What is Product Localization? A Comprehensive Guide
Can I just translate my product information and call it a day? Well, you could. It’d be fast, but not necessarily effective.
To attract local leads and turn them into customers, you need to tailor your product to their preferences. You need to communicate its value. You need…
Well, you need product localization. And this guide will show you exactly how to do it.
What is product localization?
Product localization is the customization of a product to suit the language, culture, and regulations of a target market. Localization is performed to create an engaging user experience for the intended local audience. In some cases, however, it is mandated by law.
To illustrate how companies adjust their international offerings, let’s consider two product localization examples.
Here’s the UK version of the Adidas website:

It’s no surprise to see the promotion of football kits on the main page, given that football is essentially the national pastime in the country.
And below is the Saudi Arabian version of the Adidas website:
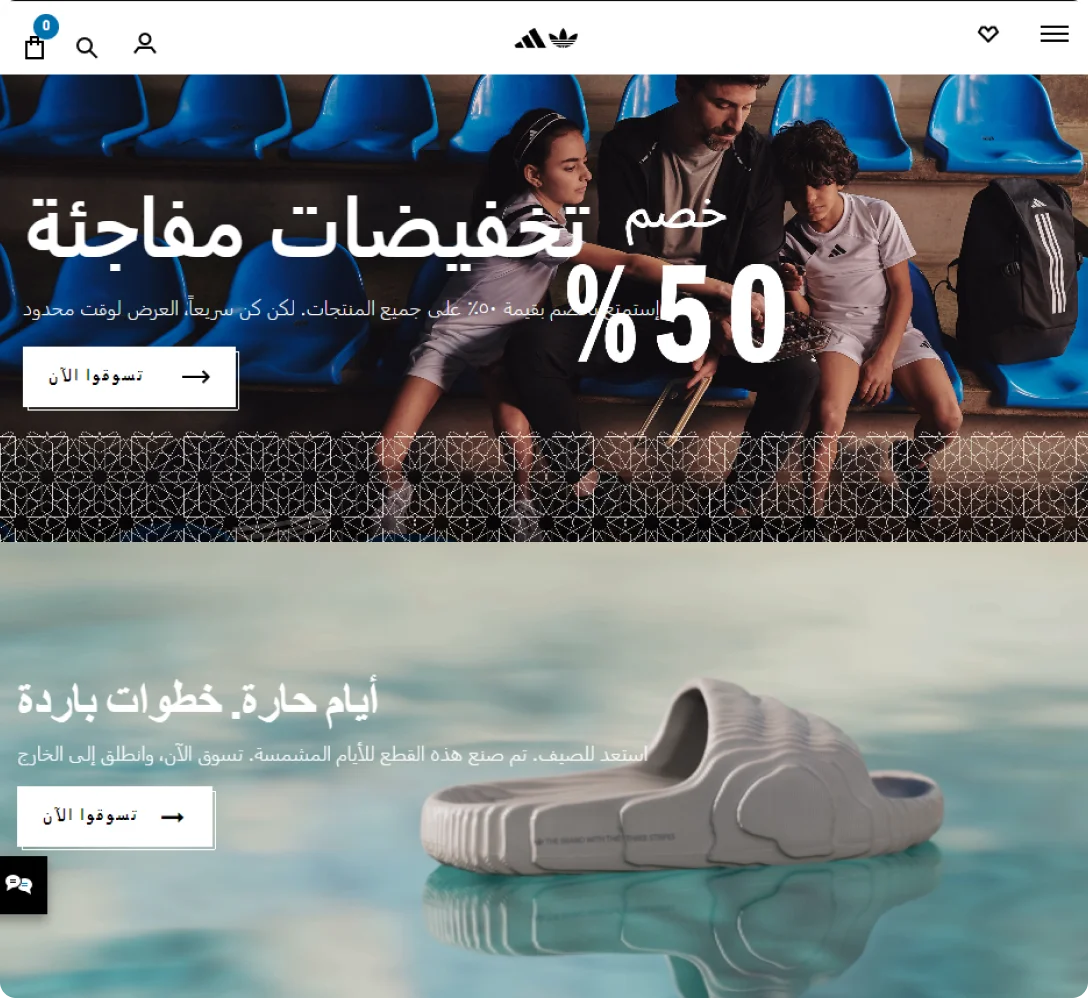
Here, Adidas caters to seasonal trends, showcasing a pair of slippers.
One company, two different website versions. Is it worth the effort?
Absolutely!
Product localization is a strategic investment to expand your market reach and build stronger relationships with customers worldwide. Other product localization benefits include:
- increased sales
- higher customer satisfaction
- improved customer loyalty
- enhanced brand authority
- consistent brand messaging
Note, however, that localization isn’t just beneficial for websites. You can also localize:
- physical products
- software
- apps
- video games
- multimedia content
How to localize your product in 7 steps
Product localization is a long, arduous, and often iterative process. But, as detailed above, the effort is well worth it.
So, buckle up and let’s dive into the step-by-step process of product localization:
Step 1: Select the target market
If you already have a target market in mind, skip this step. Otherwise, select your target market by analyzing your own or competitors’ websites.
Here’s an easy way to do it:
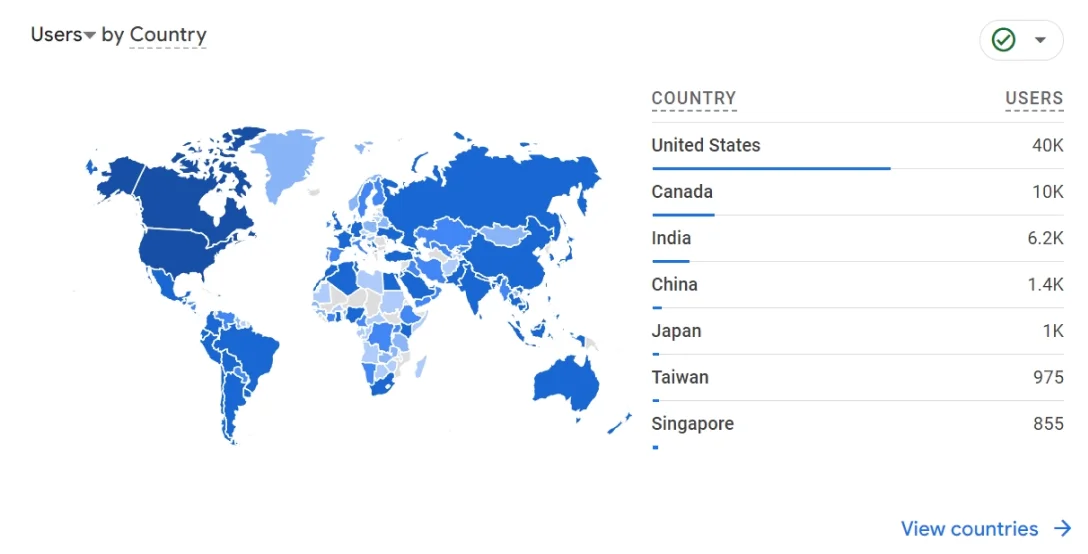
- In Google Analytics, open the Reports tab
- On the left, expand User attributes > Demographics overview
Examine the country and language data for growing interest in specific regions.
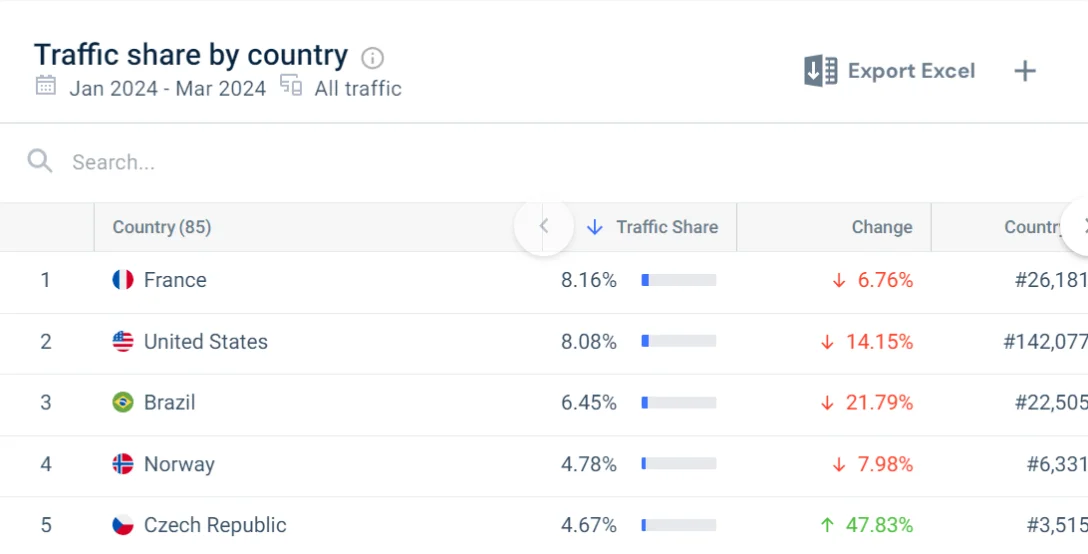
Now analyze your competitors’ traffic to see if there’s demand for their products abroad:
- In SimilarWeb, click Website analysis
- Enter your competitor's website URL
- Scroll to the Geography section
Analyze country and traffic data. Look for regions where your competitors have a strong presence, which might indicate promising markets.
Pro tip: Don't stop at just online tools. Consider using product localization services or hiring a local product localization company for a deeper analysis.
Step 2: Build a localization team
Next, assemble a localization team consisting of the following experts:
- Localization project manager oversees the entire localization process and ensures tasks are completed on time and within budget.
- Translators with expertise in your target languages and the specific domain of your product.
- Developers handle UI and UX adjustments to accommodate translated text and layouts.
- Quality assurance (QA) testers review the localized product to identify bugs, defects, and inconsistencies.
- Marketing specialists who understand consumer behavior, competitive landscape, and effective channels for marketing in the target region.
- Designers adjust visuals, layouts, and UI/UX elements.
- Legal advisors ensure compliance with local laws and regulations.
Step 3: Prepare content
Create a comprehensive inventory of all product content requiring localization. Common localizable elements include:
- User interface (UI) text: On-screen text such as buttons, menus, error messages, tooltips, and instructions.
- Marketing materials: Website copy, product descriptions, brochures, social media content, and advertising campaigns.
- Packaging and labeling: Text on product boxes, manuals, warranty information, and safety instructions.
- Technical documentation: User manuals, installation guides, and online help files.
Step 4: Translate content
Now it's time to translate your content. Google Translate is not accurate enough to entrust your business content to it. DeepL also doesn’t cut the mustard quite yet.
A better approach is to use a localization management platform, Centus, where you can create automatic translations and assign them to human editors for review. It goes like this:
- Sign up to Centus
- In the Project dashboard, click New project
- Name the project and choose the base and target languages
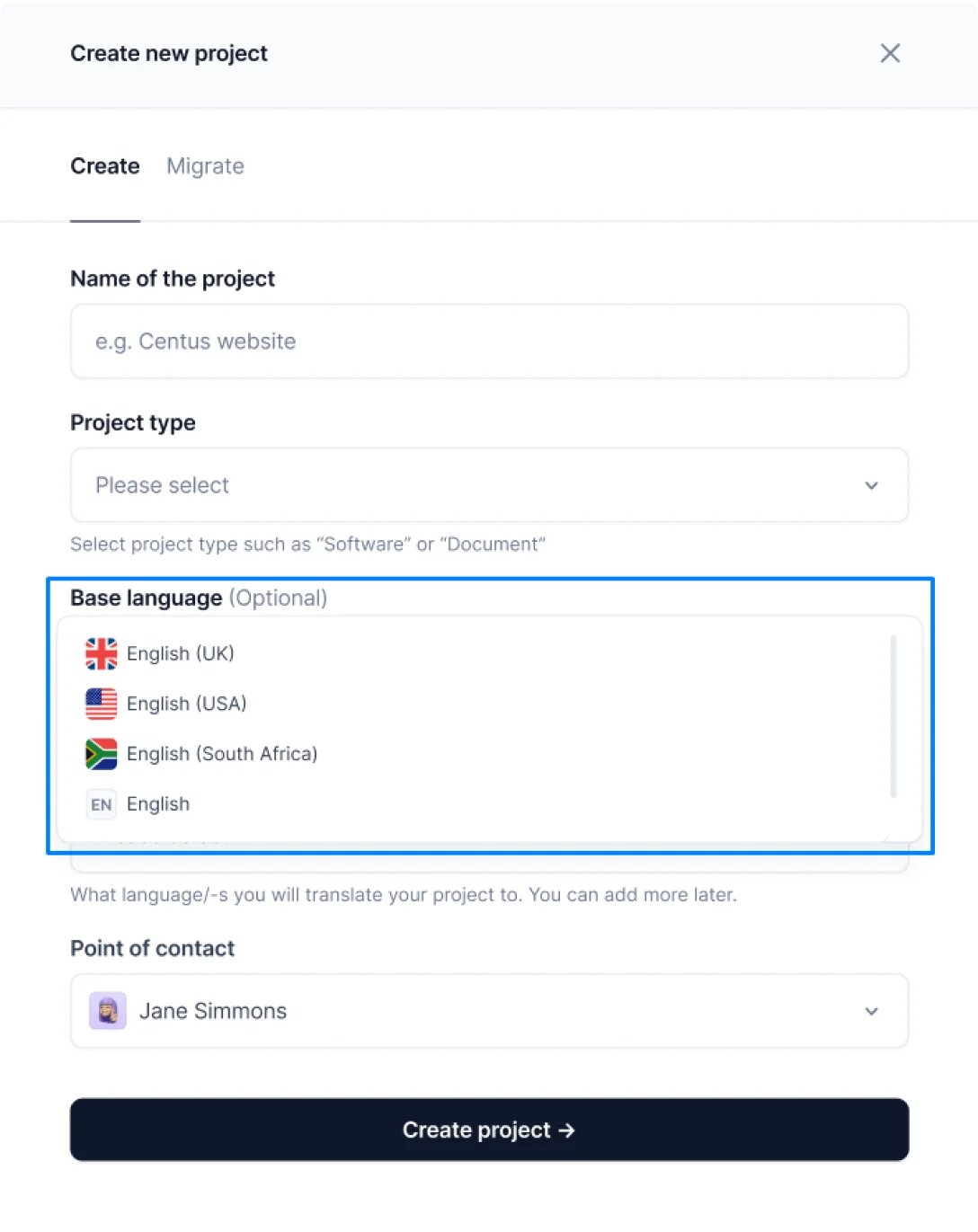
- Select the project type
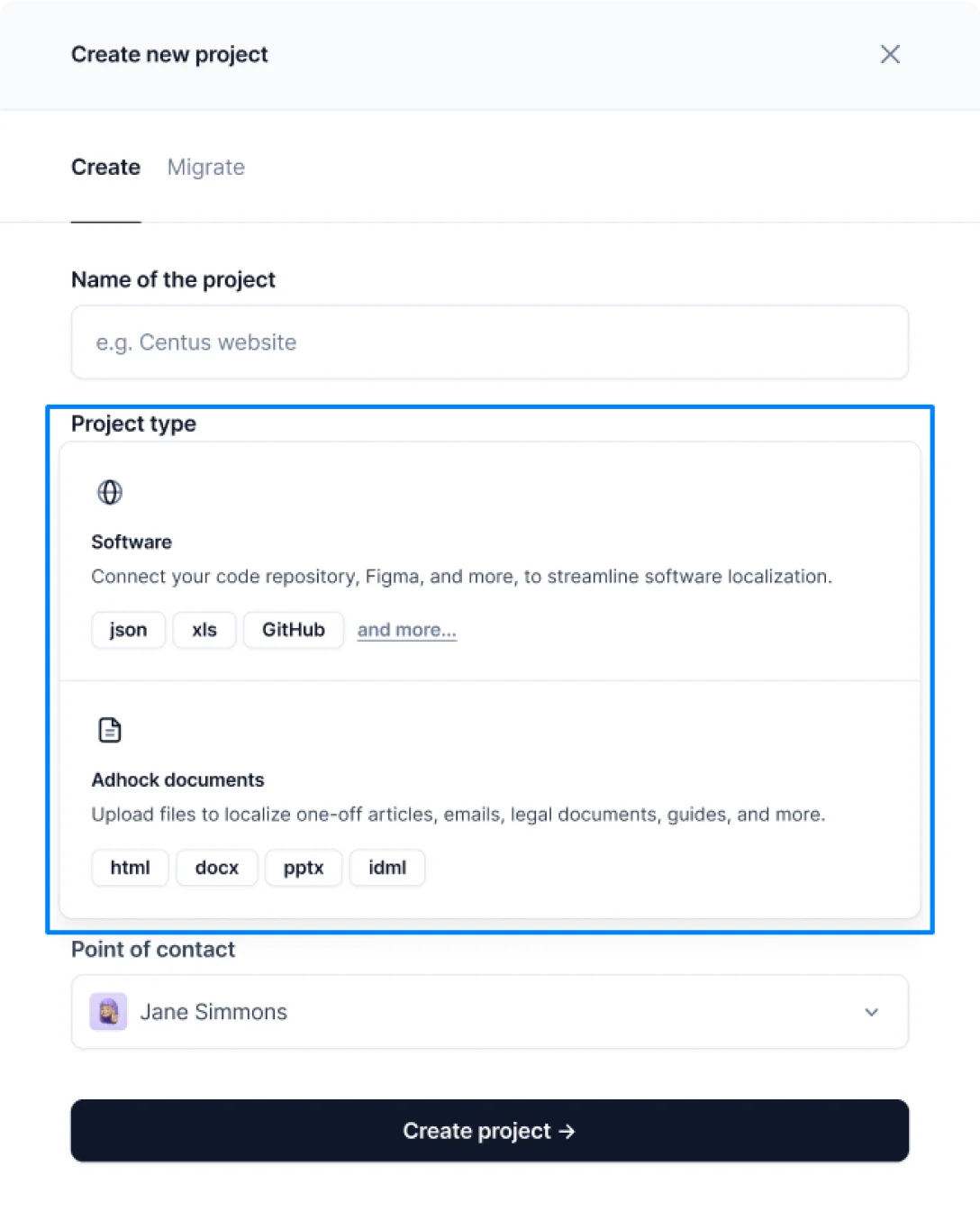
- Click Create project
- In the new project, navigate to the Imports section
- Click Select a file
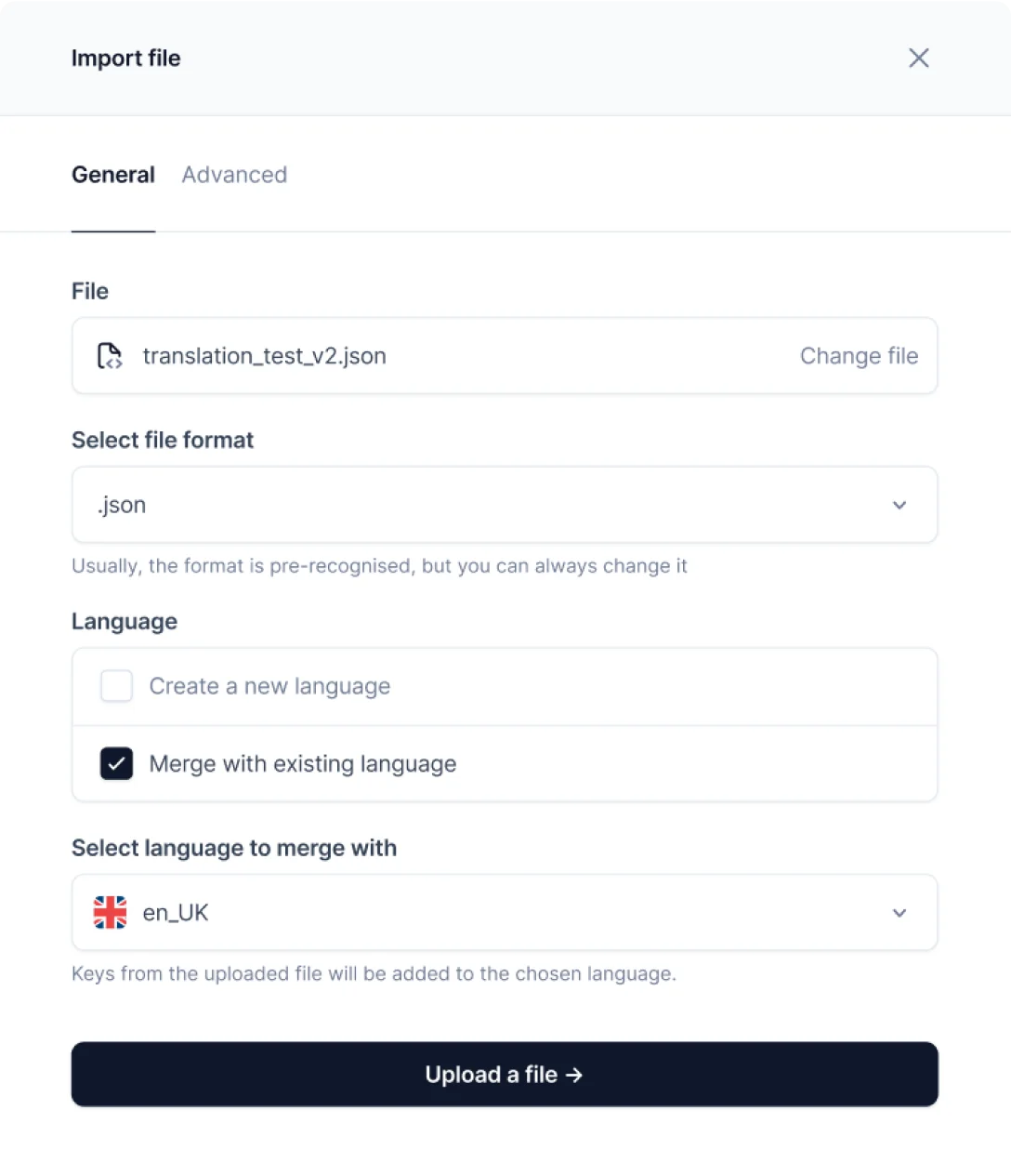
- Select the HTML, CSV, JSON, DOCX, PPTX, or other files for translation
- Click Upload a file
- In the Editor section, click empty values and choose among available translation options: Google Translate, DeepL translate, or Microsoft Translate
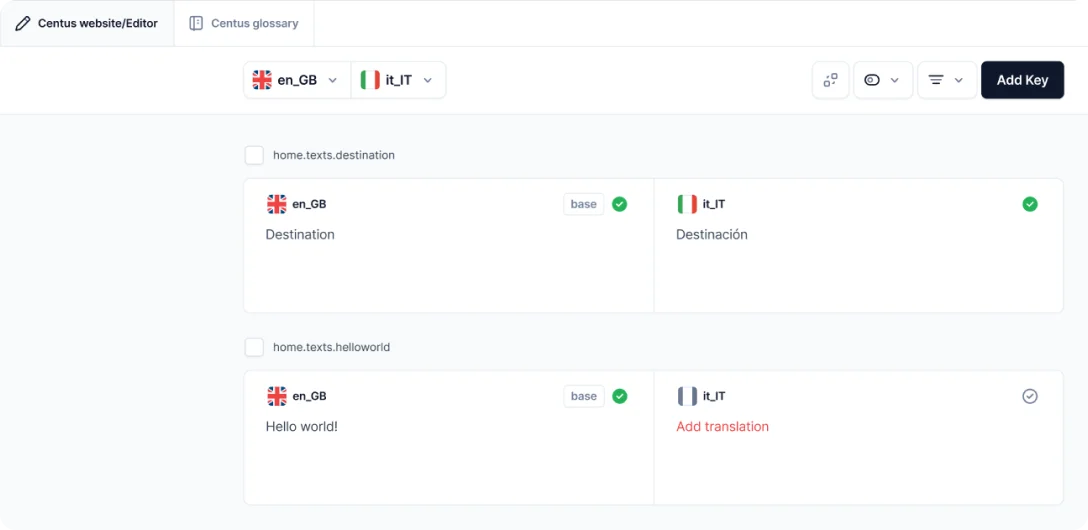
- In the Contributors section, click Add people to add a reviewer
- Enter the reviewer’s name, email, and other details
- Choose the Reviewer role from the dropdown menu
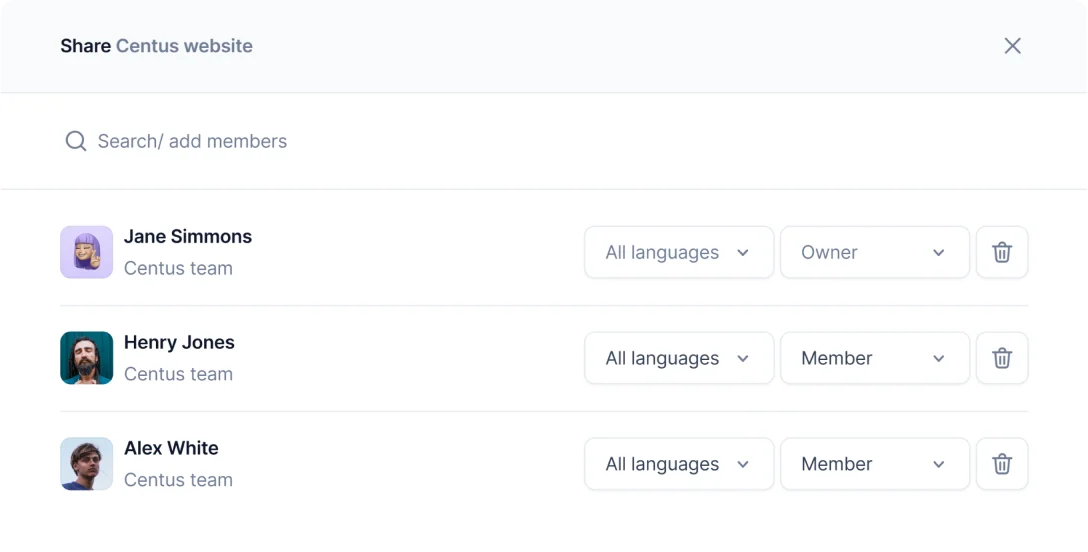
- Click Add project contributor
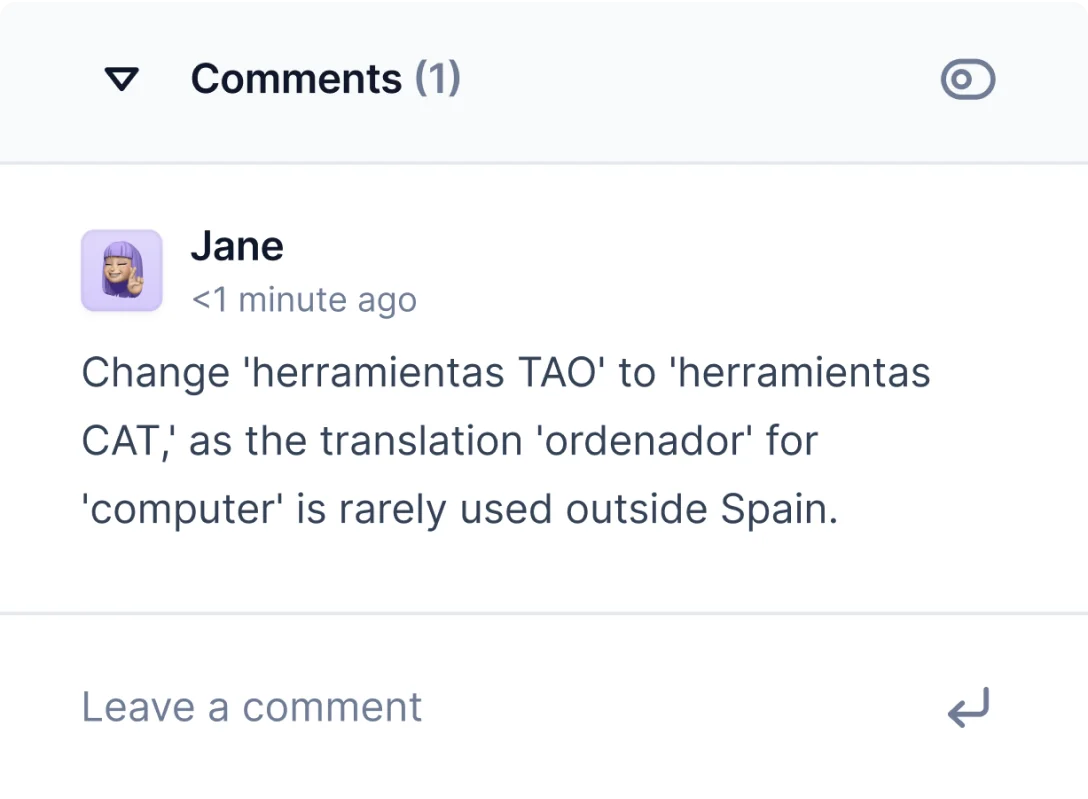
- Let the reviewer edit the translations and leave comments
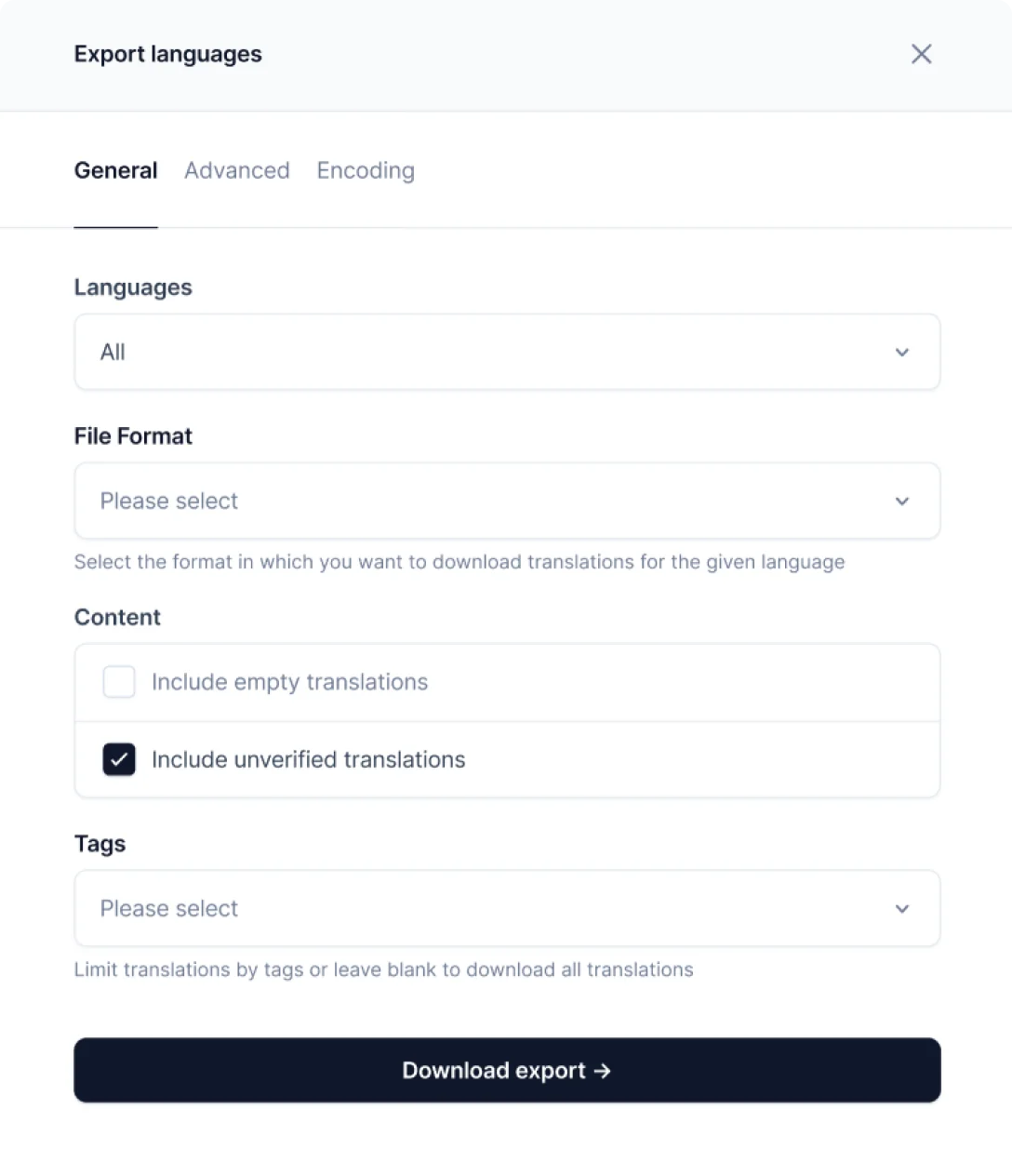
- In the Export section, choose the preferred file format
- To download translated content, click Download export
Step 5: Localize content
It’s not enough to just translate content. To properly localize it for the target region, you need to also adjust:
- Idiomatic expressions

- Humor

- Levels of politeness

- Numbers
Modify date and time formats, currency symbols, and measurement units to adhere to local conventions. For example, Germans use a full stop as a number separator, while most countries use a comma.
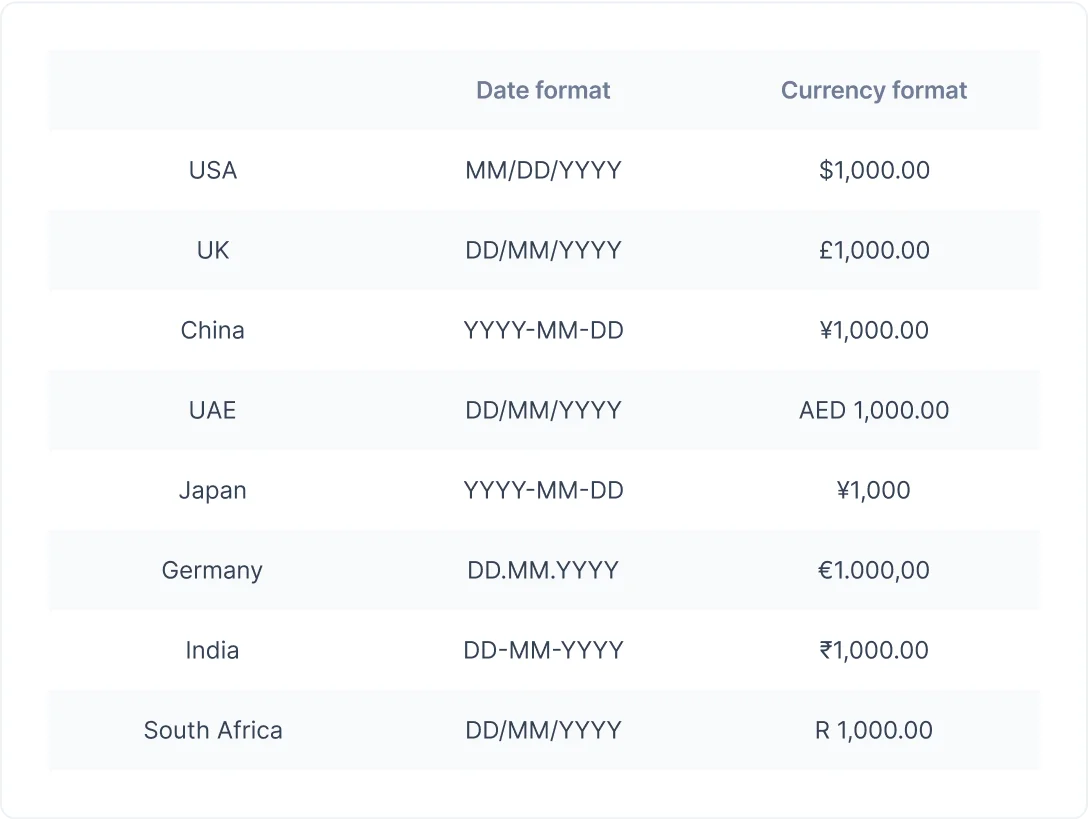
At this stage, you’ll find our number localization guide incredibly helpful.
Step 6: Localize UI/UX elements and images
Make sure to localize UI/UX elements and images for your website, app, or software. This step of the localization process is extremely tricky. Unless, of course, you have the right tool at hand. Preferably, your favorite design tool.
You see, using Centus, you can localize images in Figma or Sketch. A convenient integration allows you to pull translations from Centus to your graphic design tool to localize images in mere moments. Here’s how it’s done:
- In Centus, navigate to the Integrations section
- Find Figma and click View
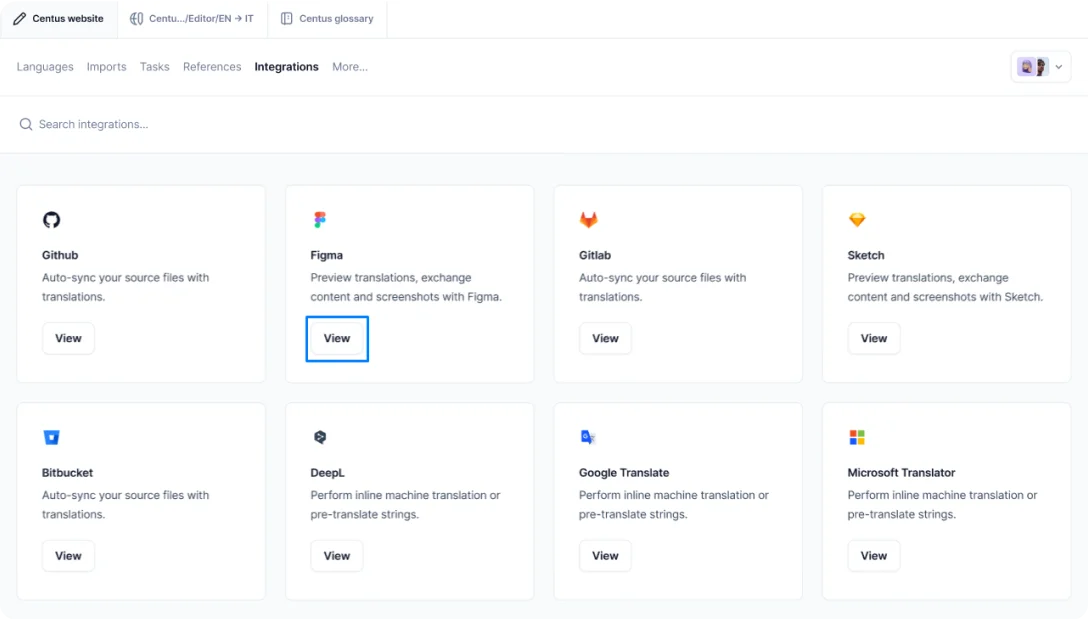
- In a window that opens, select your project
- Click Install integration
- In Figma, select text requiring translation
- Click Confirm to push changes
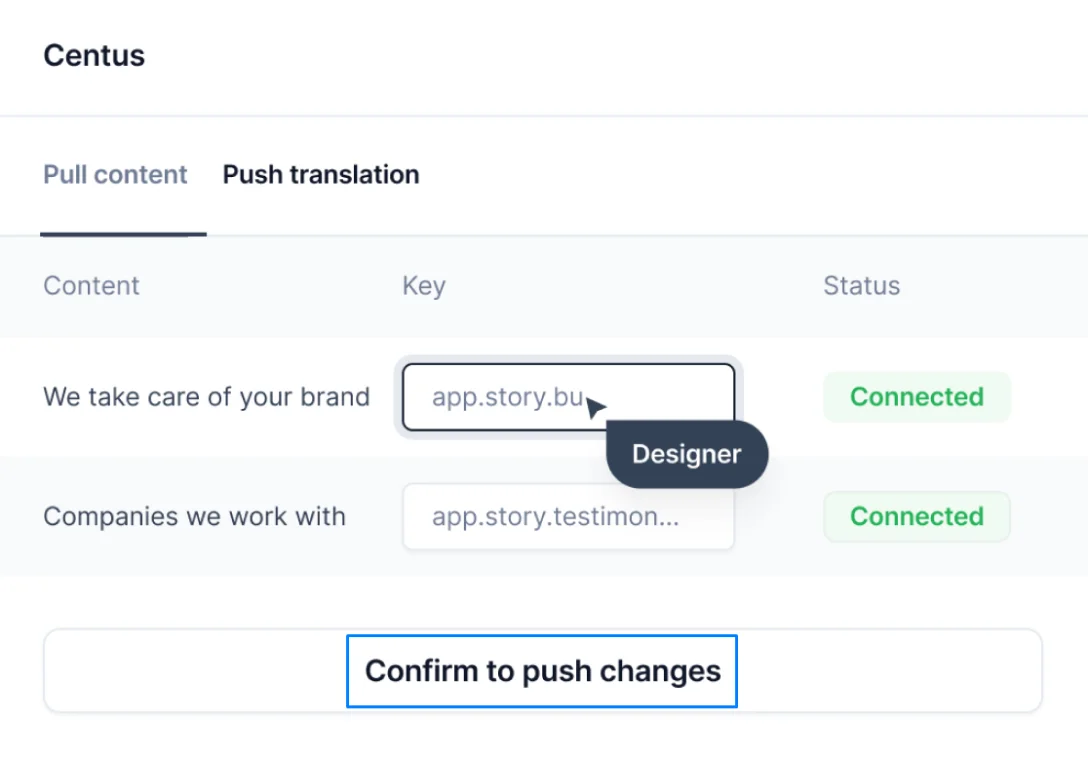
Voila! Your image contains edited and verified translations pulled from Centus. Now you can pull the remaining translations and resize the images to accommodate text expansion or contraction.
Step 6: Quality assurance and testing
Once you’re done with translation and localization, you should check if your product functions flawlessly and meets the standards of your target audience.
Centus streamlines the localization testing process by integrating tools that reduce manual effort. With these tools, you can automatically identify various issues in translated strings, including:
- Spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors
- Placeholder differences in the source and target text
- Leading and trailing whitespaces
- Bracket differences in the source and target text
- Number differences in the source and target text
- Email address differences in the source and target text
- URL differences in the source and target text
To test localized content, follow these steps:
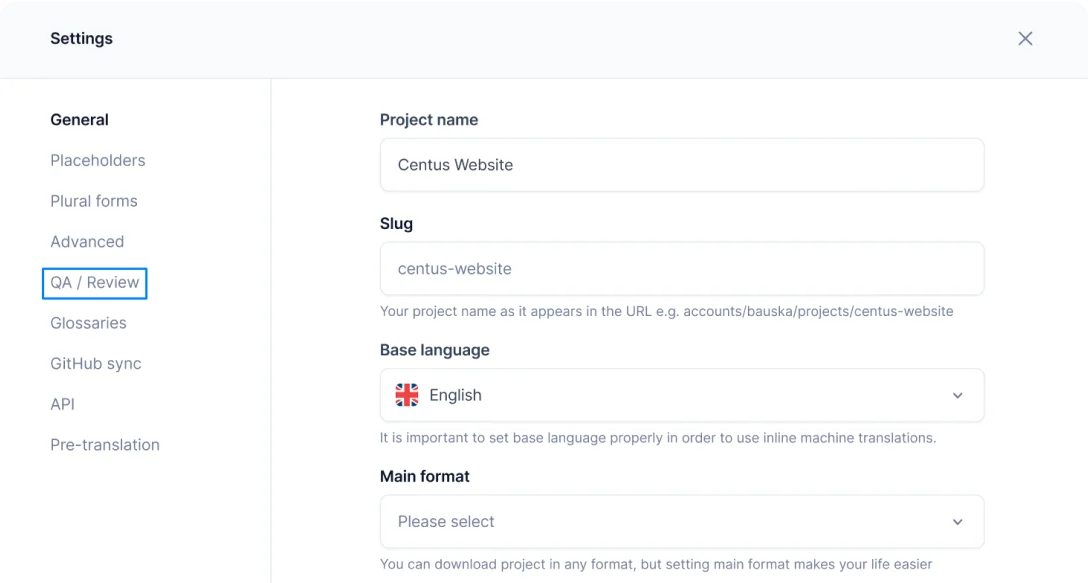
- In the Centus dashboard, click More
- Select Settings from the dropdown menu
- Choose QA/Review and select the Warning option
- Double-click your project in the dashboard
- Review the detected errors
- Fix the issues or click Ignore to close the warnings
In addition to automated content testing, perform manual testing of the following aspects of your product:
- Language and cultural accuracy
- Check grammar and spelling
- Ensure idiomatic expressions and slang are appropriate
- Make sure the content makes sense in the local context
- Legal compliance
- Verify compliance with local laws and regulations
- Check legal disclaimers and documentation
- Technical functionality
- Test links, input fields, and buttons
- Ensure date, time, and currency formats are consistent
- Test compatibility with local technology (software/hardware)
- User interface and experience
- Check text layout and alignment
- Make sure visuals are not offensive
- Test any interactive elements
- Verify navigation and workflow functionality
- Performance and stability
- Conduct load and stress tests
- Assess speed and responsiveness
- Usability
- Test with the target audience for user-friendliness
- Final checks
- Perform regression testing after making adjustments
- Review the entire product against your standards
Step 7: Address legal and compliance issues
You’re almost set to launch your product. However, don’t forget an important part of your product—the legal aspect. If your product does not comply with your target market’s legal standards you’re in a world of pain.
To ensure legal compliance, you’ll need to consult a legal lawyer familiar with your industry. They can ensure that your product adheres to:
- Data privacy laws
- Consumer protection regulations
- Product safety standards
- Intellectual property rights
- Environmental regulations
- Advertising and marketing regulations
- Import and export regulations
- Industry licensing
- E-commerce regulations
That’s it. Your product is thoroughly localized and ready for launch!
Parting thoughts
You've reached the final stage—launching your localized product. But this isn’t the time to rest on your laurels. Create targeted marketing campaigns, monitor launch, gather feedback, and iterate, iterate, iterate.
There’s plenty of work ahead, but you can do it. Especially, if you arm yourself with our guides on marketing localization and multilingual website development.
Good luck!
Get the week's best content!
By subscribing, you are agreeing to have your personal information managed in accordance with the terms of Centus Privacy Policy ->
Keep learning

11 min. read
Your Simple Guide to SaaS Product Localization
11 min. read
How to Build a Localization Strategy and Do it Right
11 min. read
7 Product Expansion Examples and Strategies
11 min. read
What Is Localization? A Comprehensive Overview

12 min. read
How to Build a Localization Workflow

11 min. read