When will machine translation software be sophisticated enough to render human translators obsolete?
Probably never. Translation isn’t just about language, it’s about context and the ability to read between the lines.
Yet technology is getting so refined that a machine translator can replace a human expert in many situations, especially when time and budget are scarce. Professional translation software is a perfect tool for businesses to cut their expenses without compromising the quality of content.
In this guide, we’ve gathered the best machine translation tools with a various combination of features to suit your unique translation needs.
Pro tip: Use the translation management system, Centus, with your preferred MT engine to combine speed with the quality only humans can provide.
Ranking criteria for the best machine translation software
Yet before we start, here are the criteria we used to rank every MT engine on the list. We’ve concentrated on metrics that are most relevant for business translation tools used for localization projects, global team communication, etc.
📘 Further reading: Best Localization Tools
Here is what we looked for in the tools we rated:
- Accuracy. That’s the key translation characteristic. Can you trust this language translator software to provide correct interpretations consistently? How reliable is its understanding of context cues and sentiment?
- Usability. Since many team members are required to use this tool within the company, intuitive interface and manageability are of the essence. You don’t want clunky software to hamper your team’s productivity.
- Speed. Businesses often need to translate large volumes of content and documentation in a narrow window of time, so processing speed and swift delivery are vital.
- Integration capability. We measured how easily each translation tool integrates with other apps and platforms used in business settings since you need a software ecosystem with seamless workflow.
- Support. Delays might cost your business money and opportunity, so timely resolution of any issues is vital. We’ve estimated how reliable and responsive customer support is for each tool.
- Innovation. Unique features can give your business an edge over the competition, so we also assessed any special functionality that can benefit a business.
- Value for money. Last but not least, the cost. Does the price tag reflect the value that you get out of this machine translation solution?
With that in mind, you should always weigh all the pros and cons specific to your situation and translation needs. Some prioritize speed and price, some focus on scalability and flexibility. Whichever is relevant to your business, we hope you will find the perfect match on this list.
Top 7 machine translation software tools
The best online translators go beyond simple translation. These powerhouses handle large volumes of text, seamlessly integrate into workflows, and offer robust features for professional results. Here are the top machine translation tools that excel in these areas:
1. Google Translate
Google Translate is probably the most well-known and accessible solution out there, enjoying half a billion daily users. It is NMT-based, free, user-friendly, and supports a whopping 234 languages (at varying levels) with 32 of them having real-time translation capabilities. No wonder it became a go-to place for quick translations for business and leisure.
 Source: Google Translate
Source: Google Translate
-
Performance (⚙️9/10): The accuracy fluctuates depending on how common the language pair is. For common languages with a lot of data like Spanish or French, accuracy is great, which unfortunately cannot be said about Greek or Polish.
📘 Further reading: Is Google Translate Accurate? 2024 Research
-
Compatibility and assistance (🔧7/10): Google Translate integrates seamlessly with other Google products and is fairly good at working with other tools like WordPress and Disqus. Because of the sheer number of users, individual tickets might not get an immediate response, but a vast knowledge base and active community forum are enough to resolve most issues independently.
-
Innovation (💡8/10): Google is regularly updated and keeps abreast of the latest developments in the field, yet it’s been a while since they launched something genuinely groundbreaking.
-
Value for money (💰8/10): Free for small volumes and personal use, Google Translate provides exceptional value. Google Cloud Translate prices start at $0.003 per character (more details on the website), which is affordable, but bears varying value depending on the language and the accuracy Google provides for it.
2. DeepL Translate
DeepL follows a different strategy and chooses quality over quantity. It supports only 33 languages (mostly European) but is famous for the superior accuracy of its translations. DeepL derives its name from “deep learning” and uses a fine-tuned proprietary neural network for natural-sounding and faithful translations.
The tool gradually expands to include other in-demand languages but keeps high fidelity front and center. This made DeepL particularly popular among researchers and academics.
 Source: DeepL
Source: DeepL
- Performance (⚙️9.5/10): For the few languages DeepL supports, its accuracy is outstanding, with nuanced and natural-sounding translations, especially for European languages. Of course, human editing is still advisable.
- Compatibility and assistance (🔧8/10): DeepL is available as a web-based tool, Chrome plugin, and a desktop app for Windows and MacOS. It also offers API integration. Customer support, however, leaves a lot to be desired with many users complaining about long response time.
- Innovation (💡8/10): DeepL uses its own neural network it keeps perfecting, making unique things possible, for example, formal/informal tone distinction.
- Value for money (💰9/10): DeepL’s free version is more restrictive than Google’s, but the Pro version is arguably more affordable. Prices range from $8.74 to $57.49 per user per month depending on functionality and translation volumes.
3. Bing Translator (formerly Microsoft Translator)
Bing Translator is a widely popular system created by Microsoft. The current simplified version was designed for access via the Bing search engine. It supports over 100 languages, including versions and dialects, which is the similar number compared to other tools on this list, yet they don’t fully overlap. For example, Bing has American indigenous languages better represented.
Apart from its native web-based interface, Bing is available as an iOS and Android app, API service, and enterprise version with custom glossaries and terminology.
 Source: Bing
Source: Bing
- Performance (⚙️8/10): Translation accuracy fluctuates depending on a particular language pair, but overall is impressive, especially for European languages.
- Compatibility and assistance (🔧9/10): Bing integrates natively with Microsoft products, but works okay with other platforms. FAQs and documentation provide ample information, plus support channels work efficiently.
- Innovation (💡7/10): Bing is very reliable, but not particularly inventive. Recent updates focus on better user experience, smooth integration, and customization rather than on innovative automatic translation services.
- Value for money (💰9/10): Free functionality is enough for everyday personal use giving 2,000,000 characters per month, which is four times Google’s limit. The paid options offer scalable solutions for businesses of all sizes, ranging from 20 million to 1 billion characters per month.
4. Baidu Translate
Dabbed “Chinese Google,” Baidu is a tech giant with an all-encompassing selection of products, including its machine translation tool. Baidu Translate currently supports an impressive number of 280 languages for text and 45 for speech translation. Apart from translation, it offers language-learning features, such as Notepad with important phrases, oral practice, videos, and daily readings.
While the interface might not be as intuitive for Western users, Baidu Translate is innovative, dynamic, and provides excellent support for Asian languages. It’s definitely a tool with great potential.
 Source: Baidu Translate
Source: Baidu Translate
- Performance (⚙️7/10): Baidu’s accuracy is unparalleled for Asian languages, particularly Chinese and its dialects, but might be less reliable for other language families.
- Compatibility and assistance (🔧7/10): Baidu is currently available only as a web-based tool and an iOS mobile app.
- Innovation (💡8/10): Baidu focuses on keeping up with the latest developments, offering live speech translation, image translation (including live camera), and voice conversion offering translated speech in the speaker’s voice.
- Value for money (💰9/10): Freemium model with generous free tier and affordable paid plans, Baidu is particularly useful for individual learners or businesses expanding into Asian countries.
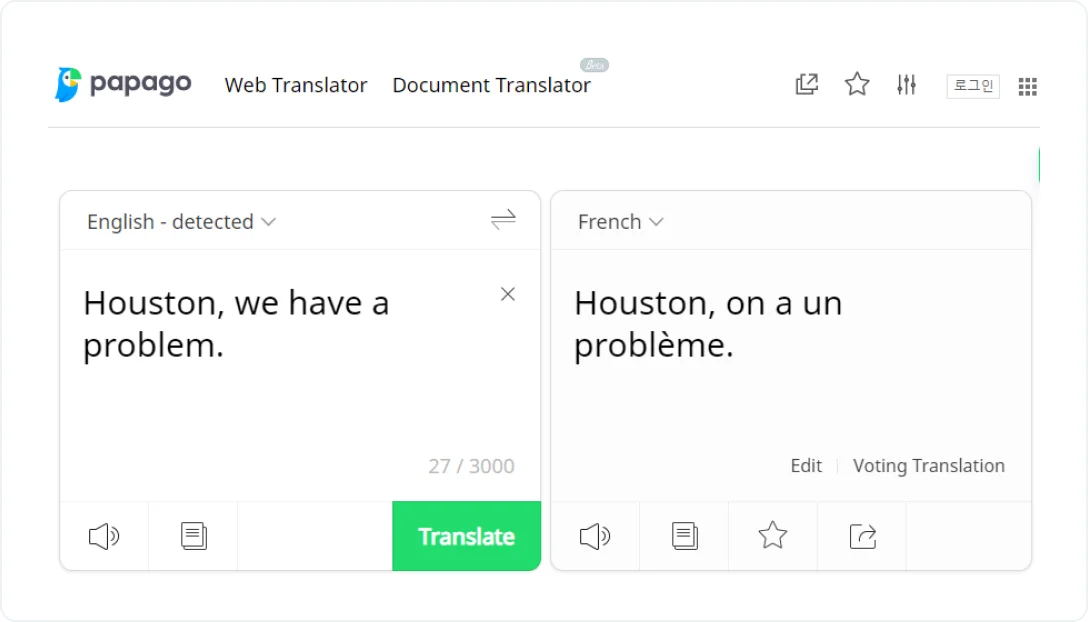
5. Papago
Papago is a new kid on the block but powered by AI, it’s set for success. It was released in 2017 by the Naver Corporation, a South Korean internet giant with a proprietary search engine. Currently, Papago, which means “parrot” in Esperanto, supports only 14 languages, mostly Asian, with a handful of European ones. It is available as a web-based text/doc translator and a mobile app.
It is marketed as an on-the-go translation tool for personal use, mainly travel and studies, with handy features like speech translation and image translation. However, you might want to keep an eye on it because more robust business-focused functionality is sure to follow.
 Source: Papago
Source: Papago
- Performance (⚙️7.5/10): Accuracy heavily depends on the language pair, with Korean and Japanese being the best translated.
- Compatibility and assistance (🔧8/10): User-friendly and intuitive, Papago is available on the web, iOS and Android.
- Innovation (💡9/10): Voice translation for live chats works smoothly and sounds natural, especially in Korean and Japanese, letting you adjust honorifics and switch tones.
- Value for money (💰10/10): For individual communication and travel, the value is great. Free ad-supported version has some limitations, while paid plans remove ads and allow bigger translation volumes.
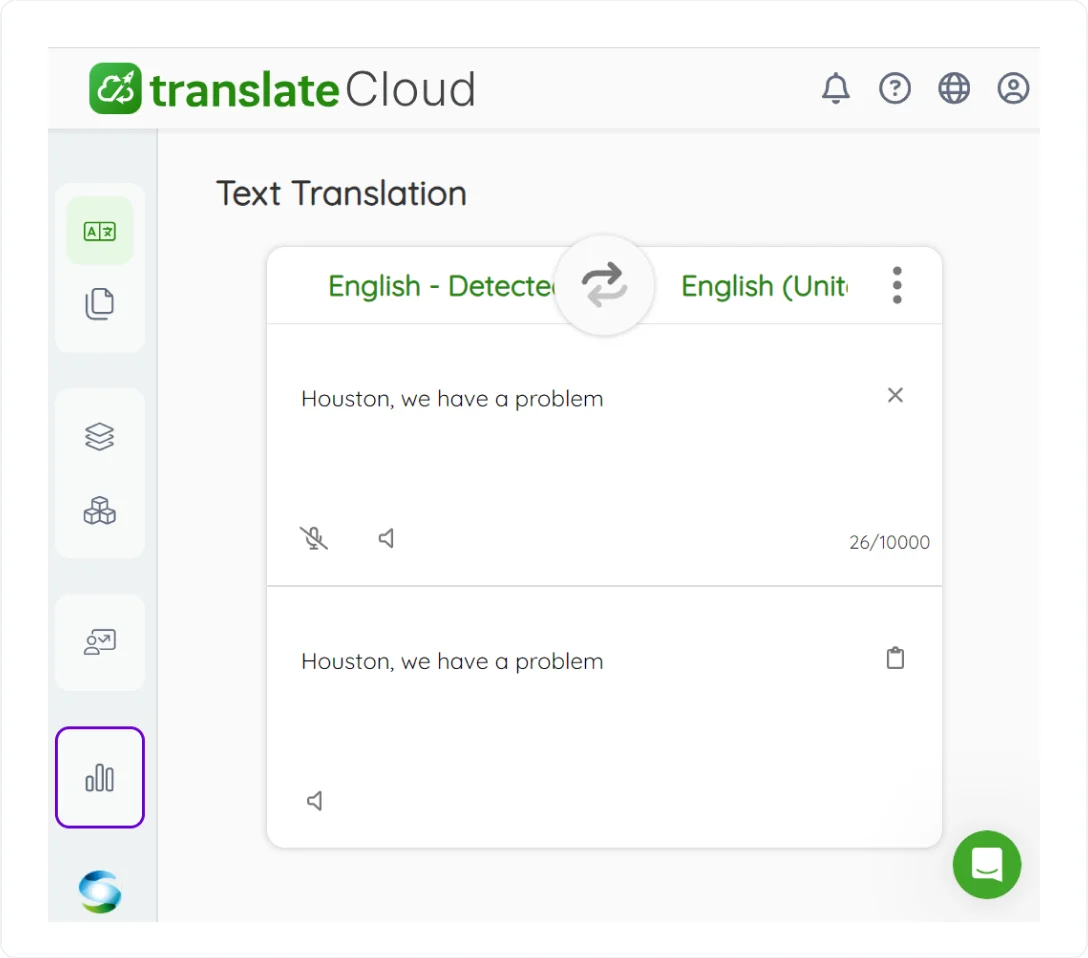
6. Systran
SYSTRAN is one of the oldest machine translation tools that managed to survive since the 1960s. It has always been rule-based machine translation technology with a later addition of a hybrid rule-based/statistical approach. SYSTRAN currently supports 55 languages.
The key to SYSTRAN’s longevity seems to be reliability and customizability. Even though the RBMT/SMT method isn’t as flexible as NMT in ready-made solutions, it can be efficiently customized for each specific application.
 Source: Systran
Source: Systran
- Performance (⚙️7/10): SYSTRAN’s fidelity fluctuates with greater accuracy for European languages and poorer results for unusual language pairs.
- Compatibility and assistance (🔧8/10): Paid versions of SYSTRAN run on MS Windows (including mobile), Linux, and Solaris. Twelve other machine translation systems have SYSTRAN integrations. Documentation and support are detailed and efficient.
- Innovation (💡7.5/10): SYSTRAN tentatively participates in NMT research collaborating on OpeNMT, but is more conservative than its competitors.
- Value for money (💰7/10): SYSTRAN offers multiple subscription plans for users and customized solutions for businesses, but some might find their services pricey for the features.
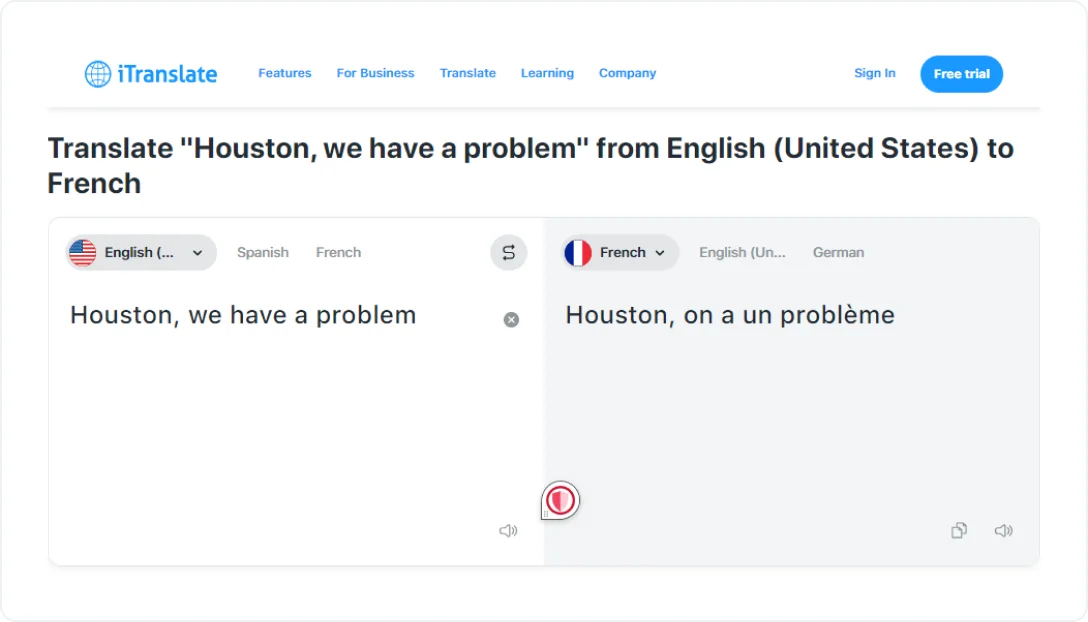
7. iTranslate
iTranslate is a mobile app created for personal use and on-the-go translations. It currently supports over 100 languages with voice, text, and camera translation, and has a keyboard extension for live chat translation. It is available for Android and iOS (+Apple Watch) and supports offline mode.
iTranslate used to exist as a family of apps: iTranslate Converse, iTranslate Translator, and a web tool, but not long ago has been consolidated into one universal app.
 Source: iTranslate
Source: iTranslate
- Performance (⚙️8/10): iTranslate offers a decent level of fidelity. However, the latest updates might have tampered with the accuracy of the voice recognition feature.
- Compatibility and assistance (🔧7/10): iTranslate is a self-sufficient mobile app and as such is available on several platforms. However, it does not support any integrations with other products.
- Innovation (💡8.5/10): With updates sometimes backfiring, iTranslate is obviously trying new things using proprietary systems. That said, their features are very similar to the competitors.
- Value for money (💰7.5/10): Full capability is only available via subscription, which many individual users consider too pricey for the functionality. This product is best suited for individual language learners and travelers.
Get the week's best content!
By subscribing, you are agreeing to have your personal information managed in accordance with the terms of Centus Privacy Policy ->
Keep learning
7 min. read
Translation Management System: A ‘Show, Don’t Tell’ Guide
6 min. read
How to Organize Content Translation Process
15 min. read
ChatGPT for Translation: Your Go-To 2025 Guide
14 min. read
Website Localization: A Beginner’s Guide
8 min. read
What Is a Computer-Assisted Translation (CAT) Tool
11 min. read