International SEO Best Practices to Boost Global Traffic
Stop leaving international revenue on the table. Yes, local markets are valuable, but sometimes, true growth lies beyond your borders. With international search engine optimization (SEO), you can tap into these unexplored markets and connect with customers across the globe.
Keep reading to learn how to attract qualified leads, boost website traffic, and convert international customers, all with proven global SEO best practices. No more guesswork, just results.
Pro tip: Follow this simple checklist to build a foolproof international SEO strategy.
What is international SEO?
International SEO is the optimization process of a website to enhance its country-specific visibility and ranking in search engine results page (SERP). Global SEO involves technical SEO optimization between multi-language site versions, and keywords optimization of localized content to meet the cultural and linguistic preferences of your target markets.
The goal of international SEO is to ensure that your business is easily found and relevant to users worldwide.
Signs to start investing in international SEO strategy
International SEO isn't just for large corporations anymore. Small businesses can also benefit from reaching a wider audience, particularly if their products or services have universal appeal. Go for it if:
- You're experiencing slow growth in your local market.
- You receive inquiries or website traffic from international customers.
- Your competitors are already targeting international markets.
- You have a product or service with global appeal.
- You have the resources to build an international brand.
How to do international SEO
Preparing for international expansion takes time and planning. Starting with international SEO early can give you a competitive advantage and ensure a smooth entry into new markets worldwide. Let’s distill this process into ten essential steps:
Identify target countries and languages
The initial phase in foreign SEO is a detailed analysis of target markets. What countries want your product or service? What languages can you target?
Here’s how to find out:
Analyze your website traffic
Analyze your website traffic to see if there’s a strong demand abroad for your product or service. Your best tool here is Google Analytics.
The first step is to analyze international traffic to your website:
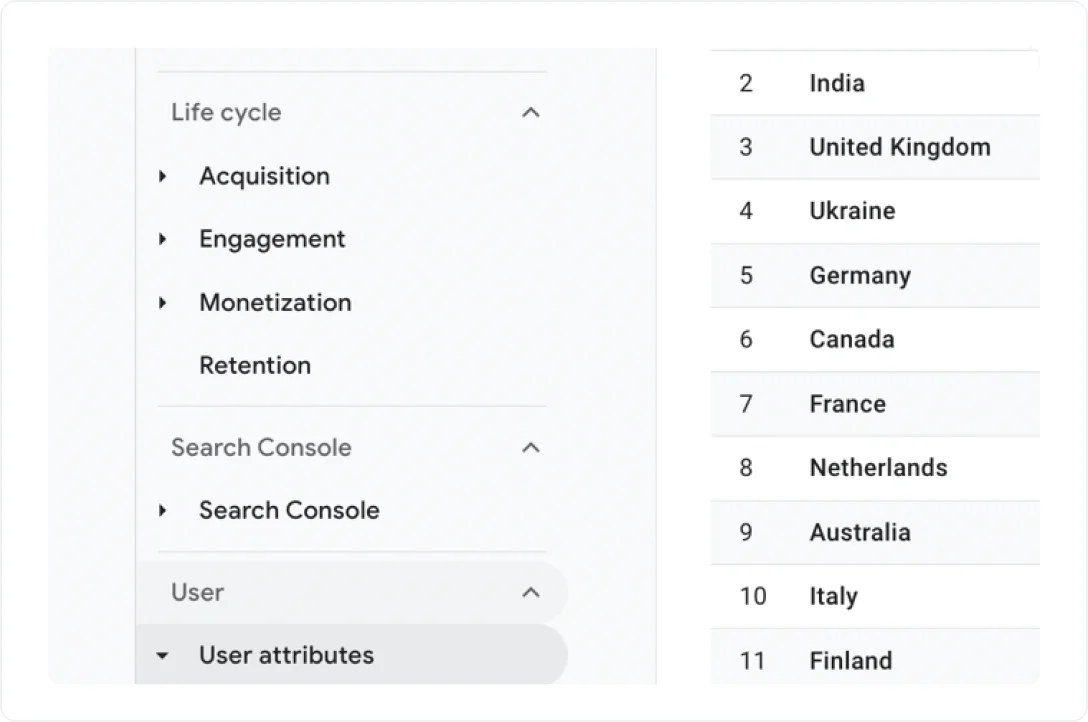
- In Google Analytics 4, go to Reports
- In the User section, click Demographics
- Click Demographic details
 Source: Google
Source: Google
Now you can examine your website’s traffic breakdown. High traffic or engagement from a particular country or language group indicates potential for targeted international SEO efforts. For granular analysis, apply the Region filter.
The next step is to examine the preferred languages of your website visitors:
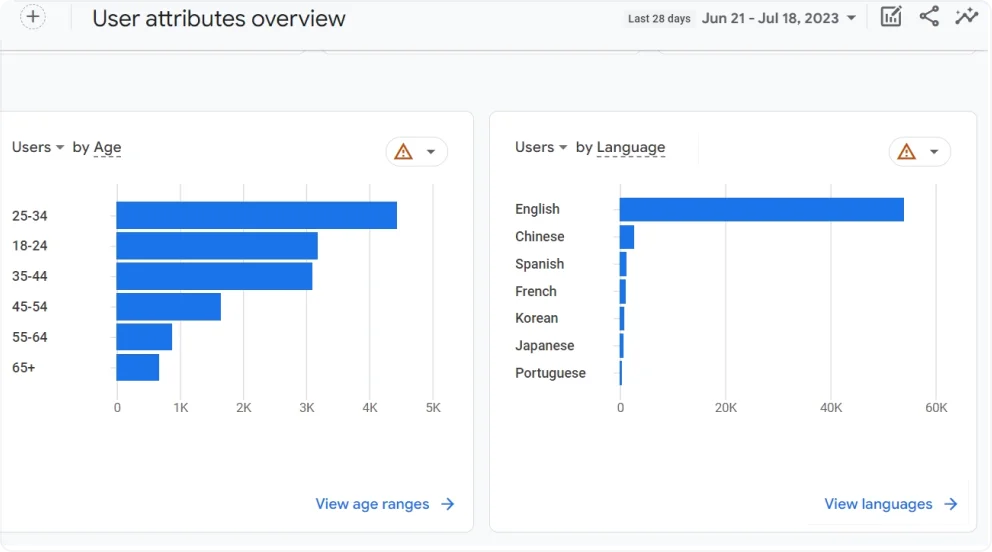
- Head to the Reports section
- Click User Attributes and then select Overview
- Locate the Users by Language card
- Click View Languages for more details
 Source: Google
Source: Google
Note: The languages shown are based on users’ browser settings, not on the language versions of your website.
Analyze your competitors’ traffic
To identify countries most suitable for your global SEO strategy, run a simple analysis of competitors’ traffic. Where do they get the bulk of their international traffic? Do you have localized versions of your website for those countries?
To check if there are traffic opportunities you’re missing, use Similarweb:
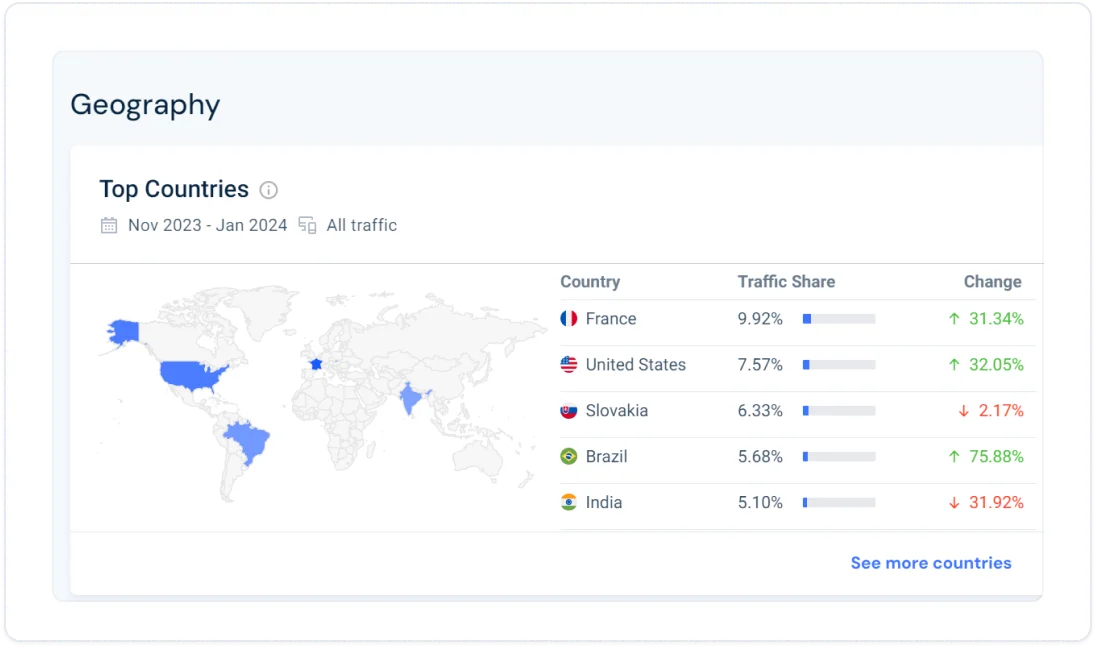
- Enter your competitor’s website in the search box
- Click Search
- Go to Overview > Website Performance
- Scroll down to Geography
 Source: Similarweb
Source: Similarweb
If you find potential target markets, check other competition within them. This way, you can understand competitors’ offerings and how to strategically differentiate yours. To this end, simply Google your product or service in the target country.
Don’t know how to search in another region? It goes like this:
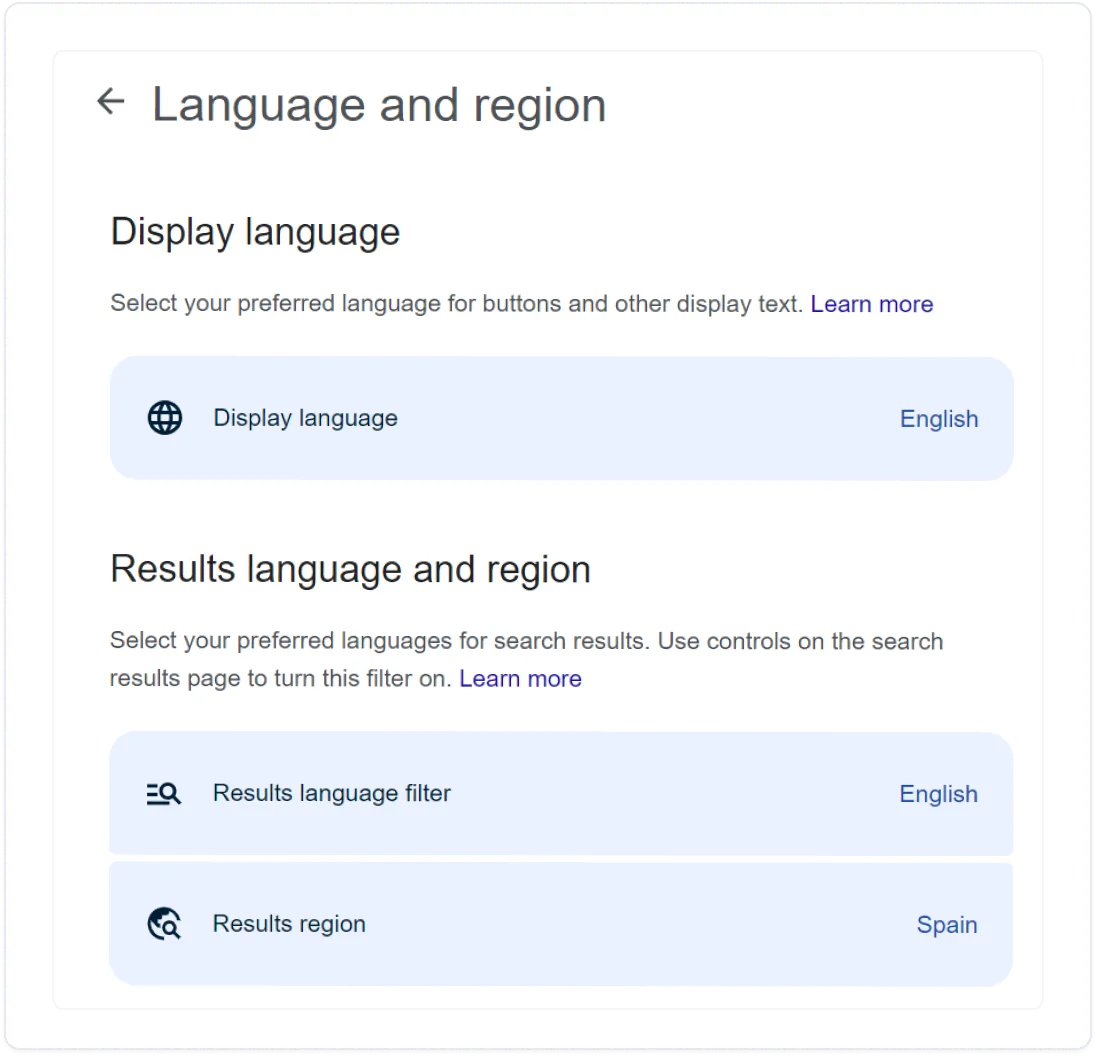
- Google your target keyword. For example, “zapatos" if you want to check shoe brands in Spain
- Go to Settings
- Click Language and scroll down to Results
- Pick your selected region and click Confirm
- Go back to the results page
 Source: Google
Source: Google
Make sure to examine your competitors’ website structure, language offerings, and content strategy.
Look for patterns in their SEO practices with Ahrefs’ site explorer. Are they using local keywords, have they localized their content, what kind of backlink profile do they have? What international SEO trends are they following? All these will help you set your global seo priorities.
Decide between language and country targeting
Sometimes you don’t need to target a whole country. For instance, if you’re catering to French-speaking customers in France, and want to expand to French speakers in Canada, you don’t necessarily have to target the entire country. Instead, you can create a subdirectory for French-Canadian keywords, and tweak your content accordingly.
- Choose country targeting if your product or service is specifically tailored for a particular country. Consider factors like local competition, cultural nuances, and specific customer needs.
- Choose language targeting if your product or service appeals to a language-specific audience across different countries. This is particularly relevant for languages widely spoken in multiple countries, like English, Spanish, or Arabic.
Evaluate search engine preferences
Different countries may favor different search engines. The Chinese search engine Baidu, for example, holds 82% of the market.
Here’s how to check international search engine market shares:
- Go to Statcounter
- Click Edit chart data
- Select a region
- Click View chart
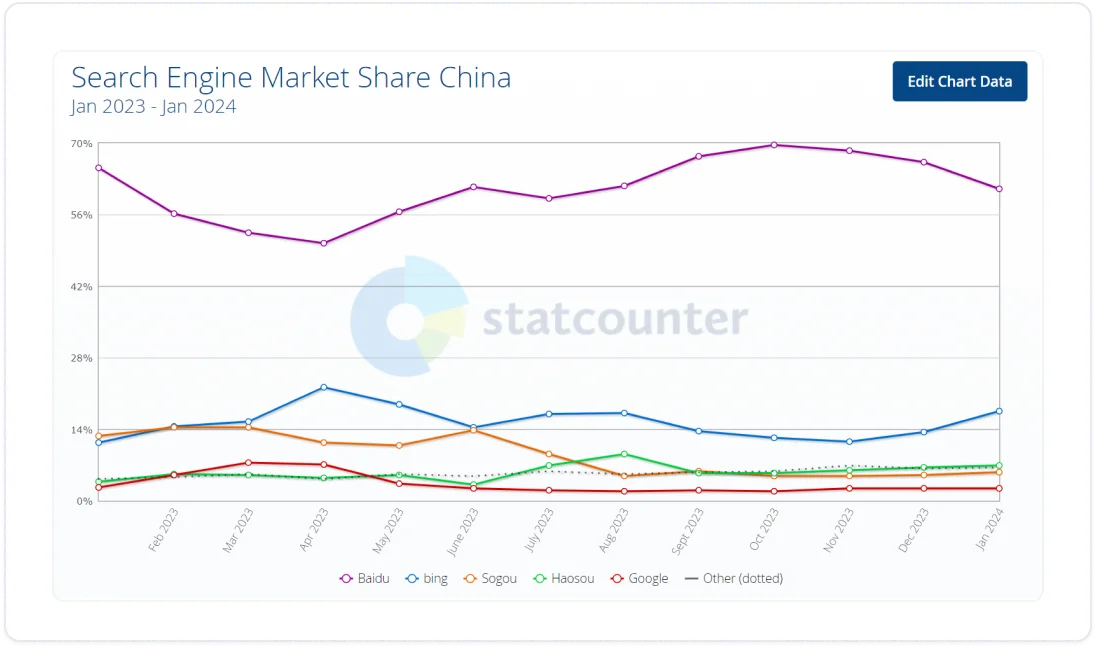 Source: StatCounter
Source: StatCounter
Evaluate seasonal keyword trends
It’s not enough to know where your foreign traffic is coming from, you should also check whether it’s evergreen or based on fleeting trends. This will help you prioritize countries with lasting traffic potential.
Follow these steps to check seasonal keyword trends:
- Go to Google Trends
- Enter the key terms related to your product
- Use the Region filter to choose a country
- In the Related queries section, find related keywords for each country
Now, look at the graph for each country to see if the search volume for your keywords is:
- Stable (evergreen): Consistent interest over time. These countries might be worth investing in due to sustained interest.
- Trendy (fluctuating): Rises and falls with specific events or seasons. Consider focusing efforts during peak periods in these countries. And if it’s just too low, it might not be right for you.
Make sure to compare keyword popularity across different countries to see where interest is strongest.
2. Conduct detailed keyword research for international SEO
Thorough keyword research is pivotal in international SEO, as it helps you tailor your website to unique search behaviors across the globe.
Start with a broad keyword list, then transcreate
Begin by compiling a list of potential keywords related to your product or service in your primary language. For instance, if you're selling handmade shoes, your initial list might include terms like "handmade shoes," "artisan footwear," or "custom shoes".
Now, you can use machine translation software like Google Translate or ChatGPT to get a rough idea of what these keywords would look like in your target market.
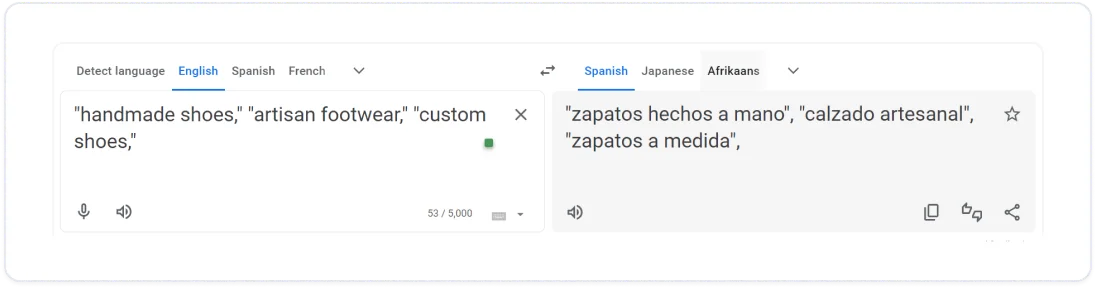 Source: Google
Source: Google
Note that words or phrases popular in one language might not be relevant or may have different connotations in another. Therefore, it’s always better to avoid direct translation altogether and, instead, find a local SEO professional to help transcreate the keywords.
Analyze local keywords
Use Google Keyword Planner to check the search volume and competition for your keywords in different regions and languages. You can also use it to find related keywords that you can rank for.
- In Google Keyword Planner, navigate to Tools > Planning > Keyword Planner
- Choose Discover new keywords
- Enter your URL or primary product keywords
- Select the language and location
- Click Get results
Review the table and identify the keywords with high search volume and manageable competition in your target markets. Also, look for language-specific variations that might require translation or adaptation.
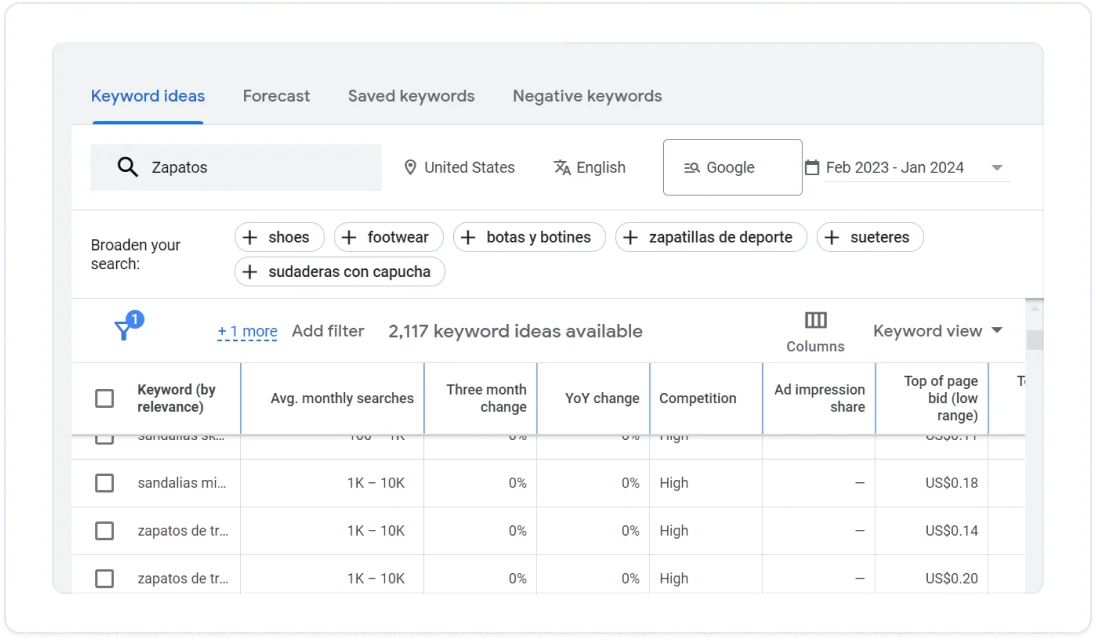 Source: Google Keyword Planner
Source: Google Keyword Planner
Analyze competitor keywords
Use SEO tools, like Ahrefs, to examine paid and organic keywords your international competitors are targeting and add some of them to your keyword strategy. However, don't just chase high-volume keywords. Analyze competition and difficulty to prioritize achievable targets with good conversion potential.
Here’s how to analyze competitors’ keywords:
- In Ahrefs’ Site Explorer, enter a competitor's website
- Select the target country
- In the Organic Search section, click Organic keywords
Look at search volume, keyword difficulty, and traffic potential. Choose keywords with a good balance of high traffic potential and low competition to incorporate them into your SEO plan.
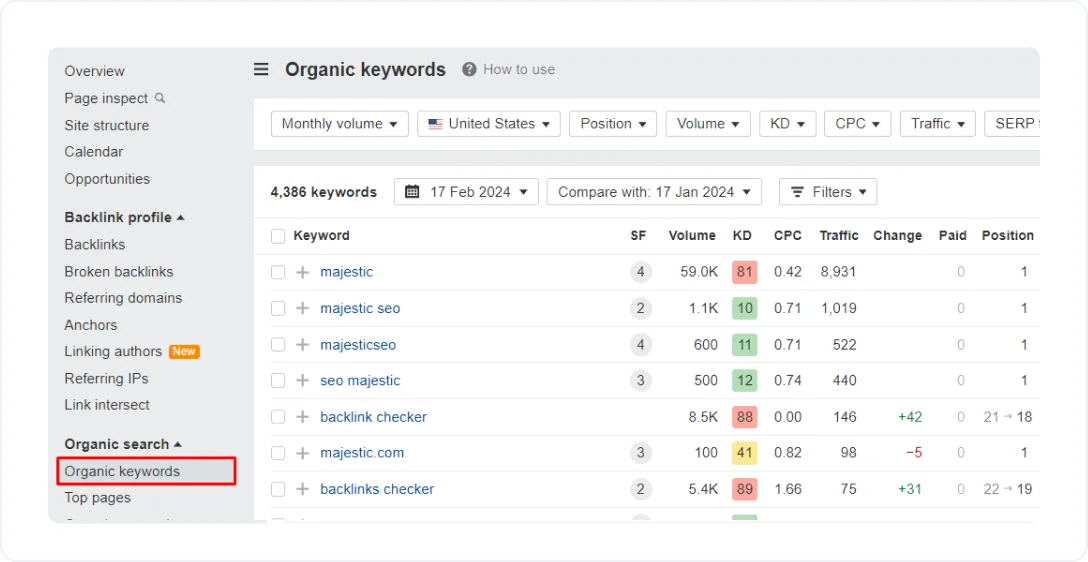 Source: Ahrefs
Source: Ahrefs
Some sites can rank for your keywords without being your competitor. For example, an SEO site can rank for a project management keyword without selling a project management solution.
To find out who your competitors are, follow these steps:
Here’s how to do that:
- Go to the Site Explorer in Ahrefs
- Enter your domain name
- Go to the Organic competitors report
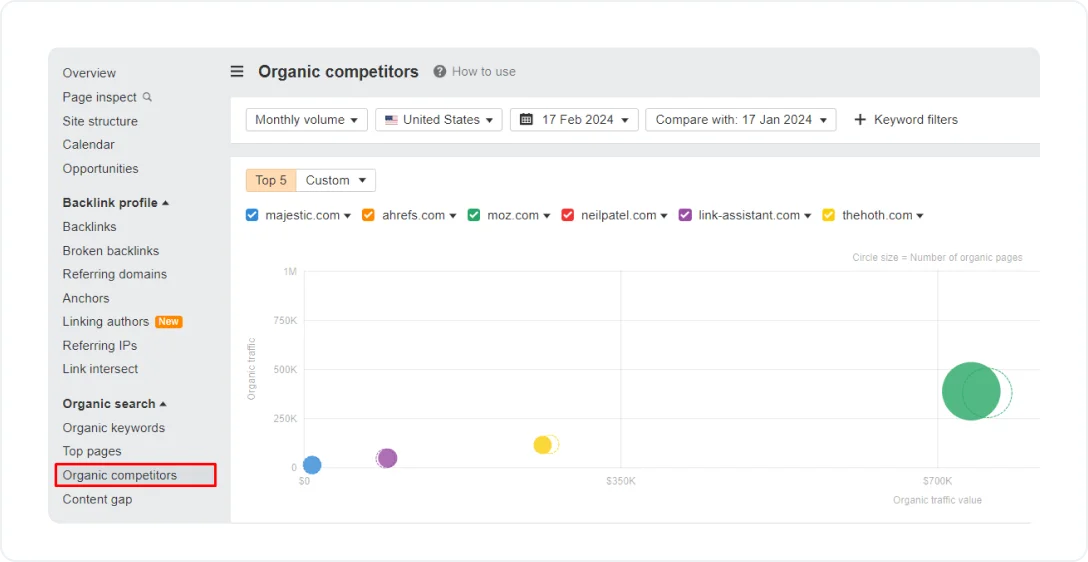 Source: Ahrefs
Source: Ahrefs
When choosing keywords, it’s important to balance informational keywords ("best hiking boots") with transactional keywords ("buy hiking boots online"). Thus, you’ll attract users at different stages of the buying journey.
And don’t stop tweaking your keyword strategy. Market trends and search behaviors change. For instance, keywords like “winter boots” become more relevant in colder months and wane in the summer.
Pro tip: Research the market’s search engines' unique parameters for crawling and indexing. For Baidu, factors like site speed and local hosting may be important, whereas Yandex prioritizes user behavior and content relevance.
3. Choose an appropriate URL structure
This is a truly important international SEO best practice, as it significantly impacts how search engines and users perceive and interact with your site. There are three main URL options to choose from—ccTLDs, subdirectories, and subdomains. And here’s how to know which one suits your website.
Country code top-level domains (ccTLDs)
These are country-specific domains such as yourwebsite.es for Spain or yourwebsite.jp for Japan. They signal to search engines and users that the content is specifically designed for that particular country.
- Pros: Clear geotargeting signals to search engines; potentially higher trust from local users; beneficial when server location is a secondary concern.
- Cons: Expensive and time-consuming to set up and maintain multiple domains; limits targeting to one country; requires managing multiple domains.
Many global brands, like Amazon, use ccTLDs to target specific countries—amazon.co.jp.
Subdomains with generic top-level domains (gTLDs)
This option uses a country-or language-specific subdomain, like es.example.com, where es indicates a section for Spanish-speaking users.
- Pros: Easier to set up; suitable for websites hosted across multiple locations or with large volumes of multilingual content; good for indexing a high volume of pages per language.
- Cons: Less clear whether it's country or language targeting; may dilute domain authority as search engines can see subdomains as separate entities.
Wikipedia uses subdomains extensively, with over 300 language versions accessible through distinct subdomains, like en.wikipedia.org (English), es.wikipedia.org (Spanish), and fr.wikipedia.org (French).
Subdirectories with gTLDs
This involves creating country-or language-specific subdirectories on your main site (e.g., example.com/es/ for Spanish content).
- Pros: Easy to set up and maintain; shares domain authority across the entire site; good for language targeting; most cost-effective option.
- Cons: More challenging to separate sites; server location and geotargeting might not be strong; limited localization benefits and potential cannibalization issues.
Apple uses subdirectories for language targeting, such as apple.com/es/ for its Spanish-speaking audience.
URL structure considerations
Keep these tips in mind when choosing your URL structure:
- Budget and resources: ccTLDs can be resource-intensive. If budget is a concern, subdirectories or subdomains might be more feasible.
- SEO goals: If strong local presence and rankings are vital, ccTLDs might be the best choice. And if you want to maintain consolidated domain authority, choose sub-directories.
- User experience: Consider how your audience interacts with different URL structures. ccTLDs often instill more local trust.
- URL parameters: Avoid parameterized URLs, like example.com/page?gl=DE, because they can confuse both users and search bots. They can also cause duplicate content issues.
- Website hierarchy: Ensure your website has a well-defined hierarchy to help crawlers understand its structure and priorities, and index it accordingly. Example: example.de/category1/subcategory1/page.
4. Localize your website
In this section of our international SEO guide, you’ll learn how to adapt your content to match the cultural, linguistic, and practical preferences of your target audience.
Translate content
Start the process with automated or machine translation tools. Then, have it refined by human editors to avoid mistranslations and cultural misunderstandings.
Let me break it down:
First, sign up to Centus and create a new project.
Then, add your HTML, XML, CSV, DOCX, or other files. Now you can use a convenient Editor to translate your website automatically.
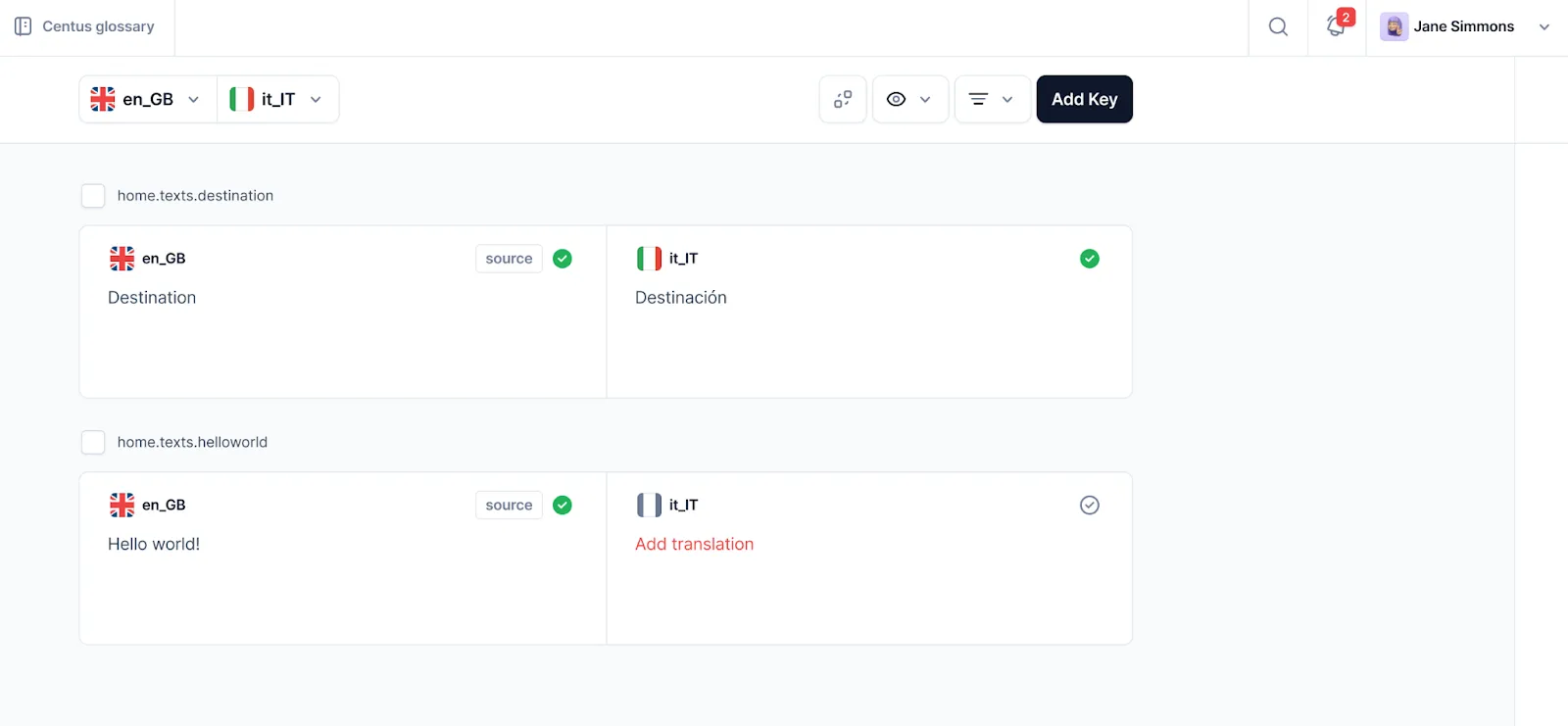
After generating automatic translations, assign them to your team for review. Your translators and editors can review content, edit it, and share feedback.
The best thing?
You can translate your site into multiple languages simultaneously.
Using Centus, dozens of translators can work on the same source files without interfering with each other. As a result, you can enter multiple markets in record time.

- Translate and localize metadata (titles, descriptions, alt text) for each language version to help users and search engines recognize the relevance of your content. Add keywords and respect character limits.
- Perform UI localization to reflect the cultural context of the new locale and boost your international SEO rankings.
- Adjust content to include local references, holidays, and events, making it more relevant to each region.
- Schedule content releases according to local time zones and events, particularly for time-sensitive information like promotions or campaigns.
Manage duplicate content and keyword cannibalization
- Dedicate each page to a single language to avoid confusing search engines and users.
- Use canonical tags to manage duplicate content across language versions and prevent keyword cannibalization.
- When using hreflang and canonical tags together, ensure they don’t conflict. Align hreflang tags with the canonical page of the same or the most relevant language.
Canonical tag example:
<link rel="canonical" href="https://yourwebsite.com/uk/product-category/product-name>
Add new content
Analyze your competitors’ content. Identify content gaps and new opportunities to fill them with quality relevant content. Use links and stats relevant to the target region, not just ones merely transplanted from your original content.
Again, Ahrefs can help you find content gaps through an analysis of your competitor’s keywords:
- Ahrefs Dashboard > Competitive Analysis
- Choose Keywords
- Enter your domain & competitor domains
- Filter by ranking positions or difficulty
- Click Show keyword opportunities to see the keywords you don’t rank for, but competitors do.
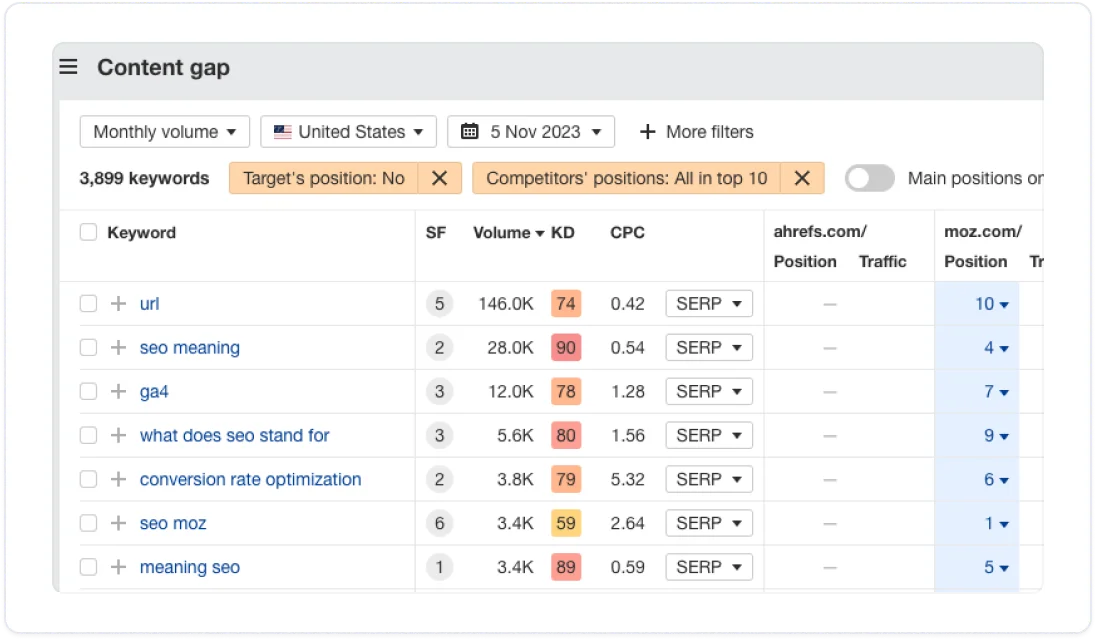 Source: Ahrefs
Source: Ahrefs
Shape your content strategy with the newly-founded keywords. Don’t forget to connect new content with existing content through internal linking to help your visitors and search engines discover it.
5. Implement hreflang tags
Hreflang tags are HTML attributes indicate to search engines languages and regions targeted by a webpage. They also help prevent duplicate content issues. Here’s how to properly implement hreflang tags:
Identify languages and regions
Determine the language and regional codes for your website's different versions. For example, en-gb for English and the United Kingdom or es-es for Spanish and Spain.
For more information, refer to the Google’s list of language codes.
Add hreflangs to your webpages
Insert hreflang tags into the HTML code of each page. These tags should be added to the <head> section of your HTML. For instance, if you have an English page targeting the US and a Spanish page targeting Spain, your tags would look like this:
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="en-us" href="http://example.com/en-us">
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="es-es" href="http://example.com/es-es">
- link rel="alternate": Indicates an alternative version of the webpage
- href: Specifies the URL of the alternate page in the target language or region
- hreflang: Defines the language and sometimes a region (e.g., en-us for the US English)
Cover all language and region variants and self-references
Ensure that each language and regional variant of your site has a corresponding hreflang tag. This includes having a tag for the default version of your site. Not including all variants of your site in hreflang annotations can result in incomplete indexing by search engines.
Your hreflang annotations should also be consistent across all pages. Each page should reference all other language and regional versions, including itself.
6. Site speed and mobile optimization
Fast-loading websites are vital for a positive user experience, especially for an international audience where internet speeds can vary. Slower sites often see higher bounce rates, as users are less inclined to wait for content to load.
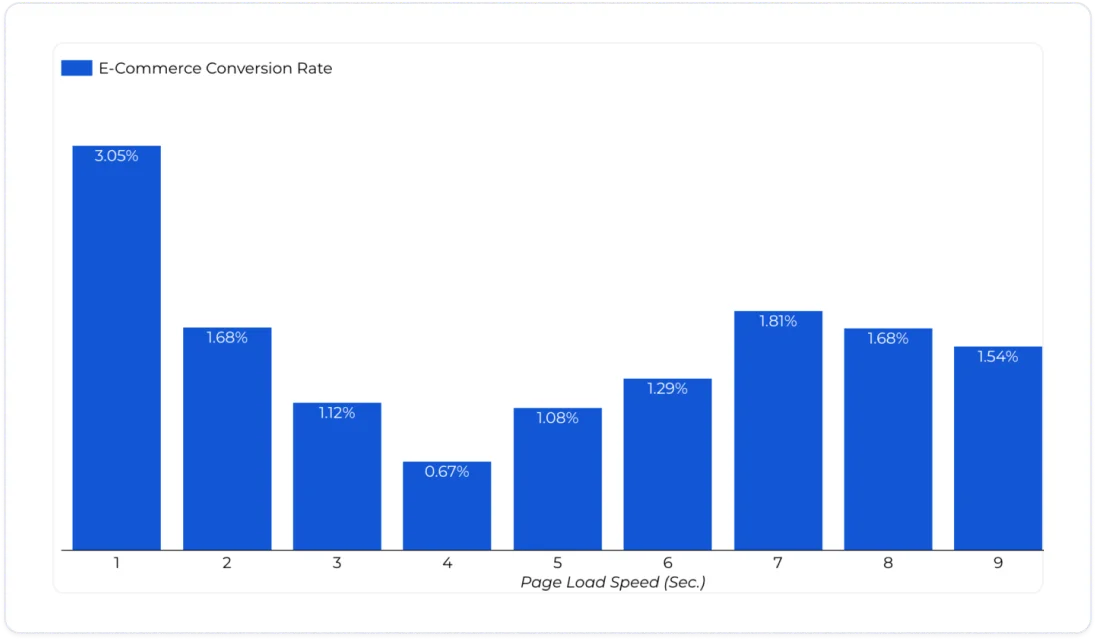 Source: Portent
Source: Portent
Additionally, search engines consider site speed a key ranking factor, making it critical for your website's visibility in global search results.
To optimize site speed:
- Implement a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to reduce latency by serving your content from a location nearest to your user.
- Compress images and optimize file formats to reduce load times without sacrificing quality.
- Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML to reduce file size and improve loading speed.
- Leverage browser caching to reduce loading times for repeat visitors.
Mobile optimization
With mobile internet usage surpassing desktop globally, a mobile-optimized website is a must-have. A site that performs well on mobile devices ensures accessibility and a wider reach.
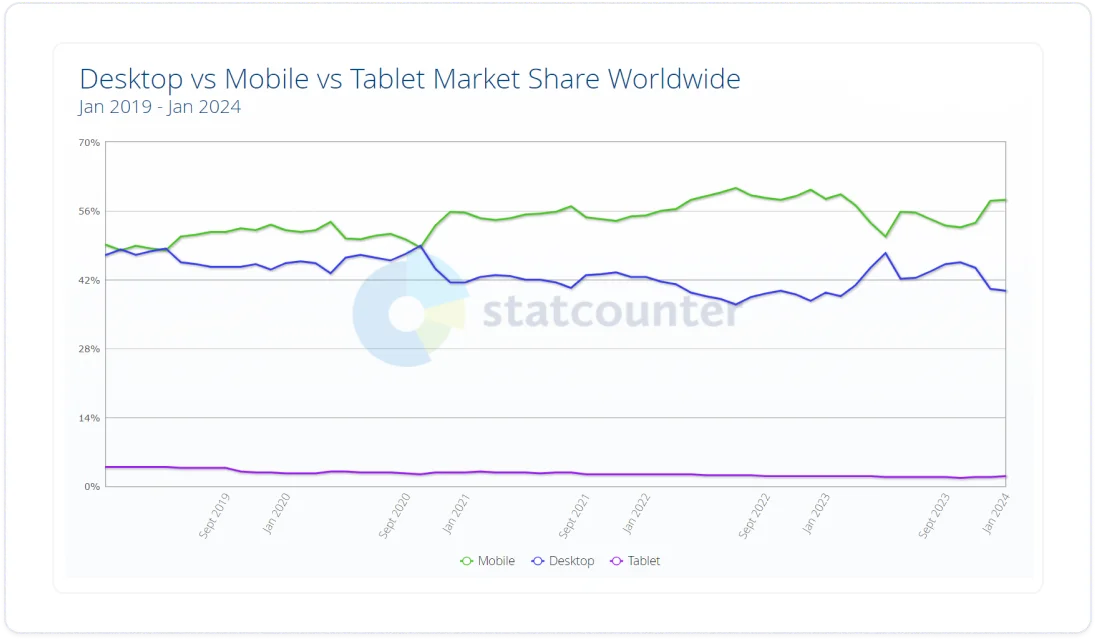 Source: Statcounter
Source: Statcounter
To optimize for mobile:
- Adopt a responsive web design that automatically adjusts content to fit various screen sizes.
- Simplify navigation to improve usability on smaller screens. Use large, easily clickable buttons and keep menus concise.
- Test your website on different mobile devices to ensure consistent performance and appearance.
- Prioritize mobile speed, considering that mobile users often have slower internet connections.
Don’t forget to use Google PageSpeed Insights to regularly check your site’s speed and follow their optimization recommendations.
7. Invest in local link-building
Link-building is a fundamental aspect of SEO, and its importance is amplified in an international context. To increase your visibility and credibility, acquire quality backlinks from relevant and authoritative websites in your target countries or language markets.
Links from trusted and popular sites within your target region signal to search engines that your content is valuable, relevant, and trusted in that specific market. Follow these tips to get them:
Identify opportunities
Start with a thorough analysis of the local competitive landscape. Look for patterns in competitors’ link profiles. Are they getting links from local news sites, industry blogs, or business directories?
Use Ahrefs (100 backlinks for free) or Majestic ($49.99/month) to see where your local competitors are getting their backlinks. Here’s how it’s done with the Ahrefs’ backlink tool:
- Visit the Ahrefs Backlink Checker
- Enter your competitor's domain or URL
- See the total backlinks, linking sites, and top 100 backlinks (page, anchor, target URL)
- The paid method allows filtering and analysis of all backlinks
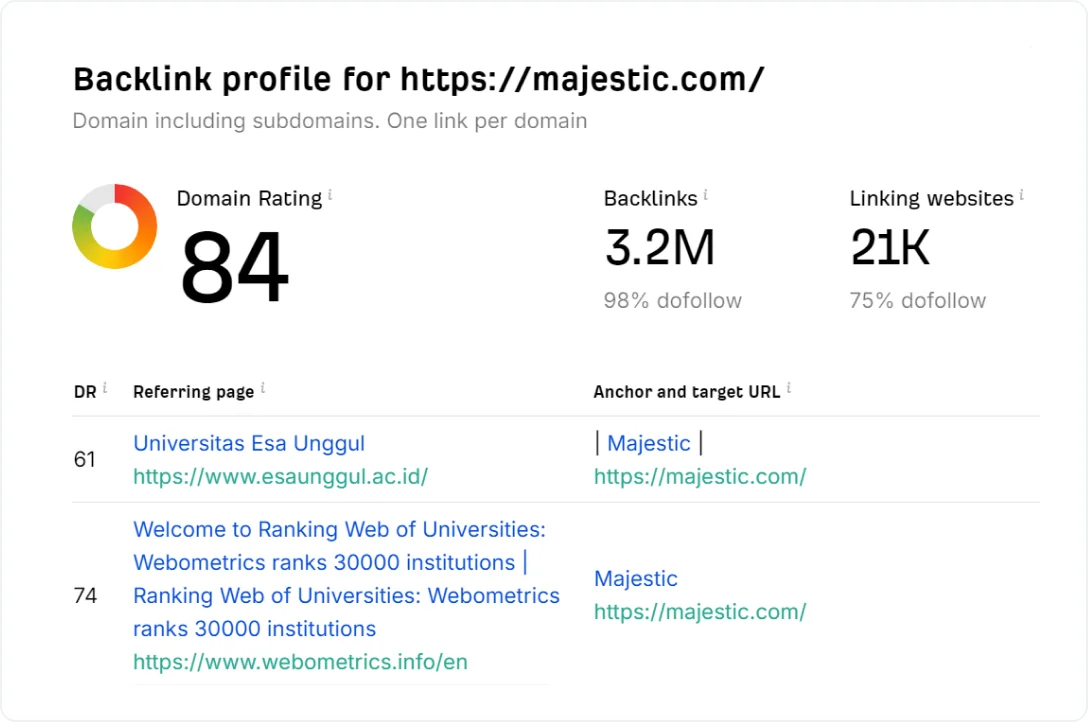 source: Ahrefs
source: Ahrefs
Create localized content
Develop content specifically designed for your target market. This could include local industry reports, guides, or articles on topics relevant to the local audience.
Consider local holidays, events, or trends that you can tie into your content. For example, a piece on how your product or service relates to a major local festival could attract attention and links from local websites.
Partner with influencers
Identify key influencers and bloggers in your target market. Tools like BuzzSumo can help you find individuals who are influential in your industry and region. Reach out to these influencers with personalized messages. Offer them valuable content or propose collaborations that could benefit their audience.
Build local relationships
Attend local industry events and webinars. Join community forums like Reddit and Quora or seminars to network with potential link partners, offline and online. Explore opportunities for guest posting on relevant local business blogs or offering expert opinions in your field.
Share your expertise and insights without overt self-promotion, and naturally, include links to your content where appropriate and valuable to the conversation.
Send personalized outreach emails
Mention specific details about the recipient's work or website to show that your request isn’t generic. Clearly explain how linking to your content will add value to their audience. For instance, if you’ve created a comprehensive guide that complements an article on their site, highlight this.
8. Don’t forget social media
Social media plays a crucial and sometimes understated role in amplifying your international SEO efforts. It's a dynamic tool for connecting with global audiences, understanding regional preferences, and driving targeted traffic to your website. Here are a few ways to to go about it:
- Research popular social media networks in your target regions
- Create localized content, share industry insights, and participate in relevant conversations
- Collaborate with local influencers to amplify your reach
- Track engagement and adapt your strategy based on what resonates with your audience
Remember, international SEO marketing is about building relationships, not just blasting links. Be authentic, find your voice, and provide value. This way you can earn valuable brand mentions and improve your overall SEO visibility.
9. Determine what success is and measure it
The final piece of your international SEO strategy involves defining success and meticulously measuring your progress. Remember, this is a marathon, not a sprint, so do not expect overnight changes. First, you need to:
- Define your goals: Start with specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals. Are you targeting increased organic traffic, conversions, or brand awareness in specific regions?
- Align goals with KPIs: For traffic-related objectives, track metrics like unique visitors, page views from specific regions, and time spent on site. For engagement goals, monitor social shares, comments, and bounce rates.
- Use Google Search Console and Google Analytics: Analyze organic traffic by country, identify top-performing keywords, and track search engine ranking positions. Set custom alerts in your tracking tools to receive immediate updates on specific changes you want to monitor, such as ranking drops or improvements.
- Social media insights: Monitor performance on each platform, track engagement metrics, and identify influential voices in your target communities.
Once you have all the data you need, review it, identify areas of strength and weakness, and adjust your international SEO strategy accordingly.
It’s important to note that international SEO isn't just about ranking higher. If you rank higher with bad or poorly translated content, you’ll lose your edge. However, by following these best practices, you can build a website that resonates with your target audience, wherever they are.
Get the week's best content!
By subscribing, you are agreeing to have your personal information managed in accordance with the terms of Centus Privacy Policy ->
Keep learning
14 min. read
Website Localization: A Beginner’s Guide

9 min. read
Website Translation Costs: How to Calculate and Manage Them
11 min. read
How to Build a Localization Strategy and Do it Right
7 min. read
What Is Market Expansion Strategy? A Guide to Business Growth
7 min. read
Translation Management System: A ‘Show, Don’t Tell’ Guide
7 min. read