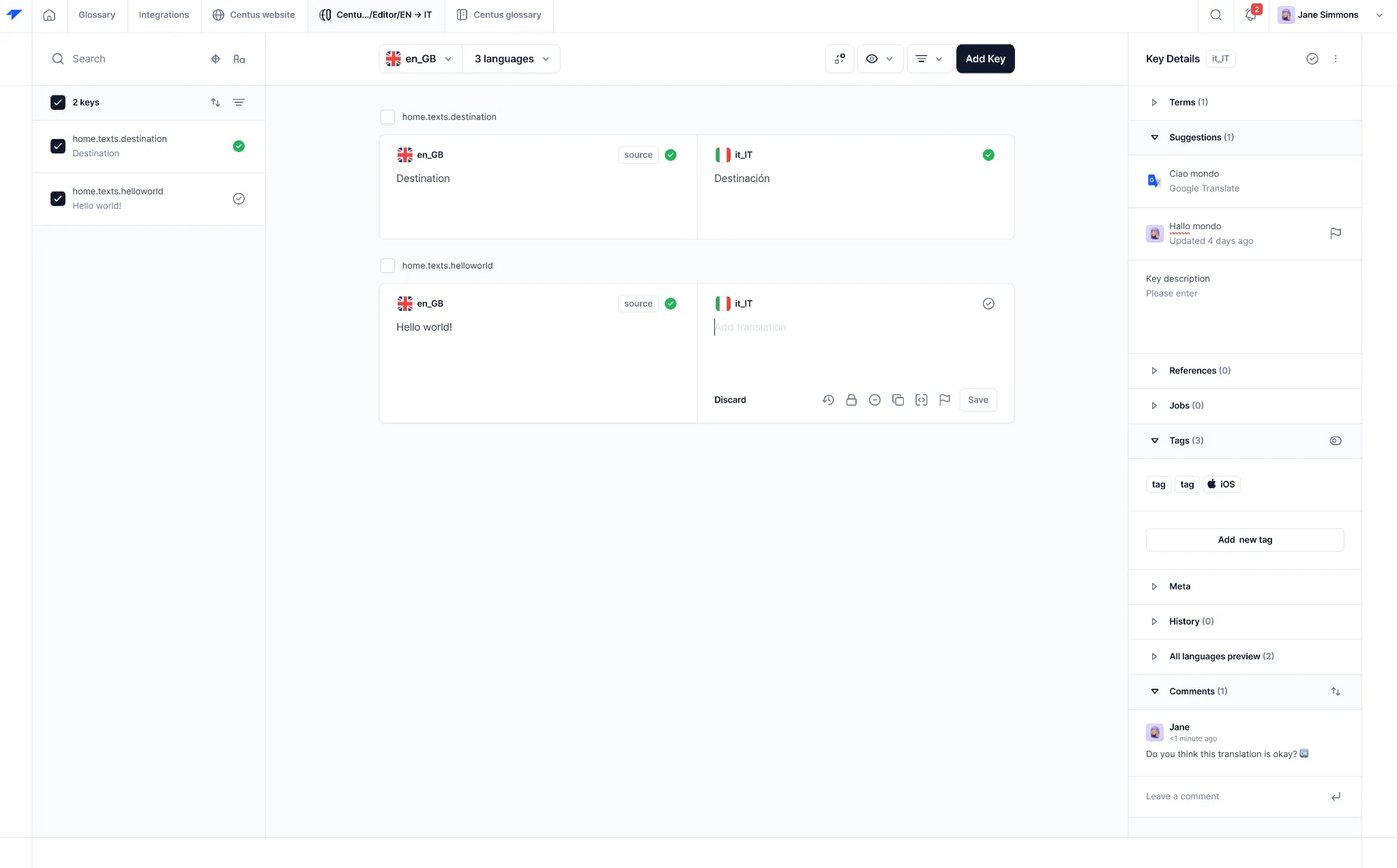
When translations are automatically generated, it’s time for the post-editing part of MTPE. It goes like this:
- In the Contributors section, click Add people to add an editor
- Enter the editor’s name, email, and other details
- Choose the Reviewer role from the dropdown menu
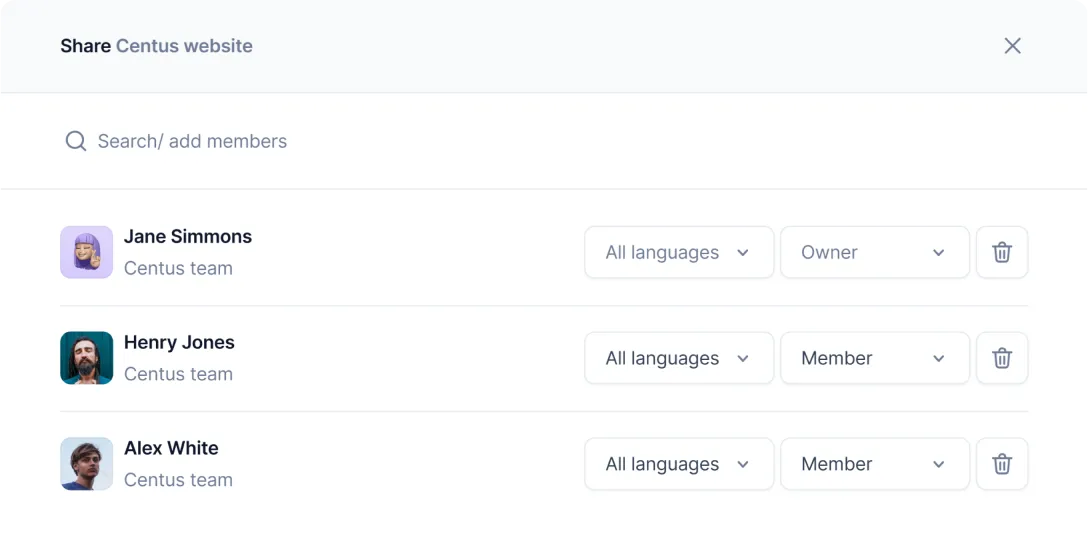
- Click Add project contributor
Now your reviewers can edit the technical content and leave comments for translators and managers.
You can add as many editors, subject matter experts, and quality assurance specialists as you wish. Once the feedback is shared and acted upon, approve and finalize the translations.
Pro tip: As a project manager, you should really insist on translating the document section by section. This gives you more control over the output and it helps you set the quality bar faster.
4. Perform quality assurance
To ensure your document is accurately translated and properly formatted, use a combination of automatic and manual QA. Let’s start with the automatic part:
Using technical translation software, like Centus, you can automatically identify these types of errors in translated technical documents:
- Spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors
- Placeholder differences in the source and target text
- Leading and trailing whitespaces
- Bracket differences in the source and target text
- Number differences in the source and target text
- Email address differences in the source and target text
- URL differences in the source and target text
But, of course, automatic localization testing won’t cut it entirely. You also need human QA experts to verify the accuracy of translated technical documents. Some things they’ll need to pay attention to:
- Completeness check to verify that all content is translated
- Functionality of embedded elements such as hyperlinks and footnotes
- Functionality of embedded media such as images, audio, and video
- Consistency across file formats
- Consistency across platforms and devices
- Version control to ensure that the right version of the document is translated
- Version control to ensure that updates in the original document are reflected in the translated document
- Adherence to grid layout and design template
- Consistent styling for fonts, headings, paragraphs, bullet points, numbered lists, etc.
Parting thoughts
Now you know how to perform technical translation step-by-step.
Always approach technical translation projects with a clear brief, term base, and the right tools.
To fast-forward your technical translations, try Centus now. And to quickly assemble a team of language experts, read this guide on how to find translators.
Good luck!
Get the week's best content!
By subscribing, you are agreeing to have your personal information managed in accordance with the terms of Centus Privacy Policy ->
Keep learning
6 min. read
Translation of Technical Terms: A Practical Guide
5 min. read
How to Automate Terminology Management for Your Business

9 min. read
7 Best Machine Translation Software Tools
18 min. read
7 Localization File Formats Explained with Examples
8 min. read