Building an Effective International Expansion Strategy
An international strategy is your foundation for overseas business expansion. It’s relatively simple, doesn’t need a massive investment, and lets you dip your toes into new markets before full commitment and a large-scale entry.
But here’s a caveat: international expansion is not as effortless as it sounds. To make it work, you’ll need something special—a low-competitive niche industry, a unique offering, or a brand already making waves.
Think you’ve got what it takes? Then let’s dive in.
What is an international expansion?
International expansion is the strategic process of entering foreign markets to grow global market share, increase revenue, and diversify risk.
International expansion strategy involves introducing existing offerings to new markets without significant changes to functionality, pricing, or design. Production and operations remain centralized in the domestic market, while the product is distributed internationally.
Often referred to as the "exporting strategy," it is one of the four primary approaches to overseas expansion.
No wonder some also call it a “drag-and-drop” or “copy-paste” approach.
Why should you consider international expansion?
Lower entry risks, minimal investments, and a good level of control make this strategy a piece of cake for SMEs and those companies who have only started their global expansion journey. However, this approach isn’t for everyone.
Why?
- First, you need a product that’s so good it doesn’t require local adjustments.
- Second, you don’t even need to lower prices to stay competitive—your product has to shine on its own.
In other words, you’ve got to be in a niche industry, boast a globally recognizable brand, or offer something genuinely innovative.
Example: During its early expansion, Netflix used an international strategy to offer the same catalog of movies and shows in multiple countries. Later, the company took the transnational approach by producing and promoting local content. Some other international expansion strategy examples include LinkedIn, Zoom, and Grammarly, all offering their services worldwide with minimal region-specific adaptations, typically limited to translation.
Benefits of international business expansion
Why do companies expand internationally? Opening new markets unlocks growth opportunities, reduces costs, and builds better business resilience. Here’s how it works:
-
More business opportunities. A robust market expansion strategy helps you build a network of international partners, increase global visibility, and, as a result, gain a competitive edge. With thorough market research, you're likely to uncover new markets or user segments for your product that you could otherwise miss.
-
Risk mitigation. International business expansion helps you diversify revenue streams and build resilience against region-specific uncertainties, market fluctuations, and economic downturns. A broader market base means less reliance on any single economy or region.
-
Reduced costs. Expanding business internationally requires initial investment, but it often leads to significant cost savings over time thanks to lower-cost labor and resources, operational efficiency, and economies of scale.
Like Netflix, many global brands start their overseas expansion with the international strategy to test their competitiveness before a large-scale entry. This approach comes with several clear benefits compared to other strategies:
-
Lower entry investments. Centralized operations and standardized offerings with limited local responsiveness make it a cost-effective way to expand across markets.
-
Simplicity and control. This strategy helps you avoid operational and management complexities as it requires less product adaptation than transnational and multi-domestic strategies. Plus, unlike a global strategy, there’s no pressure to cut costs to remain competitive in a new market.
-
Focus on core competencies. Instead of tailoring offerings to fit each new market or competing on price, you can leverage your home-country strengths.
However, not everything about the international growth strategy is smooth sailing:
-
Limited local responsiveness. Centralization and heavy reliance on home-country operations limit your flexibility and responsiveness to local challenges, which can lead to 👇
-
Vulnerability to competitors. Staying competitive becomes difficult without customization or price adaptation—unless you offer something unique. Your products might stop resonating with local customers sooner than you expect.
-
Limited economies of scale. Despite a high level of centralization, international strategy isn’t about consolidation like the global strategy. Instead, it replicates the home-market model in other regions, which can result in duplicative efforts (establishing operational units in different markets) and higher administrative and operational costs.
Before diving into the types of international market expansion, let’s explore what makes an international strategy different from keeping things local.
How does an international strategy differ from a domestic strategy?
International strategy involves expanding operations into foreign markets, while the domestic strategy focuses solely on the organization’s home market. Geographical distribution defines the following:
-
🎯 Market focus. Multiple markets require companies to deal with diverse consumer preferences, cultural differences, and ever-changing economic and political conditions. On the other hand, the domestic strategy serves the home market with predictable and well-known consumer needs and economic environment.
-
🧶 Operational complexity. In a domestic market, business operations are simple, with a unified supply chain and a predictable regulatory landscape. In contrast, foreign expansion requires you to manage multiple distribution networks across countries, each with its unique law.
-
📦 Resource allocation. A domestic strategy lets you put all your resources into one market. However, when expanding internationally, you need to decide which markets to focus on and carefully figure out the best way to allocate your resources.
4 types of international expansion strategies
There are four main market entry modes. Let’s break down how to expand your business internationally:
- Need a low-risk, low-commitment option? - Exporting
- Looking to expand quickly while accepting limited control? - Licensing
- Seeking a middle ground between control and entry risks? - Partnership
- Ready for immediate access and long-term commitment? - Investment
Exporting
Exporting is a low-risk strategy to expand business internationally and enter new markets by selling goods or services produced domestically.
-
Direct exporting involves selling products or services directly to customers in a new market. If you sell physical products, this may require setting up distribution channels and local sales teams. But if your offerings are digital, you can use online platforms to reach customers worldwide directly.
-
Indirect exporting involves using export agents, distributors, and other intermediaries to sell internationally without the need for a physical presence.
Example: Companies like Netflix, Spotify, Grammarly, and Coursera sell their services directly to users in foreign markets through online subscriptions.
Licensing and franchising
Licensing and franchising don’t require direct involvement to expand business internationally but can put you at risk of losing control over your brand image or the quality of your offerings in local markets.
-
Licensing is a strategy where you grant another company the right to manufacture or sell products using your trademark or intellectual property (in exchange for royalties and fees).
-
Franchising is when you allow an independent party to operate under your brand and business model, receiving an initial fee and ongoing royalties in exchange for your brand name, systems, and support.
Example: Microsoft sells its Windows software through a network of licensed local distributors and partners.
Joint ventures and strategic alliances
Joint ventures and strategic partnerships balance minimizing entry risks with gaining local control.
-
Joint venture is when two or more partners contribute their expertise and resources and share both risks and profits by forming a separate legal entity.
-
Strategic alliance doesn’t involve creating a legal entity. Partners maintain their independence while sharing marketing efforts, R&D, or technology.
Example: To adapt to Chinese local consumer behavior, Starbucks partnered with Tencent and integrated WeChat Pay into its stores in China (strategic alliance).
Foreign direct investment (FDI)
Direct investment requires you to fully commit to a new market in the long run. You establish a physical presence by directly investing capital, resources, and expertise, which ensures increased market access and greater control over operations.
-
Greenfield investment involves establishing operations (such as building new facilities and hiring local teams) from scratch in a foreign market. This allows you to retain full ownership and control while adapting your business operations to local needs.
-
Acquisition or merger allows you to quickly enter the market by buying or partnering with an established local company.
Example: An example of greenfield investment is Amazon, which controls distribution and customer experience in countries like India by establishing centers and logistics operations from the ground up. In contrast, Google’s acquisition of YouTube illustrates how companies can quickly enter a new market by leveraging the acquired platform's existing infrastructure, brand recognition, and user base.
5 Steps to build the right international expansion strategy
Here’s a quick recap before we dive in 👇
International growth strategy works best for businesses that can compete in foreign markets without lowering prices or heavily customizing their offerings to local needs and preferences.
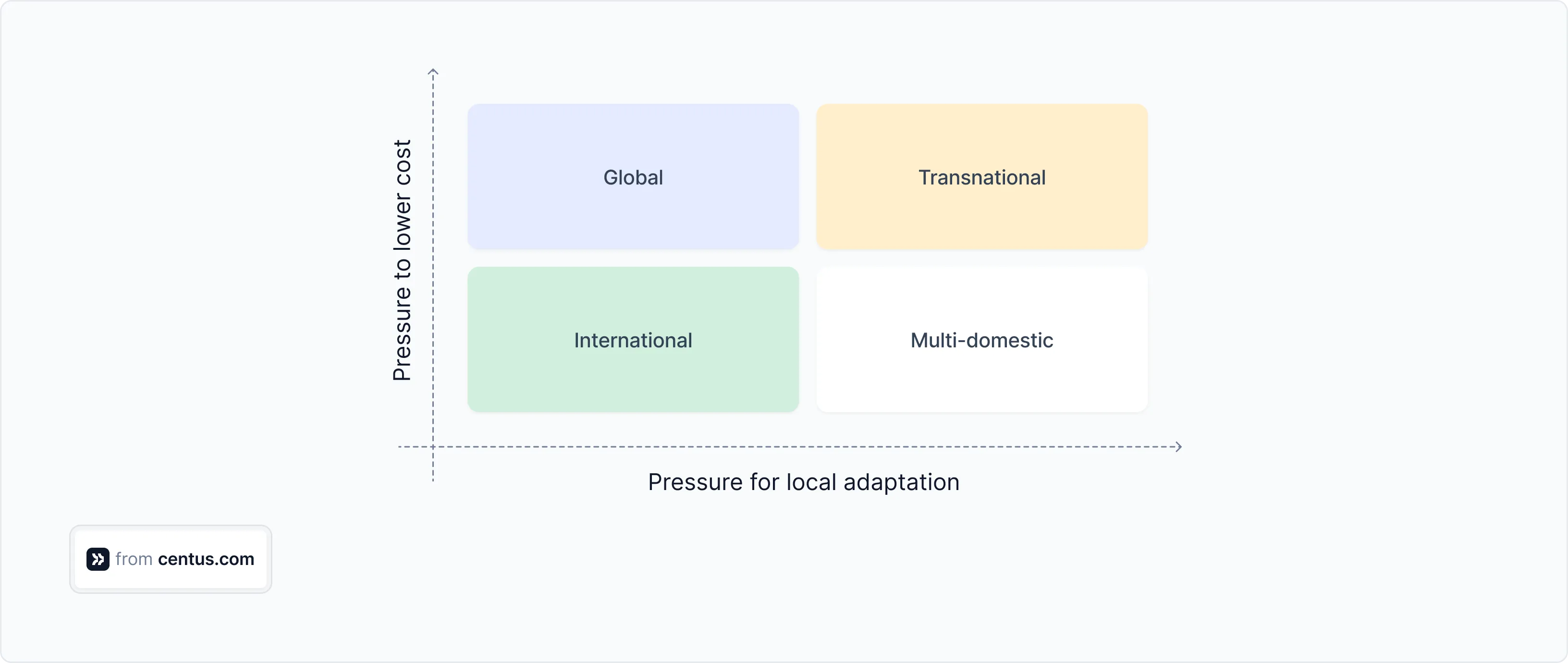
Below is a checklist to see if the international strategy fits your business:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. What level of customization do my offerings require to compete in a new market? | My offerings are unique or niche, largely standardized, and don’t require local adjustments to compete in a foreign market. |
| 2. What are the competitive pressures in global and local markets? | The competitive pressures are low on both global and local levels. |
| 3. Do I have a recognized brand? | My company has an established and trusted brand. |
| 4. Do I need to build a local presence to succeed? | I can expand internationally without major investments in local markets. |
| 5. How complex is my operational structure? | My company has centralized control and a simple operational setup. |
| 6. What is my organizational capacity for managing complexity? | My company has limited capacity to handle operational complexities. |
If you answered “Yes” to most of these questions, congrats—you’re ready for Step 1.
Note: If you answered “No” to most questions, no worries. Head over to our post on global expansion to explore whether a global, transnational, or multi-domestic strategy fits your business better.
Step 1. Set clear targets
Once management gives the green light, it’s time to set clear goals for your business expansion strategy.
-
🖼️ Start with the big picture. What high-level goals do you want to achieve in the long run?
-
📈 Break them down. Focus on more granular short-term objectives that serve as stepping stones toward those larger goals.
Chances are your company already uses a goal-setting framework, so sticking with it can keep things consistent and efficient. Here are some popular options:
- Objectives and Key Results (OKRs)
- Think big, act small, and move quickly (BSQ)
- SMART goals
- Goal Pyramid
- Backward Goals
- Big Hairy Audacious Goals (BHAG)
- One Word Goal Setting
Step 2. Perform market and customer research
Choosing the right market starts with thorough research. Ideally, you’re looking for a market with great growth potential and low entry costs. Sounds perfect, right? Unfortunately, in the real world, it rarely happens, so be ready to make compromises.
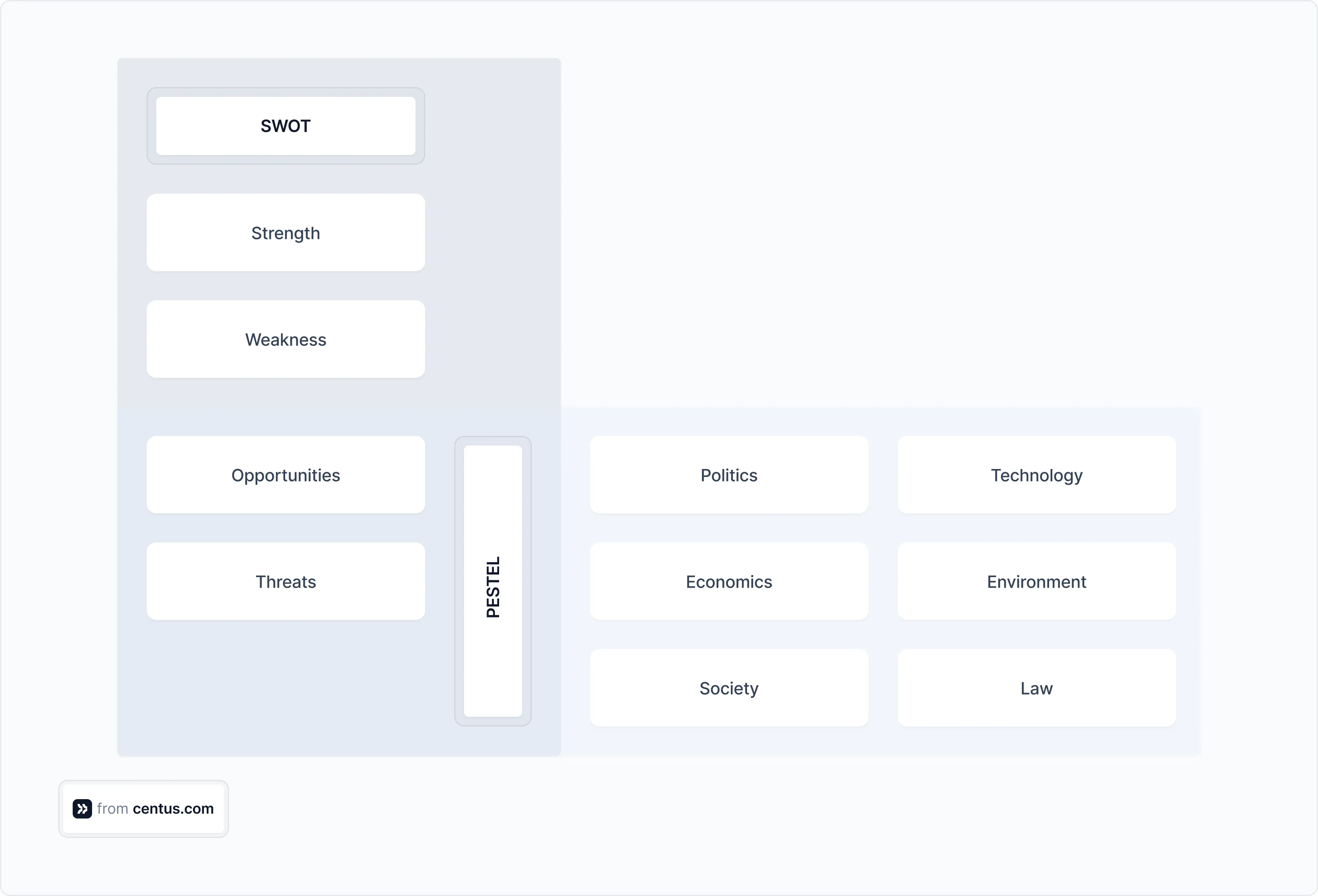
Start with a market analysis using the PESTEL framework to evaluate key macro factors: politics, economics, society, technology, environment, and law. Then, dive into a SWOT analysis to identify your company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Pay particular attention to the competitive landscape—Porter’s Five Forces framework can help you assess competition, market entry barriers, and supplier/buyer dynamics.
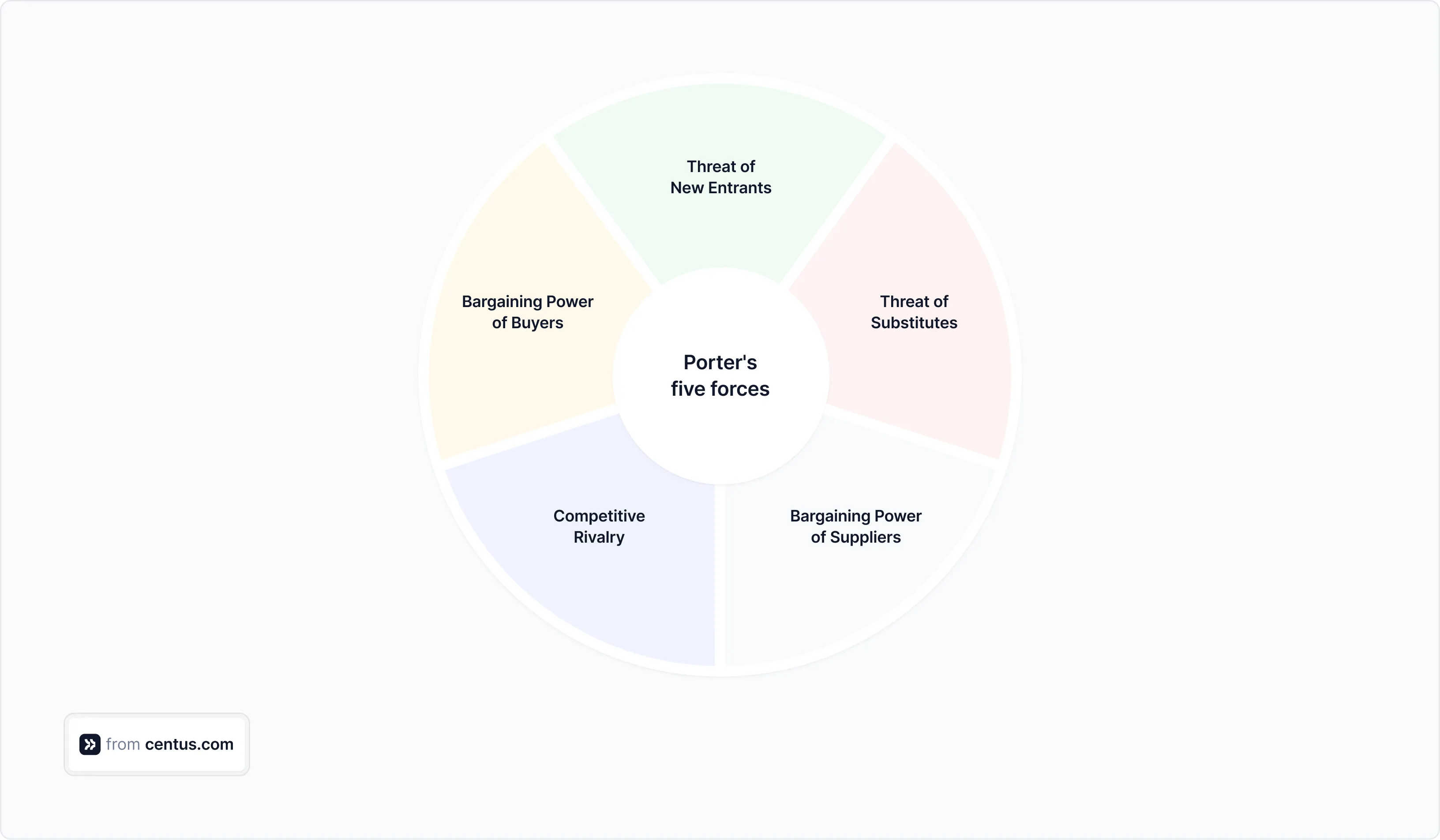
Although international growth strategy works best in low-competition environments, remember that markets evolve quickly. Many companies begin with this strategy and switch to a more flexible approach as competition heats up.
The takeaway? Be ready for change and keep your research sharp—because staying competitive is a marathon, not a sprint.
Step 3. Identify the best ways to enter the market
The simplicity of the international strategy makes entering a new market easier compared to other business expansion strategies. But here’s the key: you still need to choose the best entry method for your case.
Ask yourself:
| How quickly do I need results? | For rapid entry, look into licensing, franchising, or acquisition. |
|---|---|
| Do I have the capital for significant investments? | If not, exporting or licensing might be more practical. |
| Do I have operational expertise? | Partnerships or joint ventures can help you avoid complexities. |
| Is there a proven demand for my offerings? | If you’re unsure, start with a low-risk, low-commitment option like exporting. |
| Are there legal complexities? | Licensing, partnerships, or alliances can help you tackle local regulations. |
| How much control do I want to maintain? | If full control and integration are critical, consider foreign direct investment. |
💡Pro tip: Learn from your competitors. How have similar companies entered this market? Did they succeed with partnerships, acquisitions, or greenfield investments? Are there franchising or exporting models you can replicate?
You might even want to test the waters in a specific region or market segment before committing fully. Hybrid approaches work, too! For example, you can start with exporting and transit to joint ventures as you grow.
Step 4. Build a cross-functional team
The international strategy relies on a centralized approach to decision-making and team management, which ensures better control and consistency. While you may still need small local teams with limited autonomy for regional support and sales, you likely won’t require a large local workforce. However, there are pitfalls.
Focusing solely on home-office teams can hinder your company’s ability to address regional needs or cultural differences. You miss out on valuable insights from your local teams, let alone that you can make them feel disconnected and undervalued.
To avoid cultural misunderstandings, prioritize your team-building process and invest in cultural awareness training programs.
Step 5. Localize your product and marketing strategy
Even with minimal product adaptation, localization is non-negotiable. At the very least, you need to localize the website, product UI, and marketing materials to reach the new audiences.
To ensure your localization efforts hit the mark, map the customer journey. It will help you identify all the touchpoints your users engage with, such as:
- Display adverts and search keywords
- Landing and product pages
- Sign-up flows and payment pages
- Onboarding steps
- Emails and newsletters
- In-app messages
- Resources center content and educational materials like tutorials
Sounds overwhelming and time-consuming? It is if you don’t have a proper localization tool like Centus to help you automate the process and streamline management.

Parting thoughts
An international expansion strategy lets businesses tap into new markets with minimal risk and investment, using standardized offerings that don’t need local adjustments. But here’s the catch—localization is still essential.
Tools like Centus make it easy to localize and deliver a smooth, engaging experience for global audiences. Try Centus now!
Or keep exploring to learn how to perfect your localization management.
Centus will be here, always ready for you.
Get the week's best content!
By subscribing, you are agreeing to have your personal information managed in accordance with the terms of Centus Privacy Policy ->
Keep learning
13 min. read
Best Internal Growth Examples + 8 Expert Strategies
15 min. read
8 International Expansion Failures Examples
7 min. read
What Is Market Expansion Strategy? A Guide to Business Growth
11 min. read
7 Product Expansion Examples and Strategies
9 min. read
Top 10 International Marketing Principles
19 min. read