Localization Specialist Role and How to Become One
Imagine you are localizing a website. You’re happy to watch it grow but notice that the translated versions differ substantially from the source version. Your website developers can’t keep up with the release of new pages. And the constant updates to the source version aren’t helping.
Clearly, your localization puzzle is missing a key piece—a good localization project manager. Keep reading to find out what a localization specialist does and how they can benefit your growing company.
Who is a localization specialist?
A localization project manager, or localization specialist, is a professional who helps a product fit into international markets. They do this by managing translators, editors, and designers who modify the product’s language, design, or even features to suit local preferences. It’s a multifaceted role, with responsibilities that include:
- Project planning: Research market trends and consult with key stakeholders to create a localization strategy outlining the scope, objectives, budget, timelines, and deliverables.
- Translation management: Assemble and manage translation teams, assigning tasks to translators and editors. Break down localization milestones into smaller steps and track their completion to avoid delays.
- Budget management: Track translation costs and adjust them to stay within the allocated budget.
- Cross-departmental cooperation: Cooperate with product development, marketing, and legal teams to ensure the localized product aligns with the company's goals and complies with legal translation requirements and regulations.
- Localization quality assurance: Arrange quality control of the localized product to ensure its adherence to predefined criteria. In the case of content, localization testing is necessary to ensure it is accurate, culturally appropriate, and SEO-optimized.
- Project review: Measure localization ROI, collect user feedback and adjust the product or localization strategy accordingly.
A localization project manager’s day-to-day activities
In essence, a localization project manager is responsible for localization project logistics. Their day-to-day activities depend heavily on the type of project, their tools, and whether they work remotely or in an office.
For effective project orchestration, managers use localization platforms, like Centus. Such platforms serve as a hub where translators, editors, QA specialists, and designers can perform localization tasks.
Using localization platforms, managers can ditch multiple spreadsheets, documents, and email chains, and instead orchestrate entire projects within a single browser tab.
Now, let’s examine a day in the life of a localization specialist:
Project progress tracking
As a localization project manager, your day starts with a review of the project's progress. Here’s how it’s done using a localization management platform, Centus:
1. Review previous activities
Start by checking the completion of previously assigned tasks. Review the team members working on the project, added keys, QA issues, and project completion percentage.
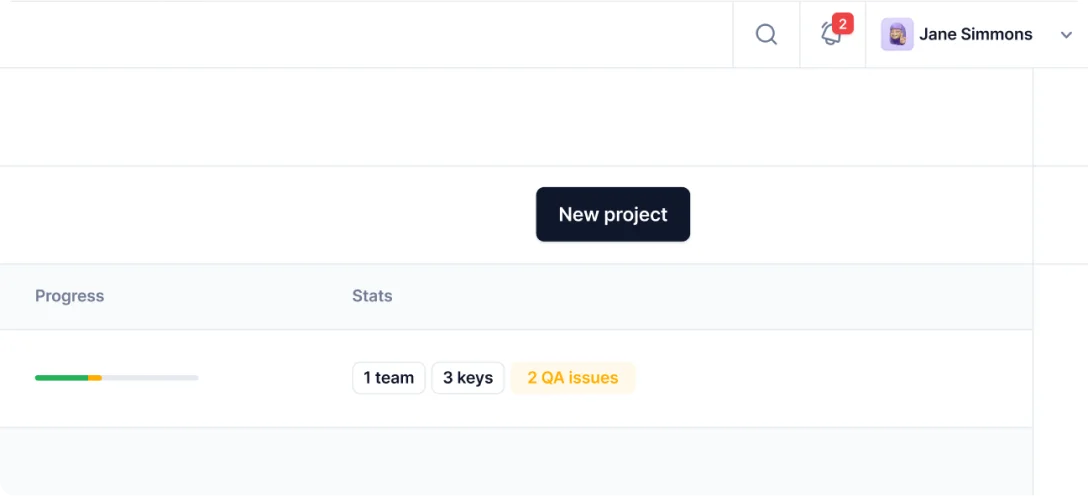
In the Centus dashboard, track the entire project timeline to better understand the milestones and contributions of each team member.

To get a granular view of your localization project’s progress, drill down to see individual tasks.

2. Check comments and messages
Nothing derails a project more than an inbox full of unanswered messages. To keep it on track, address queries from translators, editors, designers, QA specialists, or other stakeholders.
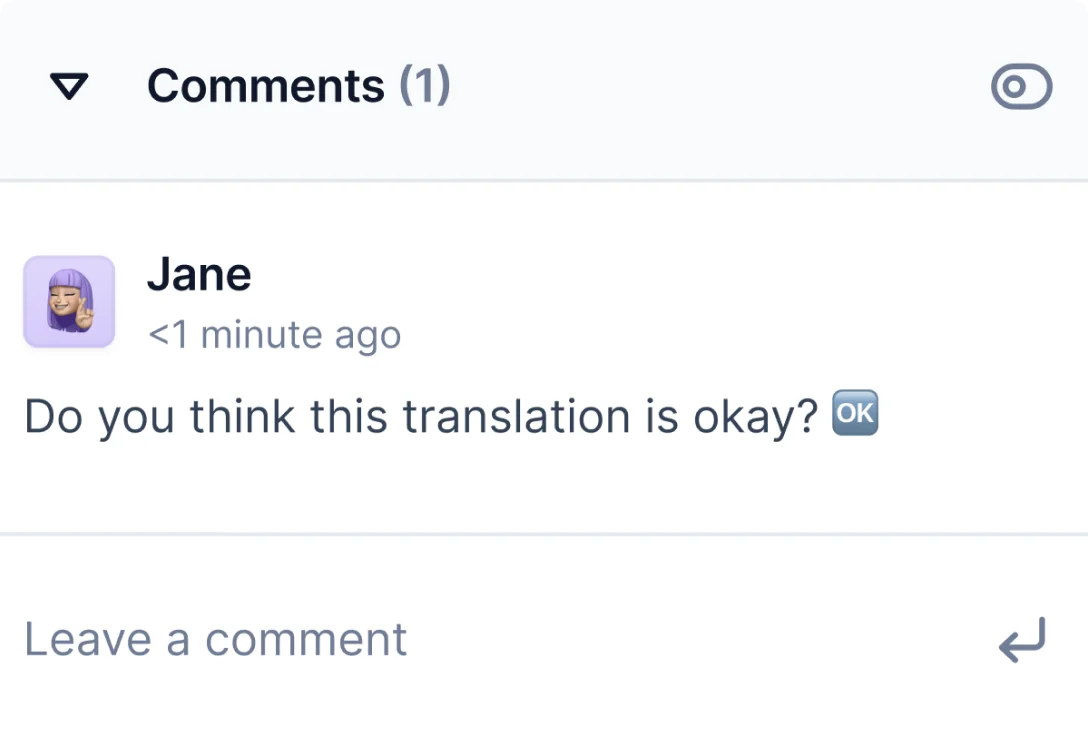
Leave comments and email mentions for individual contributors to ensure that everyone is on the same page.
3. Prepare the daily agenda
Create a list of activities with deadlines and deliverables for all project contributors. Prioritize tasks based on their urgency and the availability of external contributors. Highlight critical tasks that require additional attention to ensure their timely completion.
Project orchestration
Once you’ve caught up with the progress on pending tasks, start monitoring and orchestrating all translation project processes.
1. Conduct team meetings
Coordinate with all contributors to ensure project alignment and address obstacles. Deliver the daily agenda to the team.
2. Manage task execution
Provide direction and guidance on task implementation and resolve project bottlenecks.
For example, some project contributors might need additional context to create accurate translations or localized UI. Don’t just leave comments; provide them with screenshots, when necessary.
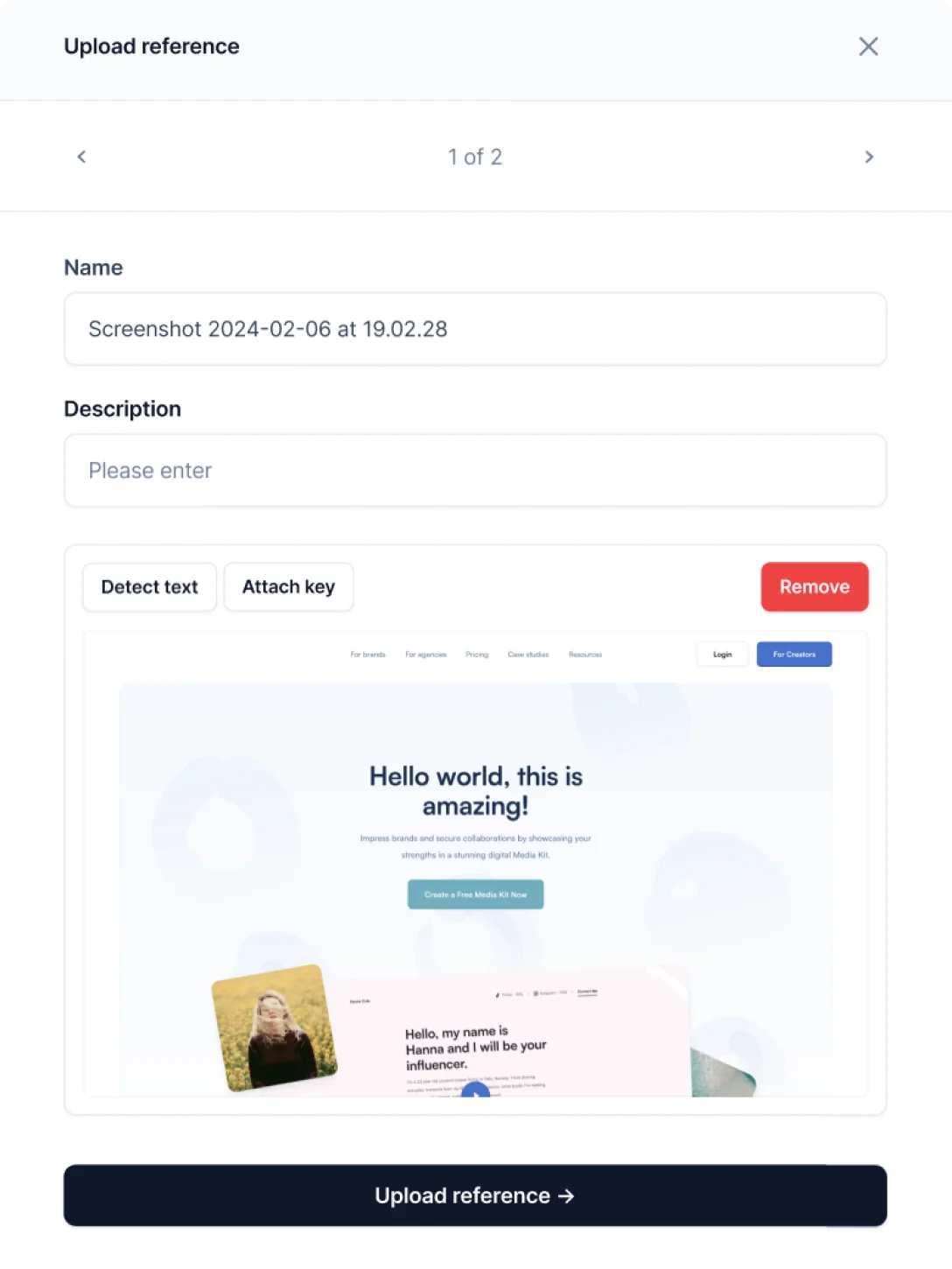
3. Manage task adjustments
Change task priorities, reassign tasks, or reallocate resources to ensure the project is delivered on time.
Progress review and reporting
Localization specialists wrap up their work day with progress review and reporting. Some of their activities at the end of each day are to:
1. Review project progress
Assess the tasks performed over a day and compare the achievements against set KPIs. Identify pending tasks or delays and add them to tomorrow’s agenda.
2. Report project status
Update the product manager about the progress of the localization project.
At this stage, some localization experts use spreadsheets, while others prefer professional localization management tools. Centus, for example, provides a bird’s eye view of all localization tasks and can be used to create reports on project progress and expenses.

How to become a localization specialist
To become a localization manager, you'll need impeccable language knowledge (both oral and written) as well as analytical and project management skills. You should also be closely familiar with SEO and CAT tools.
Below are additional requirements to excel in this field:
Formal education
This is not a mandatory requirement, however, most localization managers start their localization career with a bachelor’s degree in a related course. Preferred fields typically include international relations, marketing, project management, or languages.
Language proficiency
Although this requirement is also not obligatory, a localization project manager should be proficient in at least one widely spoken language. Such major languages include Mandarin, Spanish, Arabic, Hindi, Portuguese, and Japanese.
Licensing or certifications for a localization specialist
While it is not mandatory to possess specific licenses or certifications to become a localization director, several resources and certificates can augment your credentials and improve your expertise. They include:
- Google Project Management Professional certificate
- PMP Certification by the Project Management Institute
- Industry-specific certifications like the Localization Project Management Certification by the Localization Institute, and
- GALA Global’s Rising Star scholarship.
Other optional but helpful certifications include:
- Certified ScrumMaster (CSM) or Professional Scrum Master (PSM) certifications for localization experts focused on software or app localization.
- PMI's Agile Certified Practitioner (PMI-ACP) certification validates your proficiency in Agile project management.
Remember that while certifications can help boost your resume, valuable skills in localization are often honed through practical experience. This brings us to the next requirement.
Work experience
Aspiring localization managers should seek out entry-level marketing or localization jobs. They provide invaluable hands-on experience you wouldn’t get in a classroom.
Skills to acquire during this stage include:
- Market research
- Product management
- Project coordination
- Translation and localization techniques
- Communication
- Teamwork
- Problem-solving
How to succeed as a localization specialist
To excel as a localization specialist or get a localization manager job, you must put your best foot forward, keep upskilling, remain open to continuous learning, and develop a deep understanding of cultures.
Let’s look at the key steps to success in your localization career.
Cultivate excellent communication skills
Localization is all about conveying the right message to the right audience. And it can only be done by articulating project needs, negotiating with stakeholders, and explaining processes to your localization team.
To develop exceptional communication skills, adopt an ‘explorer’ mindset and practice communication in new settings. Also, engage in active listening and build your emotional intelligence. Finally, participate in communication communities both online and offline.
Develop cultural competency
To effectively localize a product, you must understand the customs, trends, and behavior of your audience. A culturally inappropriate translation will not just fail to connect with the target audience, but can also offend, leading to potential brand damage.
You must be able to conduct extensive research on the target market's culture. This could include continually studying their history, lifestyle, and internet habits.
Follow industry trends
The localization industry is always evolving. As a localization specialist, you must keep abreast of these changes by regularly reading industry publications and translation blogs. You should also attend localization conferences and webinars where you can learn about the latest trends and network with other professionals.
There are also groups like the Globalization and Localization Association (GALA) and the American Translators Association (ATA). They provide resources, training, and networking opportunities that can benefit you.
Use professional localization tools
A localization expert is only as good as their tools. Using industry-standard translation tools, a localization export can effectively orchestrate translation, editing, quality assurance, and even UI localization processes. Such tools fall into three broad categories: machine translation, computer-assisted translation (CAT) tools, and translation management systems.
Rather than juggling three different tools, adopt a professional localization management solution—Centus. The solution features machine translation, glossaries, translation memories, project management tools, and much more. Use Centus to perform or manage all localization activities, without ever opening a second tab.
Parting thoughts
Becoming a successful localization manager requires meaningful professional connections, upskilling, and the ability to identify—and seize—job opportunities.
Remember, the road to your dream localization job isn't a race. You can take it slow and steady. And once you are there, you might need our guide to translation management systems.
Good luck!
Get the week's best content!
By subscribing, you are agreeing to have your personal information managed in accordance with the terms of Centus Privacy Policy ->
Keep learning

12 min. read
How to Build a Localization Workflow
12 min. read
Manual and Automated Localization Testing Explained
8 min. read
How to Choose the Right Translation Technology in 2025
16 min. read
How to Perform Localization in Java
7 min. read
What is Product Localization? A Comprehensive Guide
5 min. read
Localization Quality Assurance: Your In-Depth Guide
18 min. read