Internationalization and Globalization: What’s the Difference Between?
While both can benefit your company, globalization and internationalization are not quite the same.
Today, I will explain the difference between globalization and internationalization and show you how to optimize your business strategy for each.
Let’s dive in!
Pro tip: Before entering global markets, localize your product and marketing materials to reach new audiences effectively. Use professional translation management software to streamline the process. Learn more here.
Internationalization vs Globalization: Key differences
Globalization is the process of expanding businesses across global markets, while internationalization involves designing products to simplify this expansion. Internationalization prepares; globalization executes.
To better understand the differences between globalization and internationalization, let’s see how they compare across three key dimensions: goals, scope, and players.
| Globalization | Internationalization | |
|---|---|---|
| Goals | Countries’ economic growth | Company’s economic growth |
| Scope | Entire world | Single economy |
| Players | Governments International organizations Multilingual corporations Global consumers |
Individual company Company’s customers |
Goals
Globalization focuses on connecting the economic systems of different countries by removing trade barriers. This allows a seamless flow of resources, goods, people, information, and communication technology throughout the world economy.
Internationalization is concerned with the economic growth of an individual business. Internalization requires the recreation of the brand identity and the embrace of local traditions to win over customers.
Scope
Globalization has a far-reaching scope covering multiple national economies. Any globalization campaign typically impacts the entire national and global economy.
Internationalization has a narrower scope because it impacts a single company and its target audience.
Players
A globalization strategy involves governments, multinational companies, international organizations, and global consumers. Governments collaborate extensively to establish goals and outcomes of the globalization process.
Internationalization mainly happens in the private sector and involves individual businesses. Governments play a minor role in creating regulations for international market trade.
What is internationalization?
Internationalization is the process of adapting products and services to resonate with buyers in foreign markets. Internationalization involves localizing your content, redesigning your website and product, and revamping your messaging to position your brand in the global market.
3 Benefits of internationalization
An internationalization strategy can benefit companies in many ways, such as:
- Acquiring new customers and building brand awareness in different countries
- Boosting the company’s competitiveness internationally and transitioning to a global brand
- Improving investment and revenue opportunities with access to tax relief norms, cheaper talent, and more
To realize these benefits, companies must take care of trade barriers and prepare a bulletproof internationalization strategy.
Two examples of internationalization
Here are a few examples of popular brands that have expanded to the international market:
McDonald’s internationalization strategy
McDonald’s is a classic example of internationalization. The fast food chain expanded across many countries using a balanced pattern of standardization and global localization.
Even though McDonald’s retained its brand identity and operating frameworks, it underwent a major change to support its internationalization efforts.
Specifically, McDonald’s localized its menus to appeal to every market’s customer base. The company introduced the special Teriyaki Burger in Japan and the McLobster in Canada to become a fan favorite among local buyers. Thus, McDonald’s combined a successful localization strategy with customized marketing campaigns to overcome cultural differences.

Source: IndexMundi
Toyota’s internationalization strategy
Toyota has been one of the biggest automobile brands globally—thanks to its rapid and large-scale internationalization efforts in the 1960s and ‘70s. The automotive giant acquired local production centers to launch itself in several regional markets.
What makes Toyota a brilliant case study of internationalization is its efforts in building relationships with local partners, like General Motors in the US. The manufacturer worked rigorously with local dealers and suppliers to build a strong presence in different national markets.
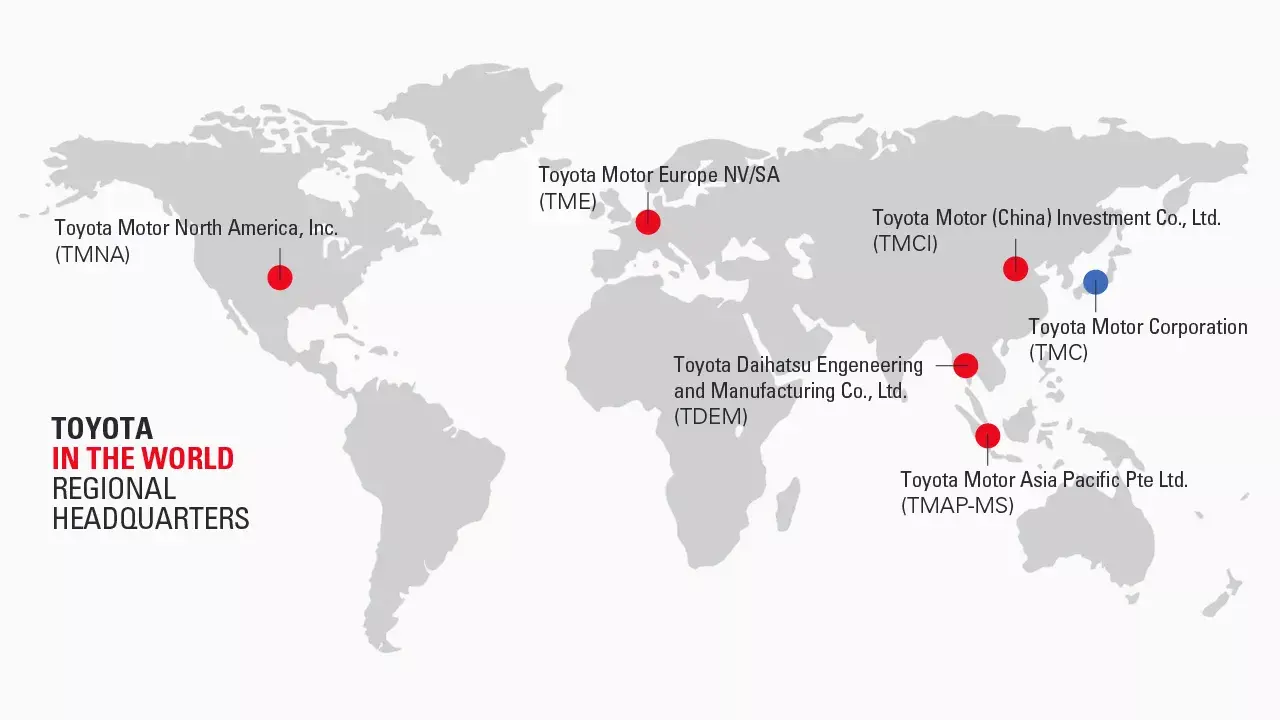
Source: Toyota
Tactics for Internationalization
Here are three main tactics for internationalizing your business:
- Plan ahead: Planning can make or break your internationalization efforts. Prepare a solid groundwork for your strategy by researching the country’s legal framework, architectural requirements, and other nuances before strategy implementation.
- Get strategic support: Go beyond your team to collaborate with more experienced individuals for building an airtight internationalization strategy. Hire local consultants from your target market to draw out a fail-proof roadmap for accomplishing your goals.
- Choose a localization tool: Localization is the most important piece of the puzzle for an internationalization campaign. Work with a fully-integrated localization tool like Centus to manage all the moving parts in your strategy without breaking a sweat.
What is globalization?
Globalization is the process of integrating economies, cultures, and resources across nations. It promotes free international trade and fosters collaboration between developed, developing, and underdeveloped countries, creating opportunities for mutual growth and exchange of ideas.
Think of globalization as the convergence of different countries. Globalization builds an integrated system for economic, social, and political change.
3 Benefits of globalization
Here are the main benefits of globalization for every country:
- Globalization facilitates the removal of trade barriers, thereby promoting international commerce
- Unrestricted flow of goods, people, and cultural values to promote lucrative and free trade
- Faster spread of opportunities and economic growth among developing and less developed countries
Companies benefit from globalization by having broader recruitment opportunities, savings cots, and mitigating risks.

Two examples of globalization
Here are two examples of how globalization works:
Automobile manufacturing in a globalized setting
The automobile manufacturing sector presents a great example of globalization.
Most automobile brands conduct R&D in their home country, like Germany for Volkswagen or Japan for Toyota. However, automobile parts are manufactured in other countries with cheaper labor and materials, like Mexico or India. Then, the parts are assembled in different locations to be sold in multiple countries across the world.
This manufacturing and supply chain framework interconnects multiple economies creating an integrated economic system.
Multinational companies in a globalized setting
Multinational corporations operating satellite offices in many countries is another example of how globalization works. For example, a multinational corporation can have its headquarters in the US with multiple satellite branches across Europe and Asia. Its workforce, resources, and technology are divided between multiple nations, benefitting each country and bringing them together on a global scale.
Tactics for globalization
Here are three key tactics that can be used to implement a globalization strategy:
- Digitalization: Supply chain management is one of the most critical factors behind the success of globalization. Digitizing these workflows can enable smarter decision-making based on strategic data and produce the desired ROI.
- Localization: Expanding operations in the local market is another way to reduce the risks associated with cultural barriers and implement globalization effectively. A localization suite should be used to streamline the localization process.
- Licensing and franchising: Businesses can embrace globalization by licensing or franchising their services. This tactic allows establishing a global presence with minimal employee supervision, reduced financial risk, and increased brand awareness.
Get the week's best content!
By subscribing, you are agreeing to have your personal information managed in accordance with the terms of Centus Privacy Policy ->
Keep learning
7 min. read
Software Internationalization Best Practices for Developers
15 min. read
8 International Expansion Failures Examples
9 min. read
Top 10 International Marketing Principles

13 min. read
Building a Multidomestic Strategy with Examples

9 min. read
What Is a Transnational Strategy? A Simple (But Complete) Guide
13 min. read